A Geographic Exploration of the Middle East and Africa: Bridging Continents and Understanding Regions
Related Articles: A Geographic Exploration of the Middle East and Africa: Bridging Continents and Understanding Regions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Exploration of the Middle East and Africa: Bridging Continents and Understanding Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Exploration of the Middle East and Africa: Bridging Continents and Understanding Regions
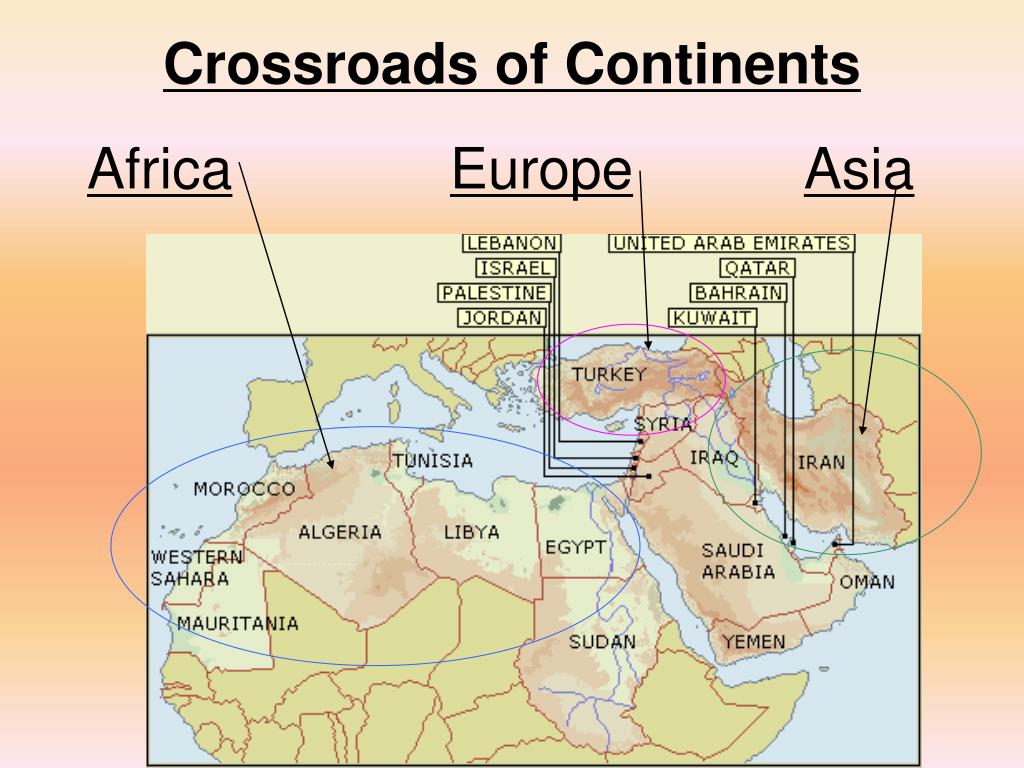
The Middle East and Africa, while geographically distinct, are often intertwined in historical, cultural, and economic narratives. Understanding the complex relationship between these regions requires a clear and comprehensive understanding of their individual landscapes, cultures, and histories. This article aims to provide such an understanding, focusing on the geographical and political landscape of the Middle East and Africa, emphasizing the interconnectedness that exists between these vast and diverse areas.
The Middle East: A Crossroads of Cultures and Conflicts
The Middle East, a region often defined by its proximity to the Mediterranean Sea and the Arabian Peninsula, is a melting pot of diverse cultures and civilizations. Its geopolitical significance stems from its strategic location, connecting Asia, Africa, and Europe. This strategic location has also made the region a focal point of historical conflicts and political instability.
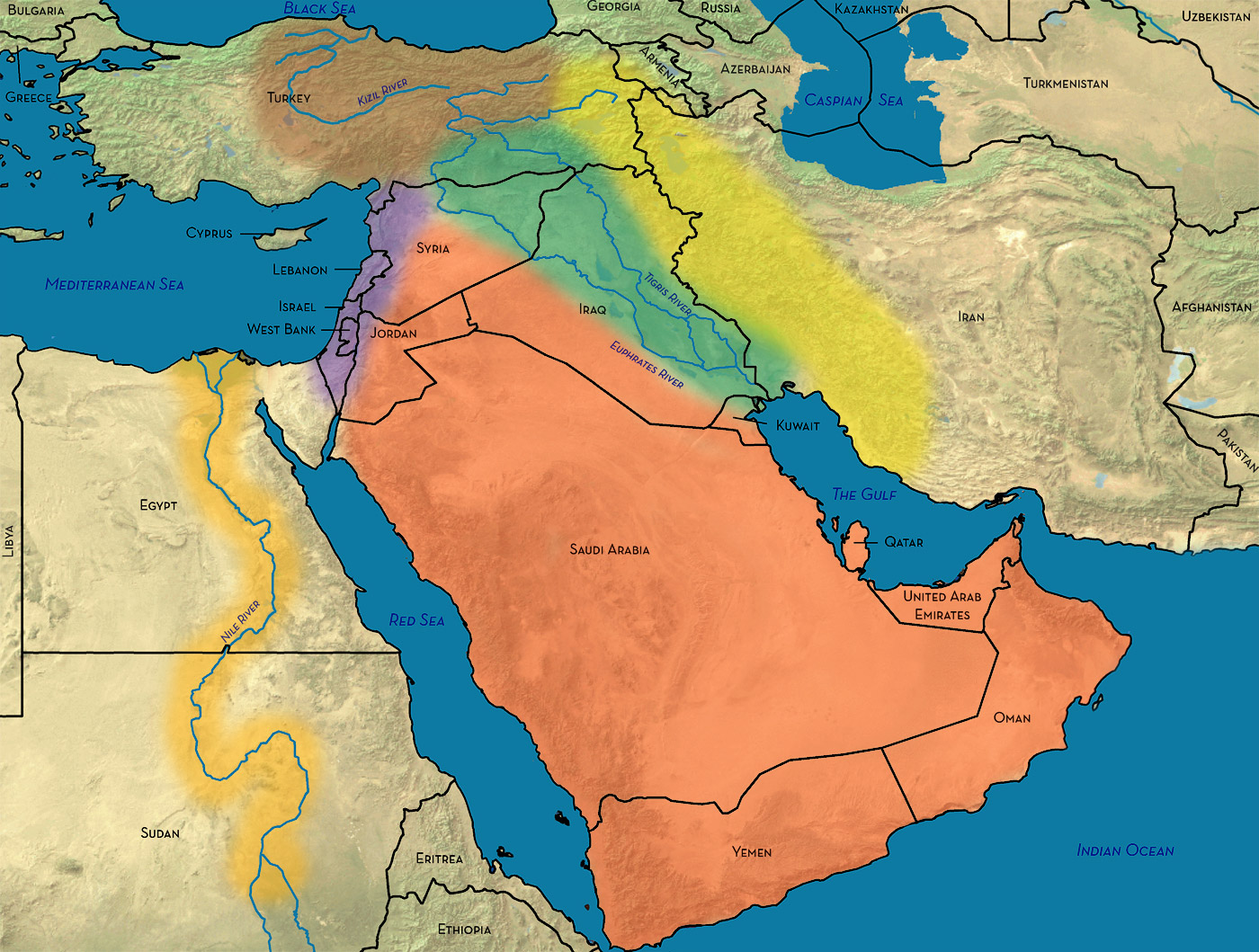
Key Features of the Middle East Map:
- The Arabian Peninsula: Dominated by the vast desert landscape, the Arabian Peninsula is home to some of the world’s largest oil reserves. This region is also the birthplace of Islam and is home to numerous Islamic holy sites.
- The Levant: This region, encompassing countries like Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, and Israel, is characterized by its fertile lands and a history of cultural exchange between the Mediterranean and the Middle East.
- The Persian Gulf: This body of water, crucial for global oil production, is surrounded by countries like Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates.
- The Nile River: Flowing through Egypt and Sudan, the Nile River is a lifeline for these countries, providing water for agriculture and supporting a significant population.
- The Suez Canal: A vital waterway connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea, the Suez Canal is a major trade route and a key strategic asset.
Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Potential
Africa, the second-largest continent in the world, boasts incredible diversity in its landscapes, cultures, and economies. Its rich natural resources and growing population make it a continent with immense potential for development.
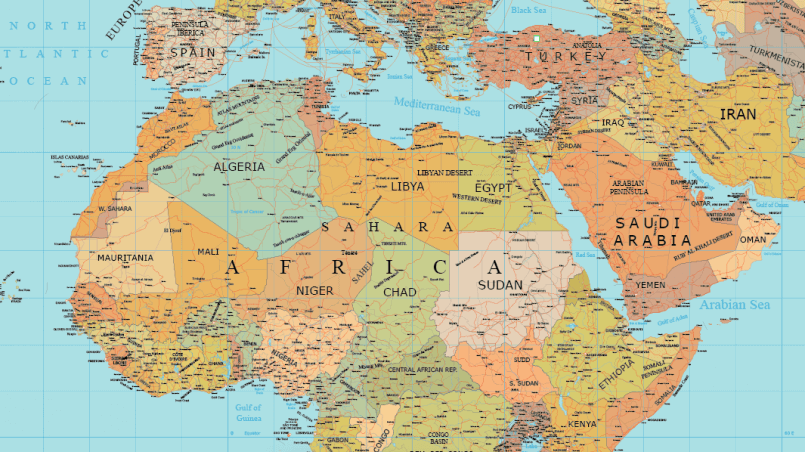
Key Features of the African Map:
- The Sahara Desert: The largest hot desert in the world, the Sahara covers a significant portion of North Africa. It poses challenges for development but also holds untapped resources.
- The Nile River: The longest river in the world, the Nile River flows through eleven African countries, impacting their economies and cultures.
- The Great Rift Valley: A geological formation stretching across eastern Africa, the Great Rift Valley is home to diverse ecosystems, including volcanoes, lakes, and wildlife.
- The Congo Basin: This region, encompassing the Congo River and its tributaries, is a biodiversity hotspot and a crucial source of water for Central Africa.
- The Sahel: A semi-arid region bordering the Sahara Desert, the Sahel faces significant environmental challenges and social issues related to drought and desertification.
Intertwined Histories and Challenges:
The historical and cultural connections between the Middle East and Africa are undeniable. The spread of Islam across North Africa, the trans-Saharan trade routes connecting the regions, and the shared struggles against colonialism all contribute to a complex and interwoven history.
However, the regions also face shared challenges. These include:
- Political instability and conflict: Both regions have experienced significant political instability and conflict, often fueled by religious, ethnic, or resource-related tensions.
- Economic disparities: Despite their natural resources, both regions face significant economic disparities, with poverty and unemployment prevalent in many areas.
- Environmental challenges: Climate change, desertification, and water scarcity are pressing environmental challenges facing both the Middle East and Africa.
Understanding the Interconnectedness
Understanding the geographical and political landscapes of the Middle East and Africa is crucial for navigating the complex dynamics of these regions. The shared history, cultural exchanges, and common challenges create a web of interdependence that cannot be ignored.
FAQs on the Middle East and Africa:
-
Q: What are the major religions practiced in the Middle East and Africa?
- A: Islam is the dominant religion in both regions, with significant Christian and Jewish populations in the Middle East. Africa is home to a diverse range of religions, including Christianity, Islam, traditional African religions, and various other faiths.
-
Q: What are the main economic activities in the Middle East and Africa?
- A: Oil production is a significant economic driver in the Middle East, while agriculture, mining, and tourism are important sectors in Africa. However, both regions face challenges in diversifying their economies and reducing dependence on natural resources.
-
Q: How does climate change impact the Middle East and Africa?
- A: Climate change poses significant threats to both regions, including increased drought, desertification, and water scarcity. These challenges exacerbate existing social and economic problems.
-
Q: What are the major political issues in the Middle East and Africa?
- A: Political instability, conflict, and authoritarian regimes are persistent issues in both regions. The Middle East is also grappling with the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, while Africa faces challenges related to governance, corruption, and civil wars.
Tips for Understanding the Middle East and Africa:
- Study the history and culture of each region: A thorough understanding of the historical context and cultural nuances is essential for appreciating the complexities of these regions.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from various sources, including academic journals, news articles, and personal accounts to gain a balanced understanding of different perspectives.
- Support organizations working for peace and development: Contribute to organizations working to address the challenges facing the Middle East and Africa, promoting peace, education, and sustainable development.
Conclusion
The Middle East and Africa, while geographically distinct, are interconnected in numerous ways. Understanding the complexities of their landscapes, cultures, and histories is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities of these regions. By fostering dialogue, cooperation, and understanding, we can work towards a future where these regions thrive and contribute to a more just and sustainable world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Exploration of the Middle East and Africa: Bridging Continents and Understanding Regions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!