A Comprehensive Guide to Curriculum Mapping: Organizing Learning for Success
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Curriculum Mapping: Organizing Learning for Success
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Curriculum Mapping: Organizing Learning for Success. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Curriculum Mapping: Organizing Learning for Success

Curriculum mapping is a powerful tool for educators, providing a structured framework for planning, implementing, and evaluating learning experiences. It serves as a visual representation of the educational journey, outlining the key concepts, skills, and assessments that students will encounter throughout a specific time frame, such as a semester or a school year. This structured approach fosters coherence and alignment within the curriculum, ensuring that learning is purposeful, sequential, and ultimately, more effective.
Understanding the Essence of Curriculum Mapping
Imagine a meticulously crafted roadmap guiding travelers through a vast and complex landscape. This roadmap, in essence, is analogous to a curriculum map. It provides a clear and concise overview of the educational terrain, highlighting key landmarks, potential challenges, and the optimal route to navigate them.
At its core, a curriculum map outlines the following:
- Learning Objectives: These are the measurable goals that students are expected to achieve by the end of a particular unit or course. They provide a clear direction for instruction and assessment.
- Content Standards: These are the specific knowledge and skills that students are expected to master, often derived from national or state curriculum frameworks. Curriculum maps ensure that these standards are addressed in a systematic and comprehensive manner.
- Instructional Activities: This section details the teaching strategies and learning experiences that will be employed to facilitate student understanding and skill development.
- Assessment Strategies: A curriculum map outlines the methods used to evaluate student progress against the established learning objectives and content standards. This can include formative assessments for ongoing feedback and summative assessments to gauge mastery at the end of a unit or course.
- Time Allocation: The map clearly defines the amount of time dedicated to each unit or topic, ensuring that the curriculum is adequately covered within the designated timeframe.
Types of Curriculum Maps
Curriculum mapping can be implemented in various ways, depending on the specific needs of the educator and the learning context. Some common types include:
- Subject-Specific Maps: These maps focus on a single subject, such as mathematics or English. They provide a detailed overview of the content, skills, and assessments within that particular discipline.
- Grade-Level Maps: These maps encompass all subjects taught at a specific grade level, providing a holistic view of the curriculum for that particular year.
- School-Wide Maps: These maps offer a comprehensive overview of the curriculum across all grade levels, ensuring consistency and alignment across the entire school.
- Unit Maps: These maps provide a detailed breakdown of the content, skills, and assessments for a specific unit of study within a larger course.
Benefits of Curriculum Mapping
The implementation of curriculum maps yields numerous benefits for educators, students, and the overall educational process:
- Improved Planning and Coherence: Curriculum mapping facilitates a systematic and organized approach to curriculum planning, ensuring that all essential content and skills are addressed in a logical sequence. This enhances the coherence and flow of instruction, creating a more meaningful learning experience for students.
- Enhanced Student Learning: By providing a clear roadmap for learning, curriculum maps help students understand the big picture and connect individual lessons to the overall goals of the course. This fosters a deeper understanding and promotes greater student engagement.
- Effective Assessment and Evaluation: Curriculum maps streamline the assessment process by aligning assessments with learning objectives and content standards. This ensures that student progress is accurately measured and evaluated, providing valuable insights into their learning journey.
- Increased Accountability and Transparency: Curriculum maps serve as a transparent and accountable document, outlining the educational goals and the strategies employed to achieve them. This allows stakeholders, including parents, administrators, and the community, to understand the curriculum and its alignment with educational standards.
- Facilitates Collaboration and Communication: Curriculum maps foster collaboration among teachers within a department or grade level, ensuring consistency and alignment across different courses. They also facilitate effective communication with parents and students, providing a clear understanding of the learning expectations and the assessment methods employed.
Creating a Curriculum Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
Developing a comprehensive and effective curriculum map requires careful planning and consideration. Here’s a step-by-step guide to assist educators in this process:
- Identify Learning Objectives: Begin by clearly defining the specific learning objectives that students are expected to achieve. These objectives should be measurable, specific, and aligned with the relevant content standards.
- Determine Content Standards: Identify the specific knowledge and skills that students are expected to master based on national or state curriculum frameworks.
- Plan Instructional Activities: Select a variety of instructional strategies and learning experiences that will effectively engage students and facilitate their understanding of the content and skills. Consider a mix of direct instruction, hands-on activities, group projects, and technology integration.
- Design Assessment Strategies: Choose appropriate assessment methods to evaluate student progress against the established learning objectives and content standards. Include both formative assessments for ongoing feedback and summative assessments to gauge mastery at the end of a unit or course.
- Allocate Time: Determine the amount of time that will be dedicated to each unit or topic, ensuring that the curriculum is adequately covered within the designated timeframe.
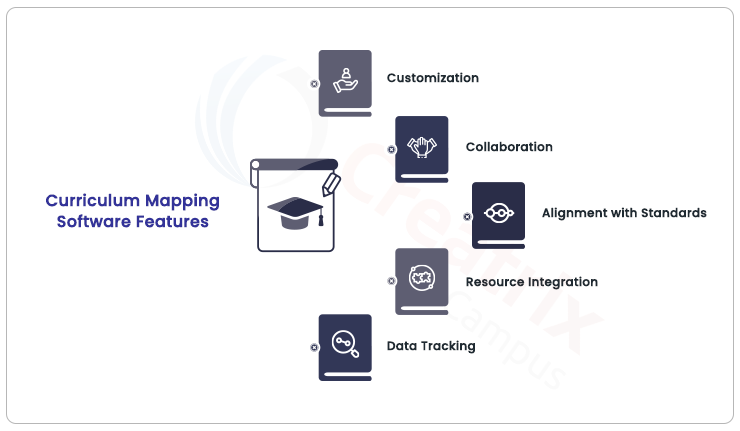
- Organize and Visualize: Organize the information gathered into a clear and concise visual representation. This can be done using a table, flowchart, or a dedicated curriculum mapping software.
- Review and Refine: Regularly review and refine the curriculum map based on student progress and feedback. Make adjustments as needed to ensure that the map remains relevant, effective, and aligned with the evolving needs of the students.
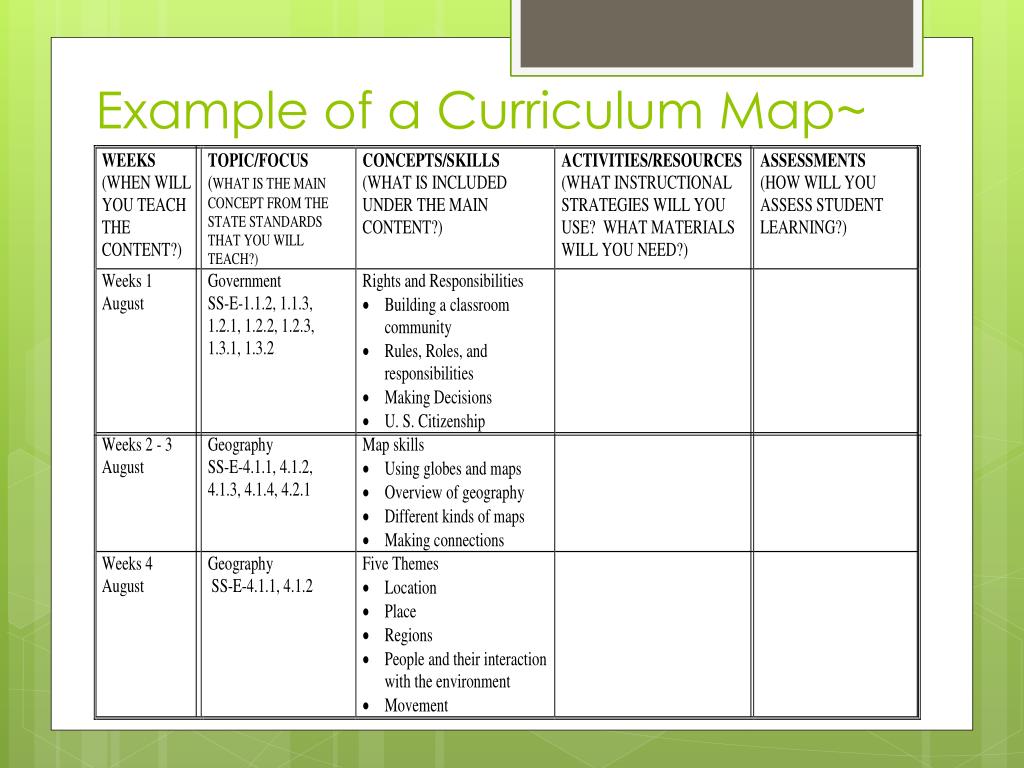
Example of a Curriculum Map
To illustrate the practical application of curriculum mapping, let’s consider a hypothetical example for a unit on "The American Revolution" in a 7th-grade history class:
**Unit





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Curriculum Mapping: Organizing Learning for Success. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!