A World Unveiled: Exploring the Diverse Landscape of Maps
Related Articles: A World Unveiled: Exploring the Diverse Landscape of Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A World Unveiled: Exploring the Diverse Landscape of Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A World Unveiled: Exploring the Diverse Landscape of Maps
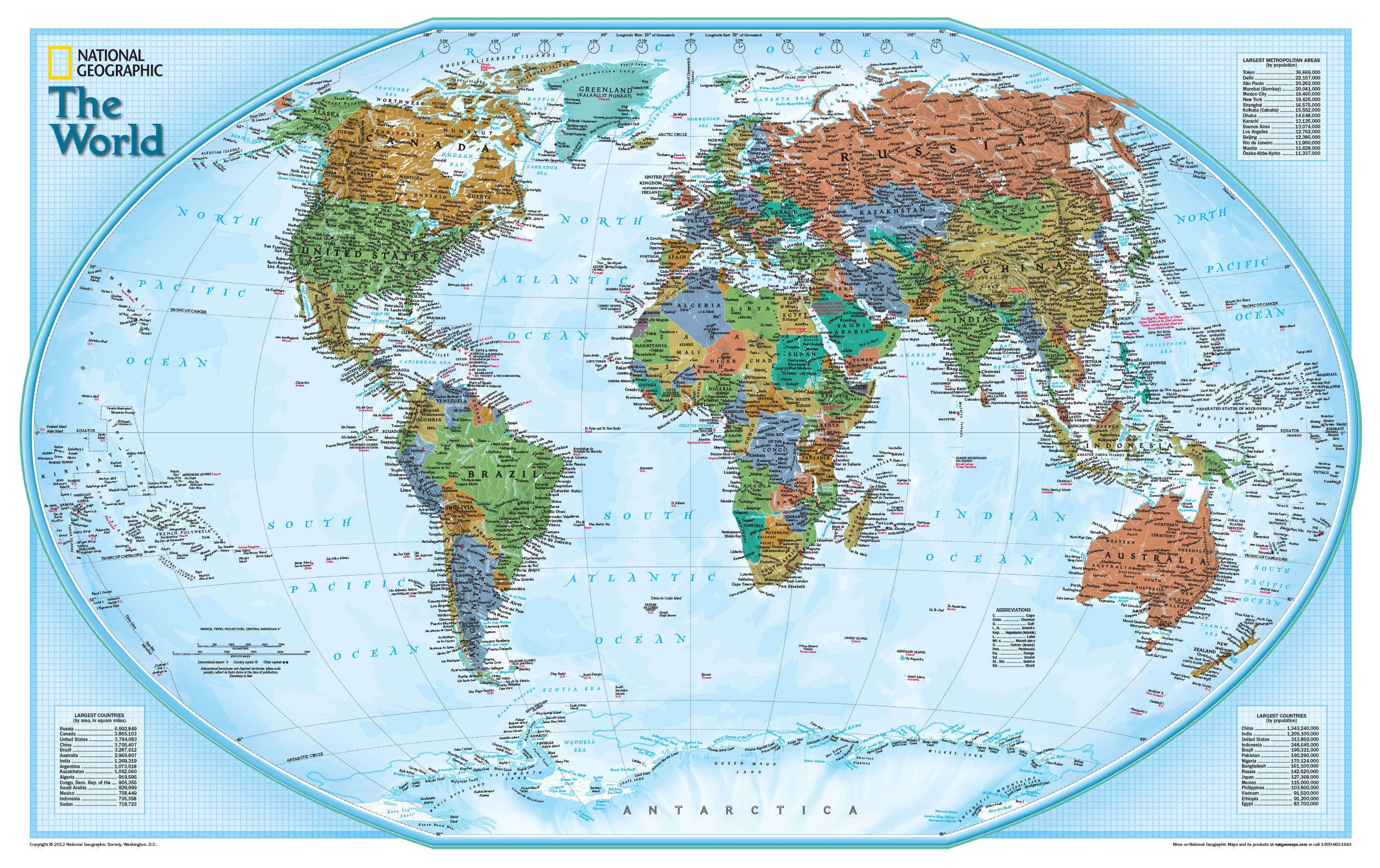
Maps are more than just static representations of the world; they are powerful tools that unlock understanding, facilitate navigation, and inspire exploration. From ancient cave paintings to sophisticated digital globes, maps have evolved alongside human civilization, reflecting our growing knowledge and interaction with the world around us.
This exploration delves into the diverse landscape of maps, highlighting their varied forms, functions, and enduring significance.
Navigating the Past: Ancient and Historical Maps
The earliest forms of maps emerged from the need to understand and navigate the physical world. Ancient cave paintings, such as those found in France’s Lascaux cave, depict hunting scenes and animal migrations, offering rudimentary representations of terrain and animal movement. These early maps served as tools for communication and shared knowledge, laying the foundation for more formalized cartography.
The Babylonian clay tablet known as the "World Map" (circa 600 BC) is considered one of the earliest surviving examples of a world map. It depicts the known world as a disc surrounded by water, with Mesopotamia positioned at the center. This map, while rudimentary, demonstrates the evolving understanding of geography and the desire to represent the world in a structured manner.
Ancient Egyptian maps, often inscribed on papyrus, were primarily used for surveying and land management. They employed a grid system to accurately measure distances and plot land boundaries, demonstrating a sophisticated understanding of geometry and spatial relationships.
Medieval and Renaissance Maps: Charting the World
The Middle Ages witnessed the rise of cartography as an integral part of exploration and trade. Medieval maps, often referred to as "mappae mundi," depicted the world as a flat disc, with Jerusalem at the center. These maps were heavily influenced by religious beliefs and incorporated elements of mythology and legend alongside geographical data.
The Renaissance period saw a shift towards more accurate and detailed cartography. The invention of the printing press facilitated the widespread dissemination of maps, leading to the development of standardized cartographic conventions. The work of cartographers like Gerardus Mercator and Abraham Ortelius revolutionized mapmaking, introducing new projections and techniques that allowed for more accurate representation of the Earth’s surface.
The Age of Exploration: Mapping the Uncharted
The Age of Exploration, fueled by the desire for new trade routes and territories, saw a surge in mapmaking. Explorers like Christopher Columbus and Ferdinand Magellan relied heavily on maps to navigate uncharted waters, charting new lands and expanding the known world.
Maps during this period were often highly detailed, incorporating information about coastlines, currents, and potential hazards. They played a crucial role in the development of maritime navigation, facilitating trade and the exchange of knowledge between continents.
Modern Maps: From Paper to Pixels
The 20th century witnessed a transformation in mapmaking, driven by technological advancements and the increasing demand for detailed and accurate representations of the world. The development of aerial photography and satellite imagery revolutionized cartography, providing unprecedented levels of detail and accuracy.
Modern maps are increasingly digital, utilizing Geographic Information Systems (GIS) to integrate various data layers, including elevation, population density, and environmental information. This allows for the creation of interactive and dynamic maps that can be used for a wide range of applications, from urban planning to disaster response.
Examples of Map Types and Their Applications
1. Topographical Maps: These maps depict the physical features of a region, including elevation, rivers, lakes, and roads. They are essential for hikers, climbers, and outdoor enthusiasts, providing detailed information about terrain and elevation changes.
2. Road Maps: These maps focus on transportation infrastructure, showing roads, highways, and major cities. They are indispensable for travelers, providing guidance for navigating unfamiliar areas.
3. Political Maps: These maps display the boundaries of countries, states, and other political entities. They are used for understanding political geography, analyzing geopolitical relationships, and studying the distribution of power.
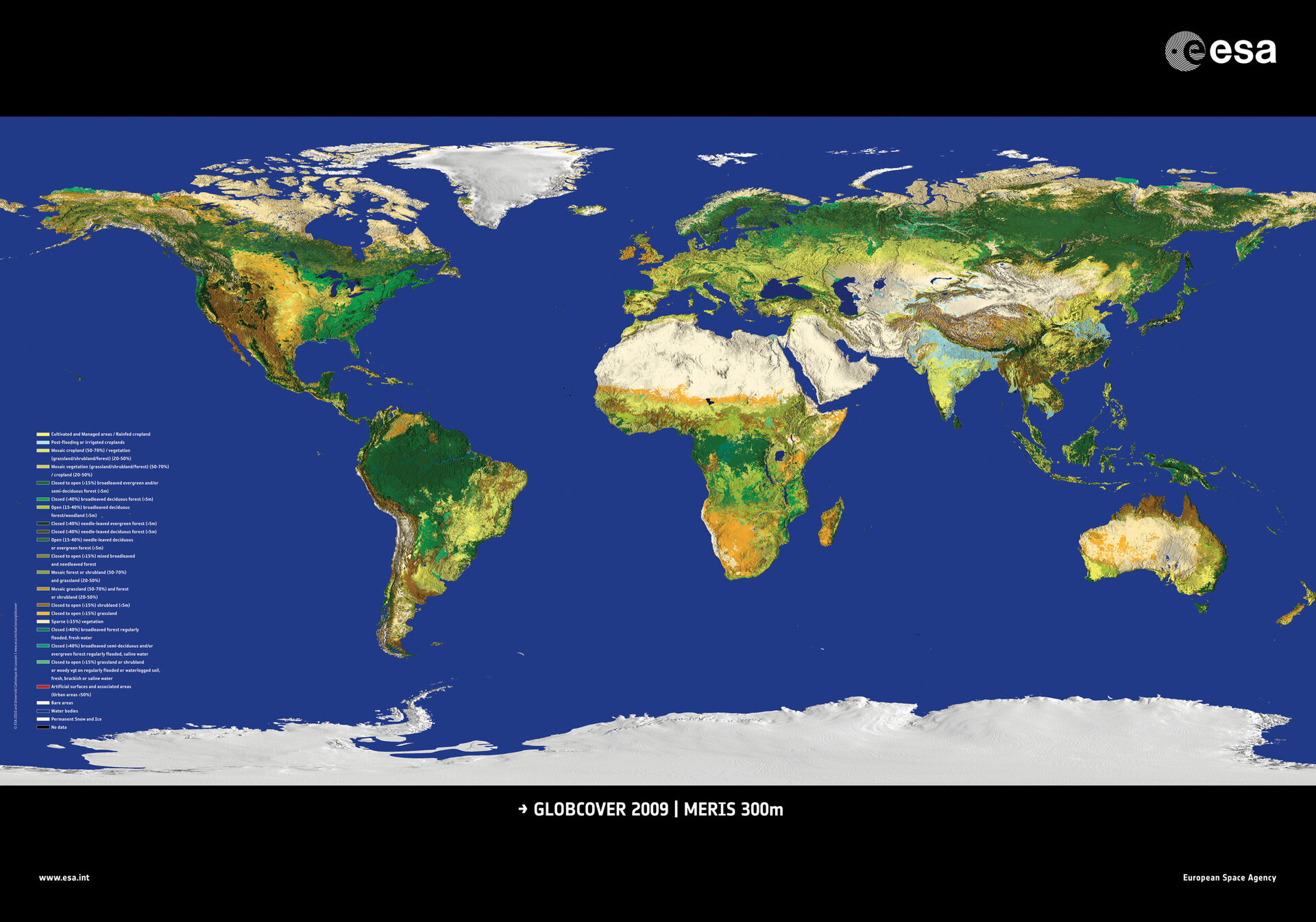
4. Thematic Maps: These maps highlight specific themes or data sets, such as population density, climate patterns, or disease outbreaks. They are valuable tools for researchers, policymakers, and educators, providing visual representations of complex data.
5. Nautical Charts: These maps are specifically designed for maritime navigation, showing coastlines, depths, currents, and navigational hazards. They are essential for safe and efficient seafaring.
6. Aerial Photographs and Satellite Imagery: These images provide a bird’s-eye view of the Earth’s surface, capturing vast areas with high resolution. They are used for a variety of applications, including urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster assessment.
7. Digital Maps: These interactive maps, often accessed through smartphones and computers, offer a wealth of information and navigation tools. They integrate data from multiple sources, providing real-time traffic updates, directions, and location-based services.
FAQs about Examples of Maps
Q: What is the difference between a map and a globe?
A: A map is a flat representation of the Earth’s surface, while a globe is a three-dimensional model. Globes offer a more accurate representation of the Earth’s shape and curvature, but maps are more practical for displaying specific regions or themes.
Q: What are the different types of map projections?
A: Map projections are mathematical methods used to represent the Earth’s curved surface on a flat plane. Different projections distort the shape, size, and distance of features on the map in different ways. Common projections include Mercator, Robinson, and Mollweide.
Q: How do maps contribute to understanding the world?
A: Maps provide a visual framework for understanding spatial relationships, facilitating the study of geography, history, and social phenomena. They help us visualize patterns, analyze trends, and gain insights into the complexities of the world around us.
Tips for Reading and Understanding Maps
1. Identify the Map’s Scale: The map scale indicates the relationship between distances on the map and corresponding distances in the real world. Understanding the scale is crucial for interpreting distances and sizes accurately.
2. Recognize the Map’s Legend: The legend explains the symbols and colors used on the map, providing a key to understanding its content.
3. Analyze the Map’s Projection: The projection used for the map can influence the shape and size of features, so it’s important to consider the projection’s limitations.
4. Consider the Map’s Purpose: Understanding the map’s intended use can help in interpreting its content and appreciating its strengths and limitations.
Conclusion
Maps are fundamental tools that have shaped human understanding of the world for millennia. They have evolved from rudimentary representations to sophisticated digital systems, reflecting our growing knowledge and technological advancements. As we continue to explore and interact with the world around us, maps will remain indispensable instruments for navigation, communication, and understanding. From ancient cave paintings to interactive digital globes, maps offer a window into the past, a guide for the present, and a blueprint for the future.
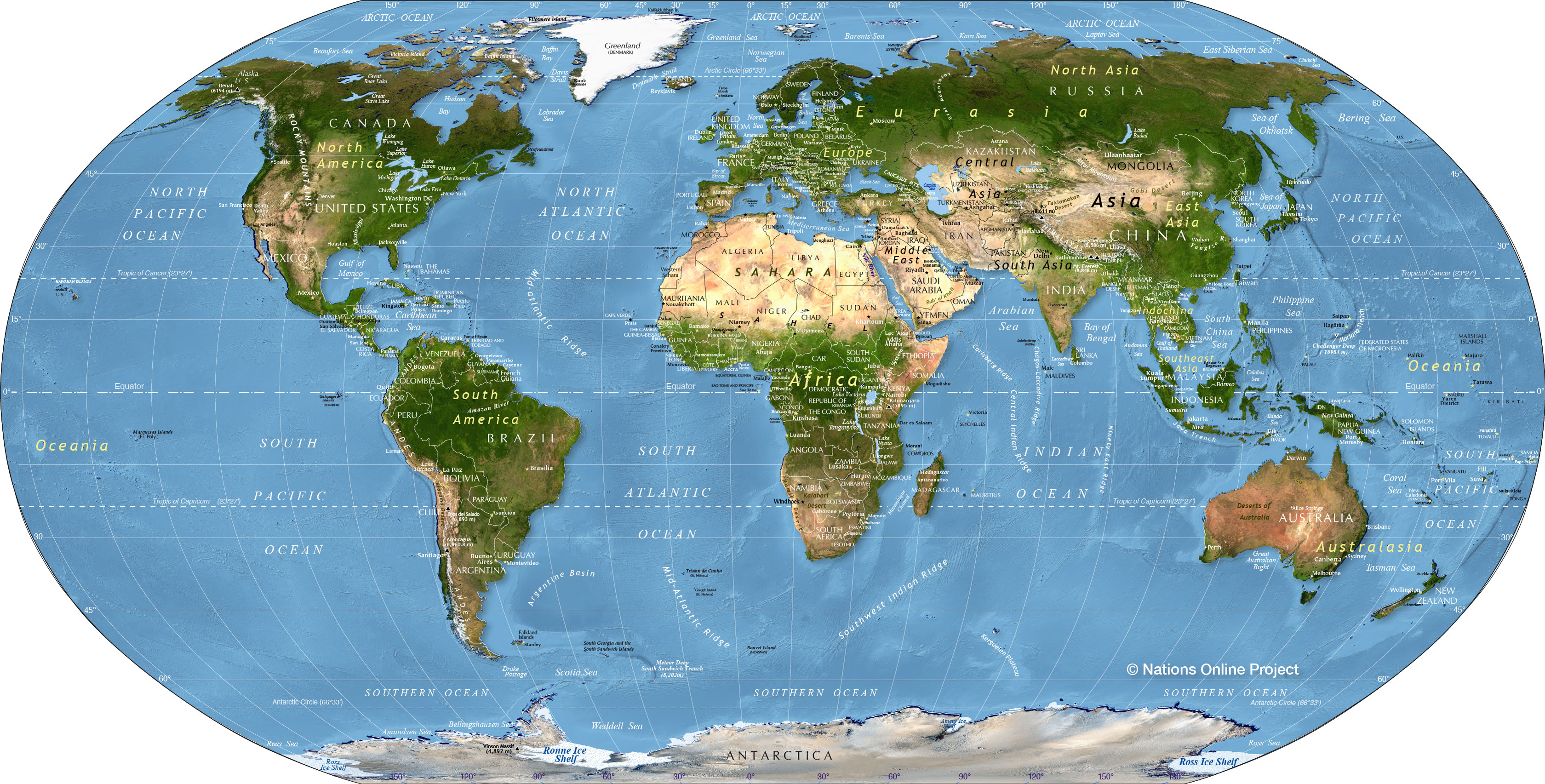




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A World Unveiled: Exploring the Diverse Landscape of Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!