A Comprehensive Guide to Dental Tooth Maps: Understanding Your Oral Health
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Dental Tooth Maps: Understanding Your Oral Health
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Dental Tooth Maps: Understanding Your Oral Health. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Dental Tooth Maps: Understanding Your Oral Health

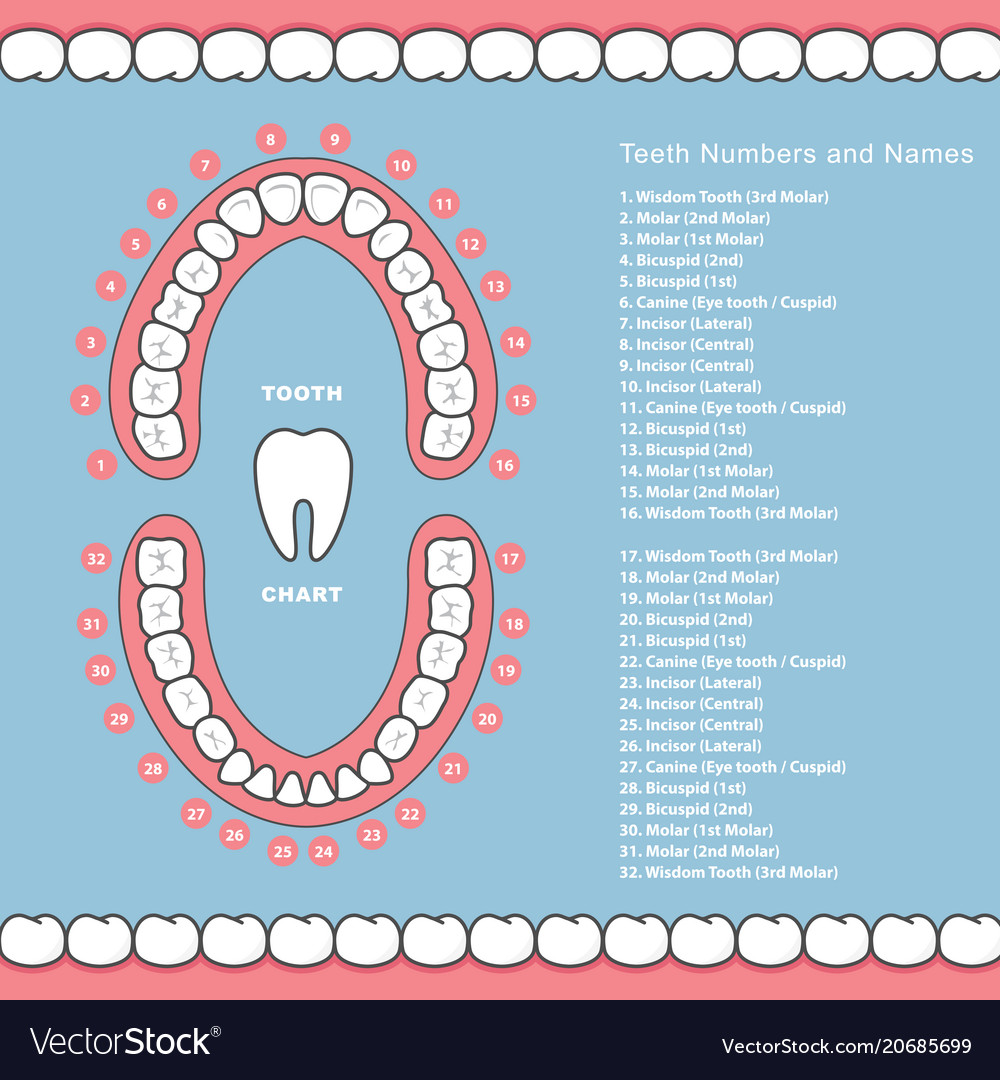
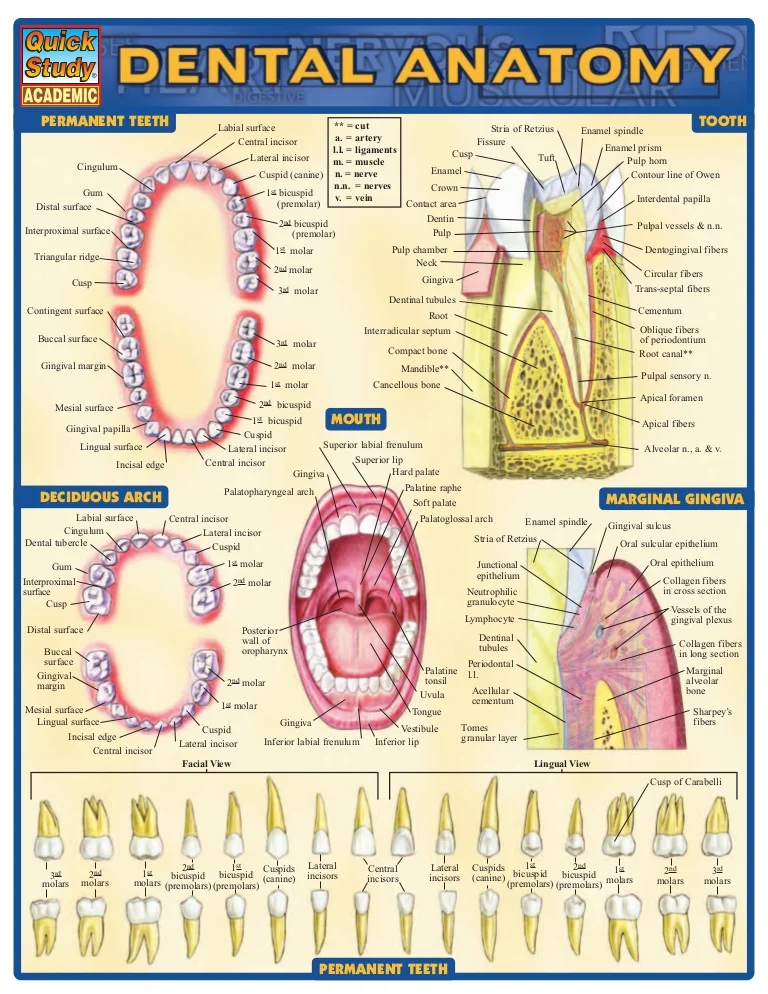
A dental tooth map, also known as a dental chart, is a visual representation of an individual’s dentition. It serves as a crucial tool for dentists, hygienists, and patients alike, offering a clear and concise overview of the current state of oral health. This map provides a detailed record of each tooth, its condition, and any potential issues, enabling effective communication and personalized treatment plans.
Understanding the Anatomy of a Dental Tooth Map
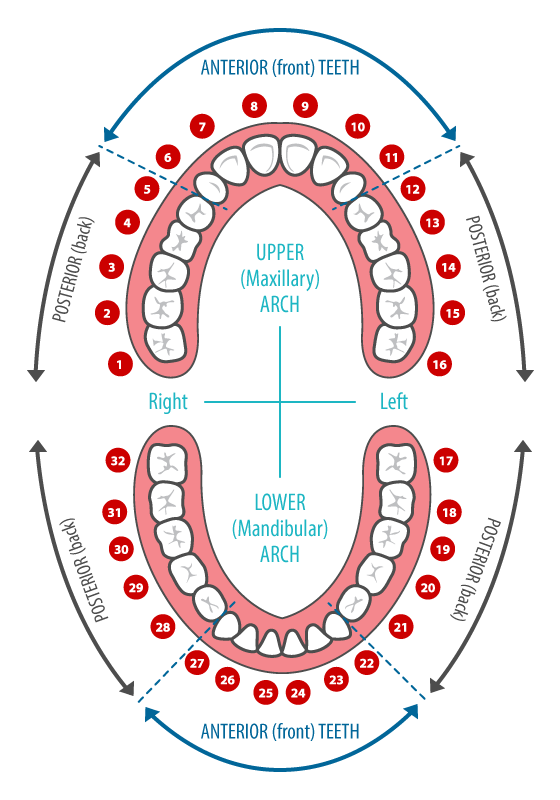
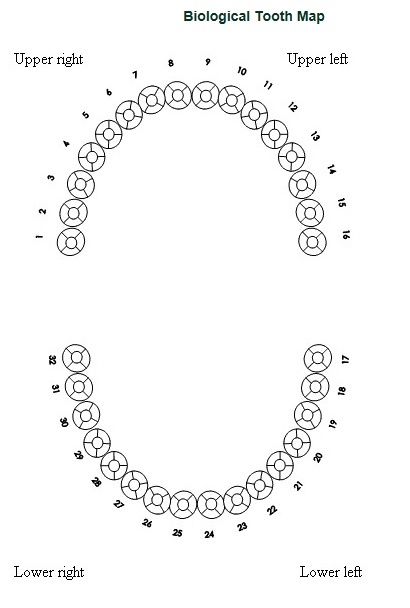
The dental tooth map is typically a diagram depicting the upper and lower arches of the mouth. Each tooth is numbered according to its position and type. The numbering system employed can vary, with the most common being the Universal Numbering System (UNS) used in North America. This system assigns a number to each tooth, starting with tooth #1 as the maxillary right third molar (wisdom tooth) and ending with tooth #32 as the mandibular left third molar.
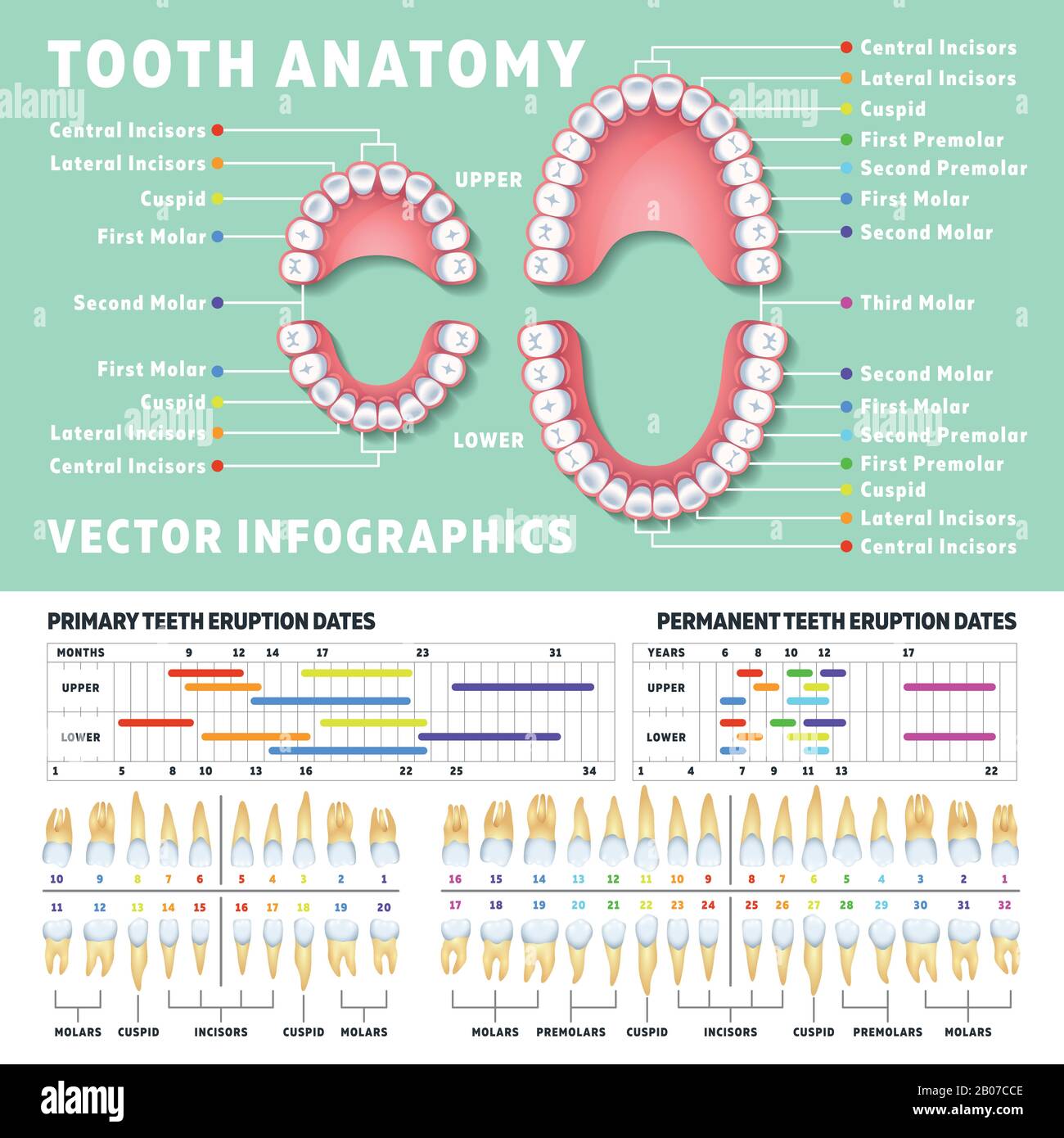
Each tooth is further categorized by its type:
- Incisors: The four front teeth in each arch responsible for biting and cutting food.
- Canines: The pointed teeth located next to the incisors, used for tearing and piercing food.
- Premolars: Two teeth located behind the canines, used for grinding and crushing food.
- Molars: The largest teeth at the back of the mouth, responsible for chewing and grinding food.
The map itself usually incorporates symbols or abbreviations to denote various aspects of each tooth, such as:
- Existing restorations: Fillings, crowns, or other restorative treatments.
- Missing teeth: Indicated by an ‘X’ or a blank space.
- Caries: Cavities or tooth decay.
- Gum disease: Inflammation or recession of the gums.
- Root canals: Completed or required procedures.
- Dental implants: Artificial tooth roots.
Benefits of Using Dental Tooth Maps
The use of dental tooth maps offers a multitude of benefits, impacting both patient care and overall oral health.
- Improved Communication: The visual nature of the map facilitates effective communication between the dentist and patient. It allows for clear explanations of the current state of oral health, potential issues, and recommended treatment plans. This fosters a collaborative approach to dental care, ensuring patient understanding and informed decision-making.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: By providing a detailed overview of each tooth’s condition, the map enables dentists to tailor treatment plans to individual needs. This ensures that the appropriate procedures are performed, addressing specific concerns and minimizing unnecessary interventions.
- Early Detection and Prevention: Regular updates to the dental tooth map allow for early detection of potential issues like caries, gum disease, or tooth wear. This proactive approach enables timely intervention, preventing the development of more severe problems and promoting long-term oral health.
- Accurate Record Keeping: The map serves as a comprehensive record of dental history, documenting past treatments, ongoing care, and any changes observed over time. This information is crucial for future appointments, ensuring continuity of care and informed decision-making by both the patient and dental professionals.
- Enhanced Patient Engagement: The visual representation of their oral health empowers patients to take a more active role in their care. It fosters a sense of ownership and encourages them to engage in preventive measures, leading to improved oral hygiene practices and overall health.
Dental Tooth Map FAQs
1. What is the purpose of a dental tooth map?
The primary purpose of a dental tooth map is to provide a visual representation of an individual’s dentition, allowing for effective communication, personalized treatment planning, and accurate record keeping.
2. Who uses dental tooth maps?
Dental tooth maps are used by dentists, hygienists, and patients. They are essential tools for communication, diagnosis, and treatment planning.
3. How often is a dental tooth map updated?
The frequency of updates depends on the individual’s oral health needs. Typically, the map is updated during routine dental checkups, which are recommended every six months.
4. Can I access my dental tooth map?
Patients are entitled to access their dental records, including the tooth map. It is recommended to request a copy from your dentist for personal reference.
5. What information is included in a dental tooth map?
The map includes details about each tooth, its condition, any existing restorations, missing teeth, caries, gum disease, root canals, and dental implants.
6. Are there different types of dental tooth maps?
While the basic structure remains similar, different dental practices may use slightly varied formats or numbering systems. However, the core information and purpose remain consistent.
7. Can I create my own dental tooth map?
While it is possible to find printable templates online, it is highly recommended to consult a dentist for accurate and professional mapping of your teeth.
Tips for Maintaining Oral Health Using a Dental Tooth Map
- Review the map with your dentist: Regularly discuss the map with your dentist to understand the current state of your oral health and any potential issues.
- Identify areas of concern: Pay attention to any symbols or notations indicating caries, gum disease, or other problems.
- Practice good oral hygiene: Brush twice daily, floss regularly, and use mouthwash to maintain optimal oral health and prevent future issues.
- Schedule regular checkups: Adhere to recommended checkups to ensure early detection and timely intervention for any potential problems.
- Follow your dentist’s recommendations: Adhere to any treatment plans or preventive measures suggested by your dentist to address specific concerns.
Conclusion
The dental tooth map is an indispensable tool for promoting optimal oral health. By providing a clear and comprehensive visual representation of an individual’s dentition, it empowers both patients and dental professionals to communicate effectively, personalize treatment plans, and maintain accurate records. By understanding the information presented on the map and taking proactive steps to address any potential issues, individuals can achieve and maintain a healthy smile for life.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Dental Tooth Maps: Understanding Your Oral Health. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!