A Geographic Overview: Lebanon and Israel in Perspective
Related Articles: A Geographic Overview: Lebanon and Israel in Perspective
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Overview: Lebanon and Israel in Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Overview: Lebanon and Israel in Perspective
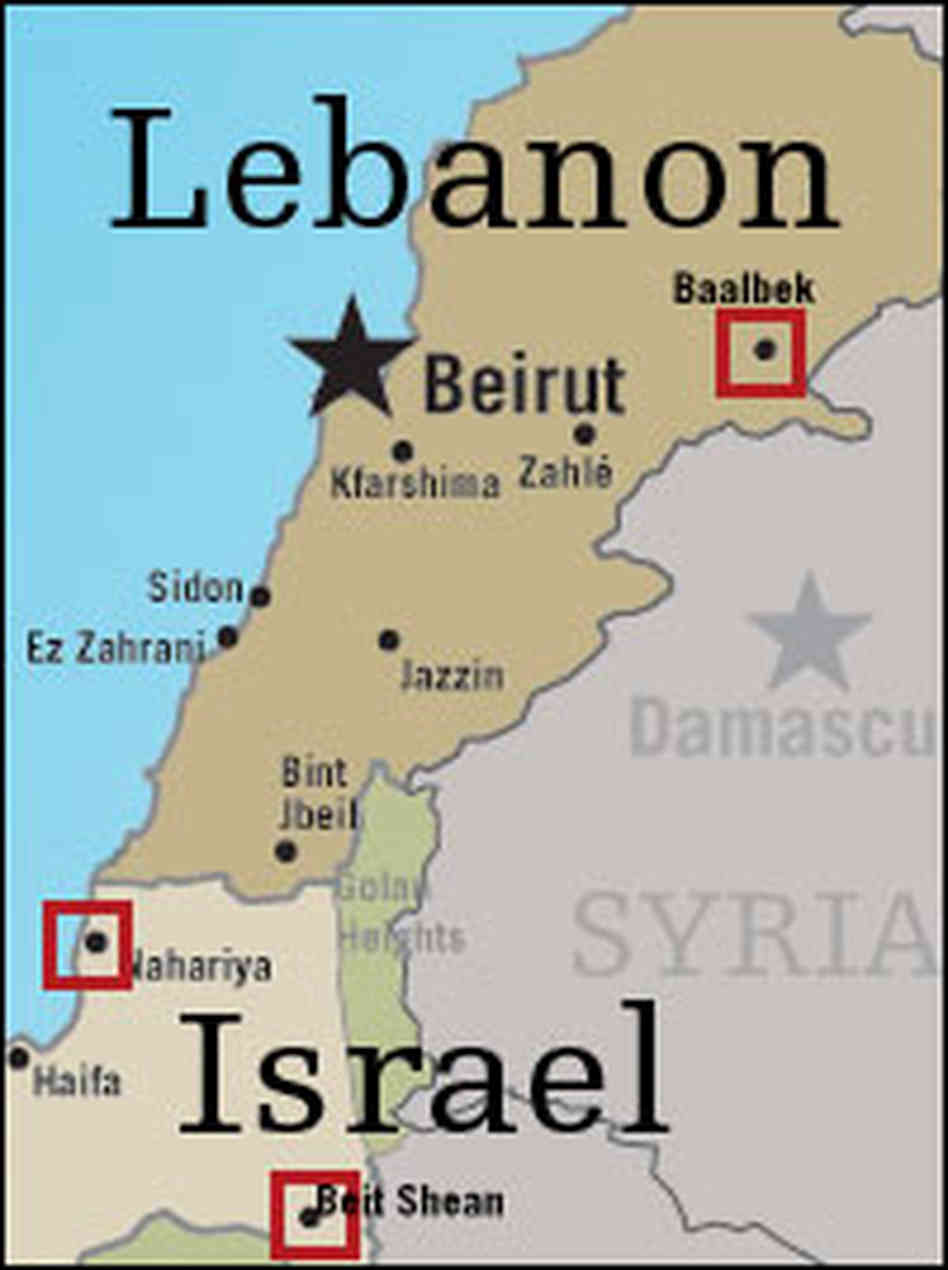
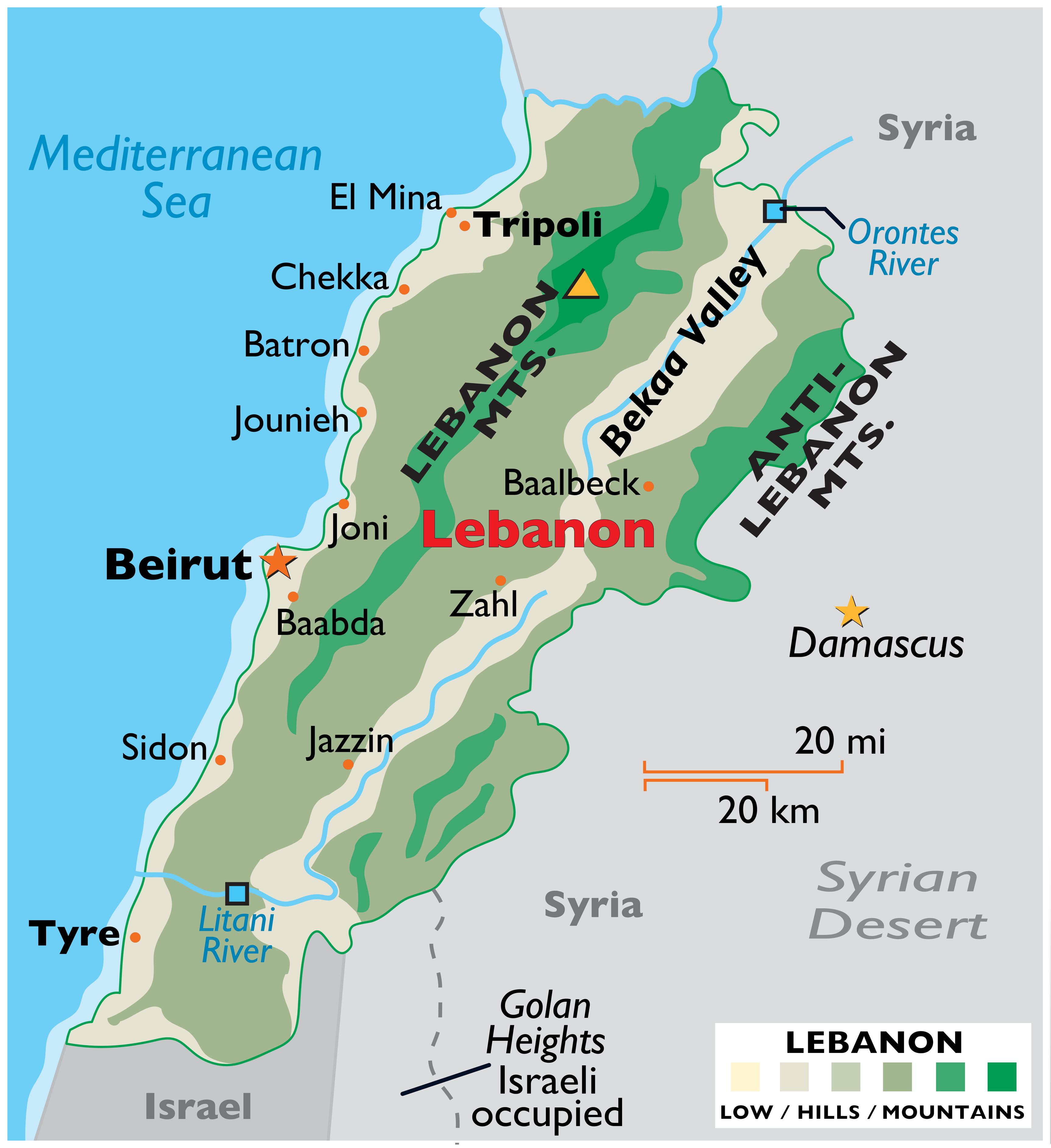
The Levant, a region nestled in the Eastern Mediterranean, holds within its borders two nations with complex histories and intertwined destinies: Lebanon and Israel. Understanding the geographic relationship between these two countries is crucial to grasping the intricacies of their political landscape, cultural exchanges, and ongoing conflicts. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the map of Lebanon and Israel, highlighting key geographical features, historical contexts, and contemporary challenges.
Geographical Context:
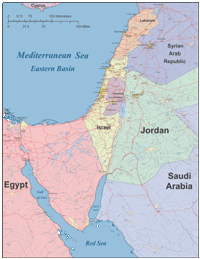
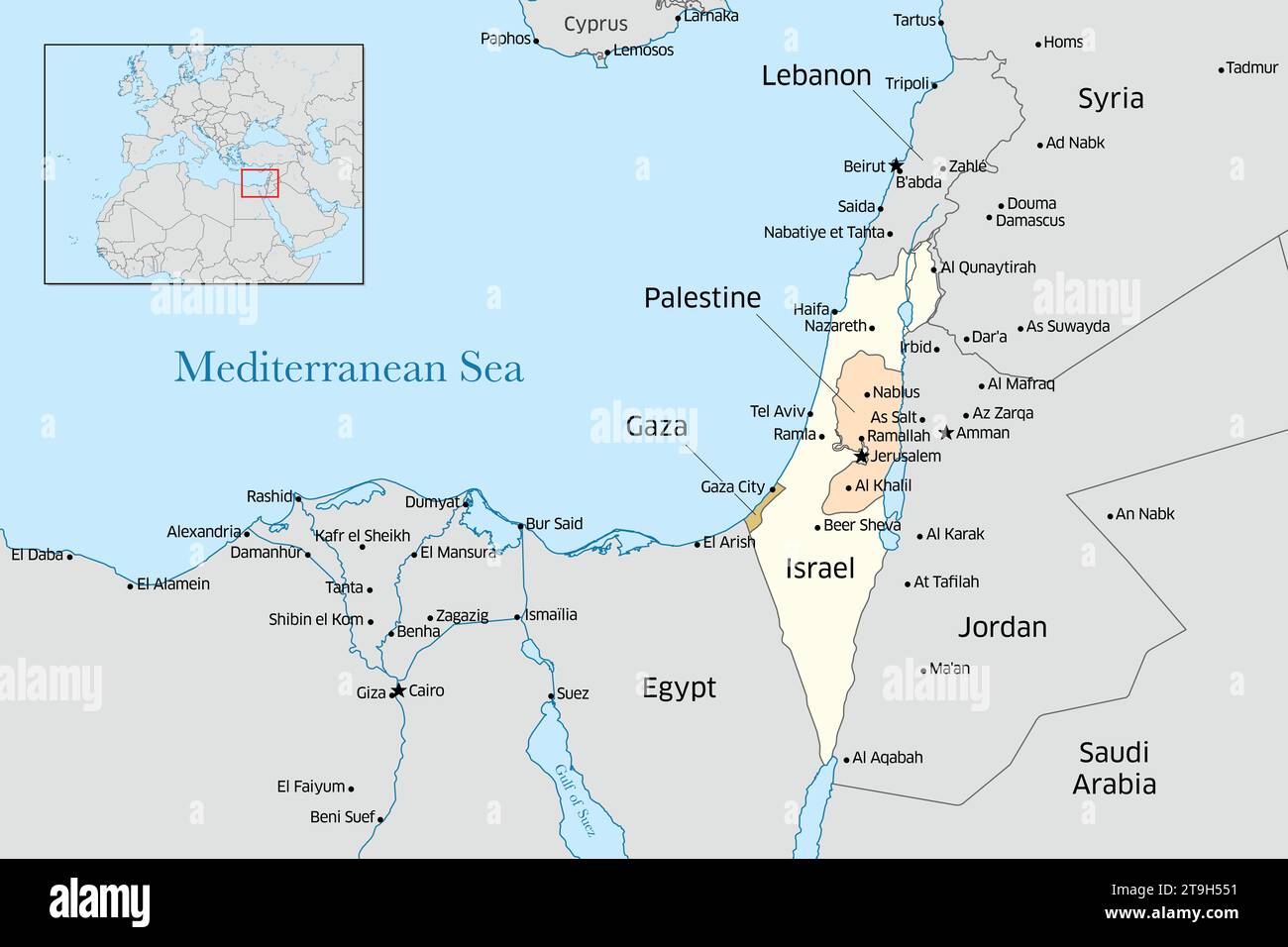
Lebanon and Israel share a narrow strip of land along the Mediterranean coast, bordered by Syria to the north and east, and by the occupied Golan Heights (a disputed territory claimed by both Syria and Israel) to the northeast. Lebanon’s terrain is characterized by a diverse topography, ranging from the fertile coastal plains to the towering Mount Lebanon range, which acts as a natural barrier between the coast and the Bekaa Valley. Israel, on the other hand, exhibits a more varied landscape, encompassing the coastal plain, the Negev Desert, the Galilee region, and the Jordan Valley.
Historical Intertwining:
The history of Lebanon and Israel is deeply intertwined. Both nations share a common heritage, rooted in ancient civilizations, including the Phoenicians, Romans, and Ottomans. The establishment of modern Israel in 1948, however, led to a tumultuous period marked by war and displacement. The 1948 Arab-Israeli War resulted in the displacement of hundreds of thousands of Palestinians, many of whom found refuge in Lebanon. This event, along with subsequent conflicts, has shaped the political landscape of both countries, leaving a legacy of mistrust and unresolved issues.
The Lebanon-Israel Border:
The Lebanon-Israel border is a complex and highly contested area. It stretches for approximately 79 miles, traversing diverse terrain, from the Mediterranean coast to the foothills of Mount Hermon. The border’s precise delineation has been a source of contention for decades, with both countries claiming portions of the territory. The presence of the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) has played a significant role in maintaining a fragile peace in the region.
Key Geographical Features:
Lebanon:
- Mount Lebanon: A mountain range that forms a natural barrier between the coast and the Bekaa Valley, offering a strategic advantage for defense.
- Bekaa Valley: A fertile valley known for its agricultural production and strategic importance.
- Coastal Plain: A narrow strip of land along the Mediterranean Sea, home to major cities like Beirut and Tripoli.
- Litani River: The largest river in Lebanon, flowing through the Bekaa Valley and providing a vital source of water.
Israel:
- Coastal Plain: A fertile region stretching along the Mediterranean Sea, housing major cities like Tel Aviv and Haifa.
- Negev Desert: A vast desert region in southern Israel, characterized by arid conditions and sparse vegetation.
- Galilee: A mountainous region in northern Israel, known for its rolling hills and agricultural production.
- Jordan Valley: A fertile valley running along the Jordan River, providing a vital source of water.
Contemporary Challenges:
The relationship between Lebanon and Israel remains fragile, marked by ongoing tensions and unresolved disputes. The following challenges continue to pose significant threats to regional stability:
- The Israeli-Palestinian Conflict: The ongoing conflict between Israel and the Palestinians has a profound impact on both Lebanon and Israel. The presence of Palestinian refugee camps in Lebanon, coupled with the unresolved status of Jerusalem and the West Bank, fuels instability and tensions.
- Hezbollah: The Lebanese Shia militia, backed by Iran, operates in southern Lebanon and has engaged in armed conflict with Israel. Hezbollah’s presence and influence continue to be a source of concern for Israel, leading to intermittent clashes and a heightened state of alert.
- Water Resources: The limited water resources in the region, coupled with competing claims, present a significant challenge. Lebanon and Israel have a history of disputes over water access, particularly regarding the Litani River and the Jordan River.
- Economic Disparities: The economic gap between Lebanon and Israel is significant, with Israel enjoying a higher level of economic development and stability. This disparity contributes to social and political tensions, particularly among Lebanese populations who perceive themselves as disadvantaged.
FAQs:
1. What is the current status of the Lebanon-Israel border?
The Lebanon-Israel border remains a highly sensitive area, with ongoing disputes over the precise delineation. The presence of UNIFIL helps to maintain a fragile peace, but tensions persist, fueled by historical grievances and the presence of Hezbollah.
2. How does the Israeli-Palestinian conflict impact Lebanon?
The Israeli-Palestinian conflict has a profound impact on Lebanon, both politically and socially. The presence of Palestinian refugee camps in Lebanon, coupled with the unresolved status of Jerusalem and the West Bank, contributes to instability and tensions within the country.
3. What is the role of Hezbollah in the Lebanon-Israel relationship?
Hezbollah, a Lebanese Shia militia, is a powerful force in Lebanon and a significant player in the regional conflict. The group’s presence in southern Lebanon and its armed confrontation with Israel pose a constant threat to peace and stability.
4. What are the main economic challenges facing Lebanon and Israel?
Lebanon faces significant economic challenges, including high levels of poverty, unemployment, and public debt. Israel, while enjoying a higher level of economic development, faces challenges related to social inequality and the cost of living.
5. What are the prospects for peace between Lebanon and Israel?
The prospects for peace between Lebanon and Israel remain uncertain, hampered by a multitude of factors, including the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, the presence of Hezbollah, and unresolved border disputes. Achieving lasting peace will require significant efforts from both sides, coupled with international support and a commitment to dialogue and compromise.
Tips:
- Study the historical context: Understanding the historical relationship between Lebanon and Israel is essential for grasping the complexities of the present.
- Follow the news: Stay informed about the latest developments in the region, including political negotiations, military activities, and economic trends.
- Engage in critical thinking: Analyze different perspectives and consider the impact of various events on the relationship between Lebanon and Israel.
- Support peace-building initiatives: Encourage and support organizations working towards conflict resolution and promoting dialogue between the two countries.
Conclusion:
The map of Lebanon and Israel reflects a complex and multifaceted reality, shaped by historical legacies, political tensions, and ongoing conflicts. Understanding the geographical context, historical background, and contemporary challenges is crucial for comprehending the region’s dynamics and the complexities of the relationship between these two nations. Achieving lasting peace and stability will require a commitment to dialogue, compromise, and a shared vision for a future where both Lebanon and Israel can thrive in peace and security.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Overview: Lebanon and Israel in Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!