A Journey Through the Andes: A Map of the World’s Longest Mountain Range
Related Articles: A Journey Through the Andes: A Map of the World’s Longest Mountain Range
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through the Andes: A Map of the World’s Longest Mountain Range. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Journey Through the Andes: A Map of the World’s Longest Mountain Range
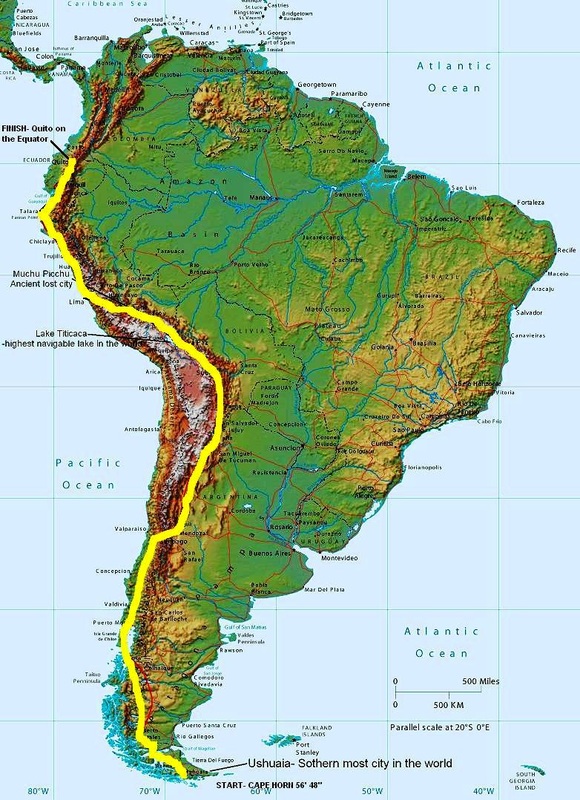
The Andes Mountains, a majestic spine of granite and snow-capped peaks, traverse the length of the western portion of South America, forming a breathtaking and vital landscape. Stretching over 7,000 kilometers (4,350 miles) from Venezuela in the north to Tierra del Fuego at the southern tip of the continent, the Andes are the longest mountain range on Earth. Their towering presence profoundly impacts the geography, climate, and culture of the surrounding nations.
A Tapestry of Diverse Landscapes:
A map of the Andes reveals a complex and varied topography. The range is segmented into seven distinct regions, each with its own unique characteristics:
- Northern Andes: This region, encompassing Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador, is characterized by high plateaus, active volcanoes, and the iconic snow-capped peaks of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta.
- Central Andes: The heart of the Andes, spanning Peru and Bolivia, is dominated by the Altiplano, a high-altitude plateau home to the world’s largest salt flats, the Salar de Uyuni. This region also features the highest peak in the Americas, Mount Aconcagua (6,961 meters).
- Southern Andes: This segment, stretching across Chile and Argentina, features the Patagonian Andes, known for their dramatic glaciers, towering peaks, and rugged landscapes.
- Cordillera Occidental: Running along the western edge of the Andes, this chain is dominated by active volcanoes, particularly in the regions of Chile and Ecuador.
- Cordillera Oriental: Located on the eastern side of the Andes, this chain is characterized by lower elevations and a greater presence of forests.
- Cordillera Central: Situated between the Cordillera Occidental and Oriental, this chain features a mix of high plateaus, valleys, and peaks.
- Cordillera de la Costa: This coastal mountain range runs parallel to the Andes in Chile, forming a distinct geographic feature.
A Cradle of Biodiversity and Cultural Heritage:
The Andes are a global biodiversity hotspot, harboring an astonishing array of flora and fauna. The high altitude, varied climates, and diverse habitats have led to the evolution of unique species found nowhere else on Earth. From the majestic Andean condor soaring above the peaks to the vibrant hummingbirds flitting among the flowers, the Andes are a haven for wildlife.
The Andes have also been a home to indigenous communities for millennia. The Inca Empire, once a powerful civilization, flourished in the central Andes, leaving behind a legacy of architectural marvels, intricate textiles, and rich cultural traditions. Today, diverse indigenous groups continue to live in the Andes, preserving their ancestral languages, customs, and knowledge systems.
The Importance of the Andes:
The Andes are not just a breathtaking landscape; they are a vital part of the South American ecosystem and a source of essential resources.
- Water Resources: The Andes are a crucial source of water for millions of people, acting as a natural reservoir for numerous rivers and lakes. The snowmelt from the high peaks feeds vital waterways, providing irrigation for agriculture and drinking water for cities.
- Mineral Wealth: The Andes are rich in mineral resources, including copper, gold, silver, and lithium. Mining plays a significant role in the economies of many Andean countries.
- Tourism: The Andes attract millions of tourists every year, drawn to their stunning beauty and unique cultural experiences. The region offers opportunities for trekking, climbing, skiing, and exploring ancient ruins.
- Climate Regulation: The Andes play a vital role in regulating the climate of South America. The mountains influence rainfall patterns, creating distinct microclimates and supporting diverse ecosystems.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite their immense importance, the Andes face a number of challenges:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures are impacting the glaciers in the Andes, threatening water resources and potentially leading to increased instability in the mountains.
- Deforestation: The loss of forests in the Andes is impacting biodiversity, soil erosion, and water availability.
- Mining: While mining provides economic benefits, it also poses risks to the environment and local communities.
- Poverty: Many communities in the Andes live in poverty, lacking access to basic services like education and healthcare.
FAQs about the Andes:
- What is the highest mountain in the Andes? Mount Aconcagua, located in Argentina, is the highest peak in the Andes and the highest mountain outside Asia, reaching a height of 6,961 meters (22,838 feet).
- What are the main countries that the Andes Mountains pass through? The Andes Mountains traverse seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina.
- What are the major rivers that originate in the Andes? The Andes are the source of many major rivers in South America, including the Amazon, Orinoco, Paraná, and Magdalena.
- What are some of the major cities located in the Andes? Major cities located in the Andes include Quito (Ecuador), Lima (Peru), La Paz (Bolivia), and Santiago (Chile).
- What are some of the challenges facing the Andes? The Andes face challenges such as climate change, deforestation, mining, and poverty.
Tips for Exploring the Andes:
- Research your destination: Each region of the Andes offers unique experiences, so research your interests and choose a destination that aligns with your preferences.
- Be prepared for altitude: The high altitude can cause altitude sickness, so acclimatize gradually and be prepared for the effects.
- Respect local customs: The Andes are home to diverse indigenous communities, so learn about their customs and traditions and show respect.
- Pack for all weather conditions: The weather in the Andes can be unpredictable, so pack layers of clothing and be prepared for rain, sun, and cold.
- Consider hiring a guide: A local guide can provide valuable insights into the culture, history, and natural wonders of the Andes.
Conclusion:
The Andes Mountains are a testament to the power and beauty of nature. Their towering peaks, diverse landscapes, and rich cultural heritage make them a truly remarkable region. Understanding the importance of the Andes and the challenges they face is crucial for ensuring their preservation and continued prosperity. By appreciating and protecting this vital ecosystem, we can ensure that future generations can continue to experience the wonder and majesty of the world’s longest mountain range.


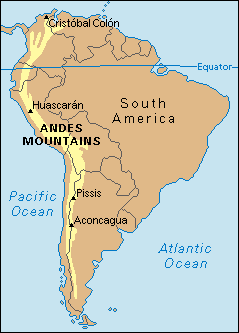


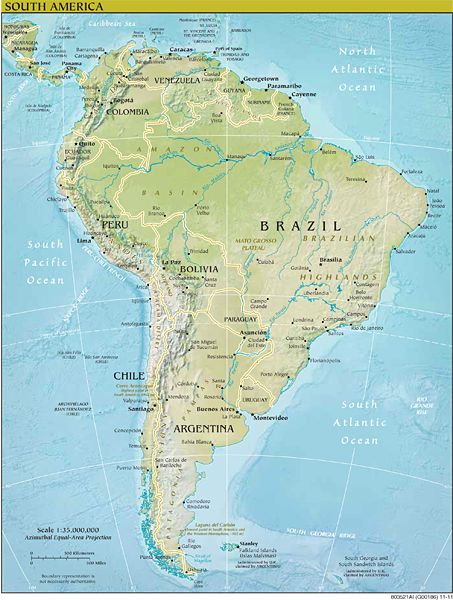

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through the Andes: A Map of the World’s Longest Mountain Range. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!