A Tapestry of Landforms: Unveiling the Physical Geography of the Middle East
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Landforms: Unveiling the Physical Geography of the Middle East
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Landforms: Unveiling the Physical Geography of the Middle East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Landforms: Unveiling the Physical Geography of the Middle East
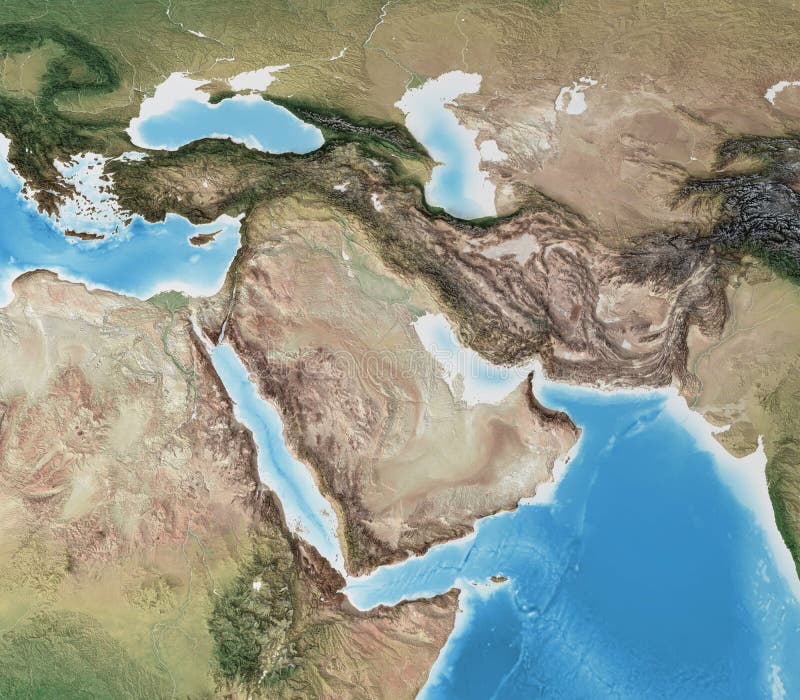
The Middle East, a region often defined by its political and cultural complexities, also boasts a fascinating and diverse physical landscape. Understanding the region’s geography is crucial for appreciating its history, its challenges, and its potential. This article delves into the key physical features that shape the Middle East, highlighting their impact on the region’s environment, resources, and human settlements.
A Land of Contrasts: From Arid Deserts to Fertile Valleys
The Middle East is characterized by a striking contrast between vast, barren deserts and fertile valleys, each playing a significant role in the region’s ecological balance and human development.
-
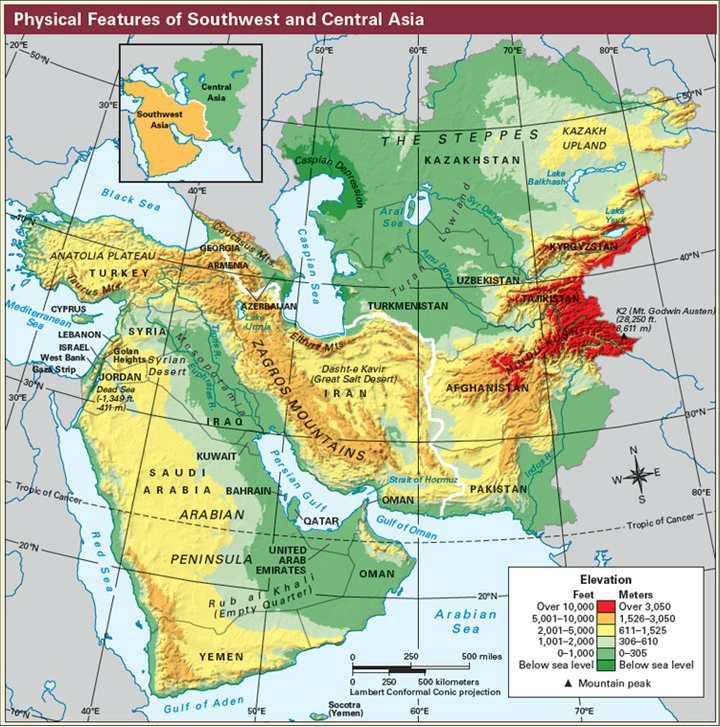
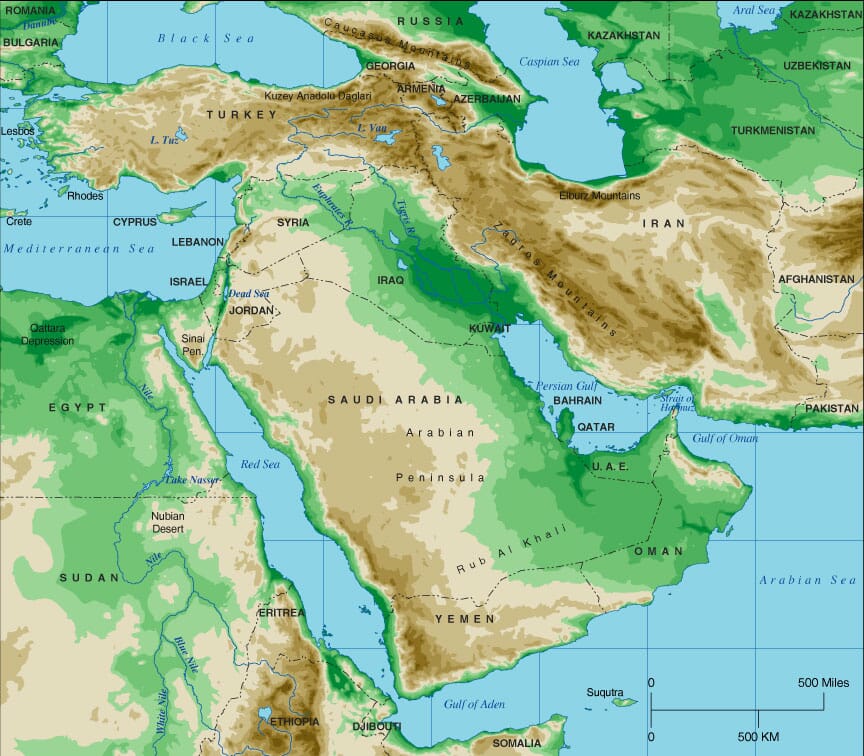
Deserts: Dominating the landscape, the Arabian, Syrian, and Sahara deserts cover significant portions of the Middle East. These arid regions, sculpted by wind erosion and characterized by sparse vegetation and extreme temperatures, present unique challenges for human habitation and resource management.
-
Valleys: The Tigris and Euphrates river valleys in Mesopotamia, the Nile Valley in Egypt, and the Jordan Valley in the Levant are oases of life amidst the desert. These fertile valleys have historically supported dense populations and thriving civilizations, their fertile soils providing the basis for agriculture and economic growth.
The Shaping Force: Mountains and Plateaus
Mountains and plateaus play a crucial role in shaping the Middle East’s climate, water resources, and human settlements.
-
Mountains: The Zagros Mountains in Iran, the Taurus Mountains in Turkey, and the Lebanon Mountains in Lebanon are significant mountain ranges, influencing rainfall patterns and creating distinct microclimates. These mountainous regions often serve as natural barriers, shaping migration patterns and political boundaries.
-
Plateaus: The Iranian Plateau, the Anatolian Plateau, and the Arabian Plateau are elevated landforms that influence the region’s climate and water resources. Their high altitudes often result in cooler temperatures and distinct ecosystems, supporting unique flora and fauna.
Waterways: Lifeblood of the Middle East
Water is a precious resource in the arid Middle East, with rivers, lakes, and groundwater playing a vital role in sustaining life and development.
-
Rivers: The Tigris and Euphrates, the Nile, the Jordan, and the Karun are major rivers that flow through the region, providing irrigation for agriculture, drinking water for populations, and transportation routes. However, water scarcity and competition for water resources are growing challenges in the Middle East.
-
Lakes: The Dead Sea, the Caspian Sea, and Lake Van are notable lakes in the region, each possessing unique characteristics and facing environmental challenges. The Dead Sea, known for its high salinity, is a significant resource for minerals and tourism. The Caspian Sea, the world’s largest inland body of water, holds vast reserves of oil and gas, making it a geopolitical hotspot.
The Impact of Physical Features on Human Life
The diverse physical features of the Middle East have profoundly shaped human settlements, economic activities, and cultural development.
-
Agriculture: Fertile valleys and oases have historically supported agriculture, providing food and income for generations. However, water scarcity and land degradation pose increasing challenges to sustainable agricultural practices.
-
Energy Resources: The Middle East is home to vast reserves of oil and natural gas, making it a key player in the global energy market. The exploitation of these resources has driven economic growth but also contributed to environmental concerns and geopolitical tensions.
-
Tourism: The region’s diverse landscapes, from the majestic mountains to the stunning deserts, attract tourists from around the world. Tourism can be a vital source of income but also poses challenges related to environmental conservation and cultural preservation.
Understanding the Importance of the Middle East’s Physical Features
The physical features of the Middle East are not merely geographical markers; they are fundamental elements that have shaped the region’s history, its present, and its future.
-
Resource Management: Understanding the distribution and availability of water, land, and energy resources is crucial for sustainable development and conflict resolution.
-
Environmental Challenges: The Middle East faces pressing environmental challenges such as desertification, water scarcity, and climate change. Addressing these issues requires a comprehensive understanding of the region’s physical geography.
-
Geopolitics: The Middle East’s physical features have played a significant role in shaping political boundaries, migration patterns, and regional conflicts. Understanding these connections is essential for navigating the complexities of the region’s geopolitics.
FAQs on the Middle East’s Physical Features
-
What are the major deserts in the Middle East? The Arabian Desert, the Syrian Desert, and the Sahara Desert are the major deserts in the region.
-
What are the main mountain ranges in the Middle East? The Zagros Mountains, the Taurus Mountains, and the Lebanon Mountains are significant mountain ranges in the Middle East.
-
What are the major rivers in the Middle East? The Tigris and Euphrates, the Nile, the Jordan, and the Karun are major rivers in the region.
-
What are the main lakes in the Middle East? The Dead Sea, the Caspian Sea, and Lake Van are notable lakes in the Middle East.
-
What are the environmental challenges facing the Middle East? The region faces challenges such as desertification, water scarcity, and climate change.
Tips for Understanding the Middle East’s Physical Features
-
Use a map: A physical map of the Middle East can help you visualize the region’s landforms, water bodies, and major cities.
-
Explore online resources: Websites and databases provide detailed information on the region’s physical geography, including climate data, geological formations, and environmental issues.
-
Read books and articles: Books and articles by geographers and historians offer insightful perspectives on the relationship between the Middle East’s physical features and its people.
-
Travel to the region: Experiencing the Middle East firsthand can deepen your understanding of its diverse landscapes and the challenges faced by its people.
Conclusion
The physical features of the Middle East are a tapestry of contrasting landscapes, each contributing to the region’s unique character and challenges. From the vast deserts to the fertile valleys, from the towering mountains to the vital waterways, the Middle East’s geography has shaped its history, its resources, and its future. Understanding the region’s physical features is essential for appreciating its complexities, navigating its challenges, and fostering sustainable development for generations to come.
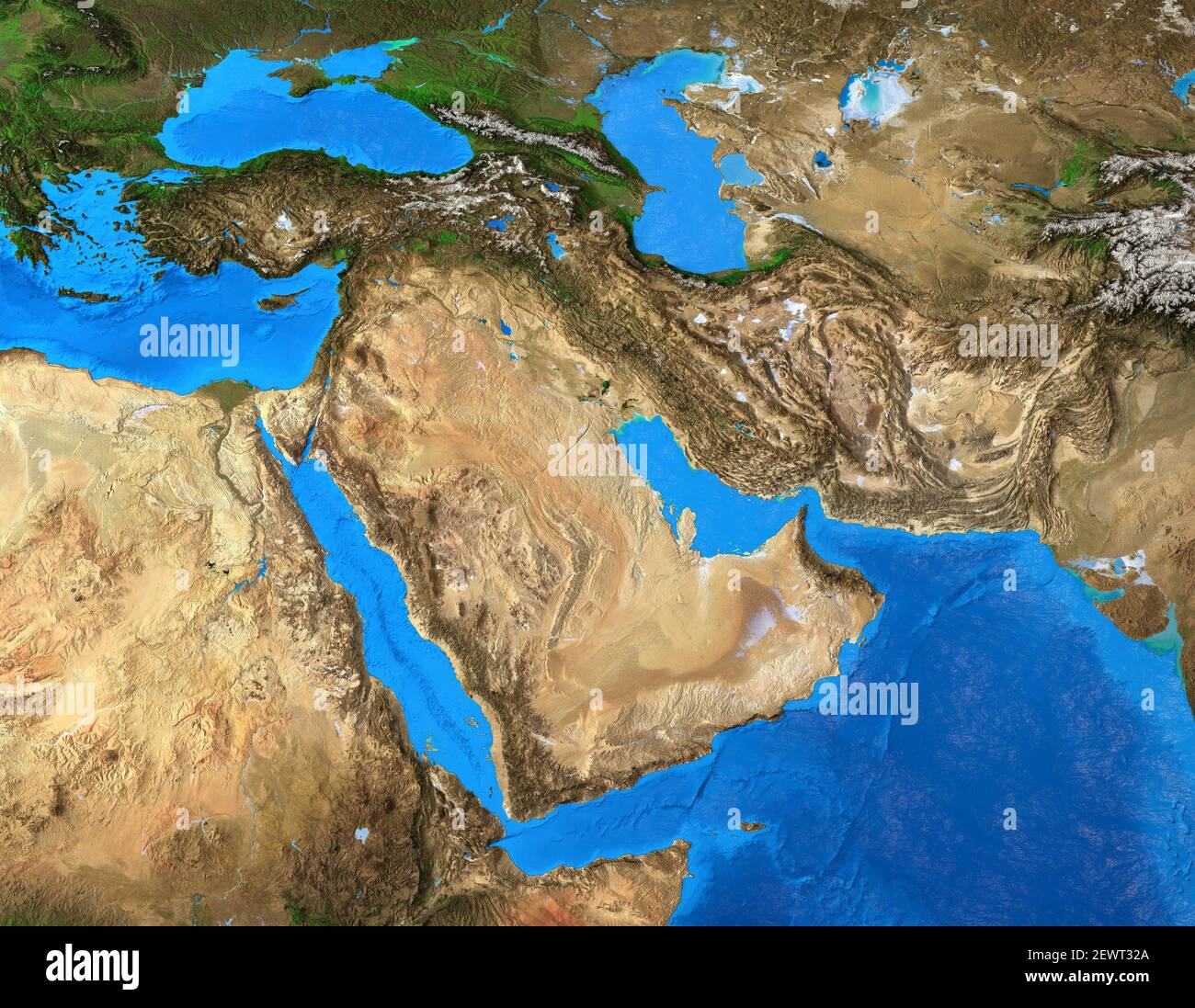

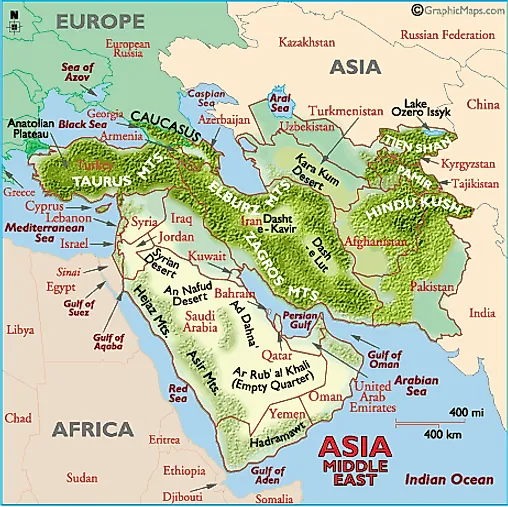

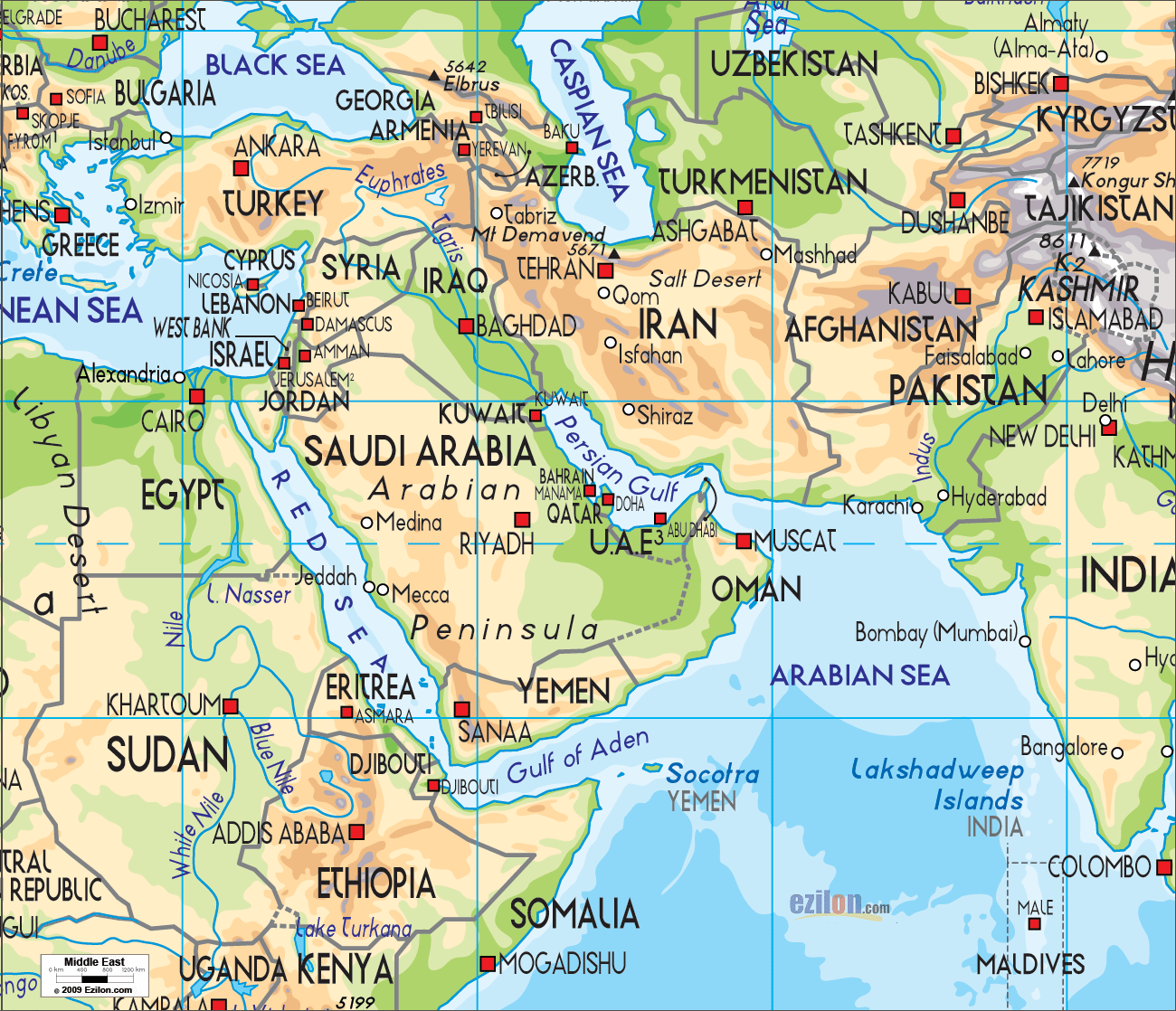
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Landforms: Unveiling the Physical Geography of the Middle East. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!