Charting the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Product Positioning Maps
Related Articles: Charting the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Product Positioning Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Product Positioning Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Product Positioning Maps
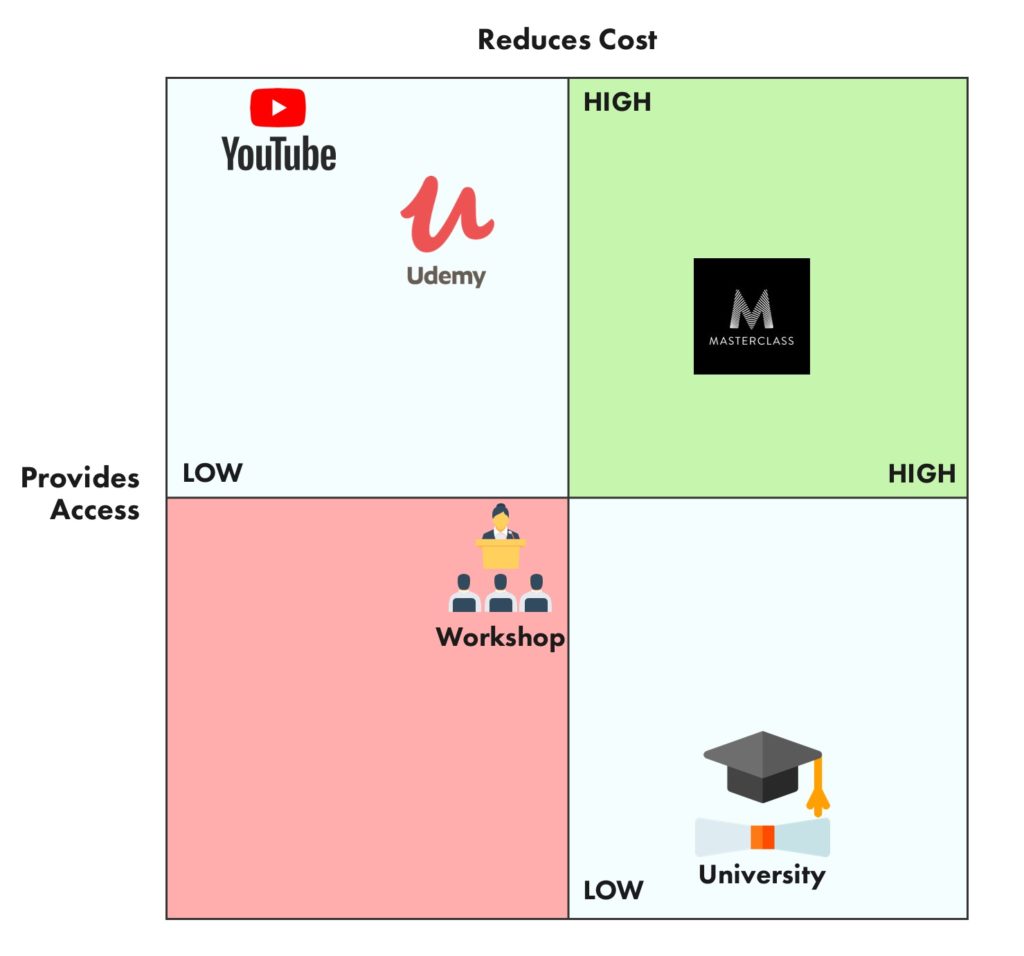
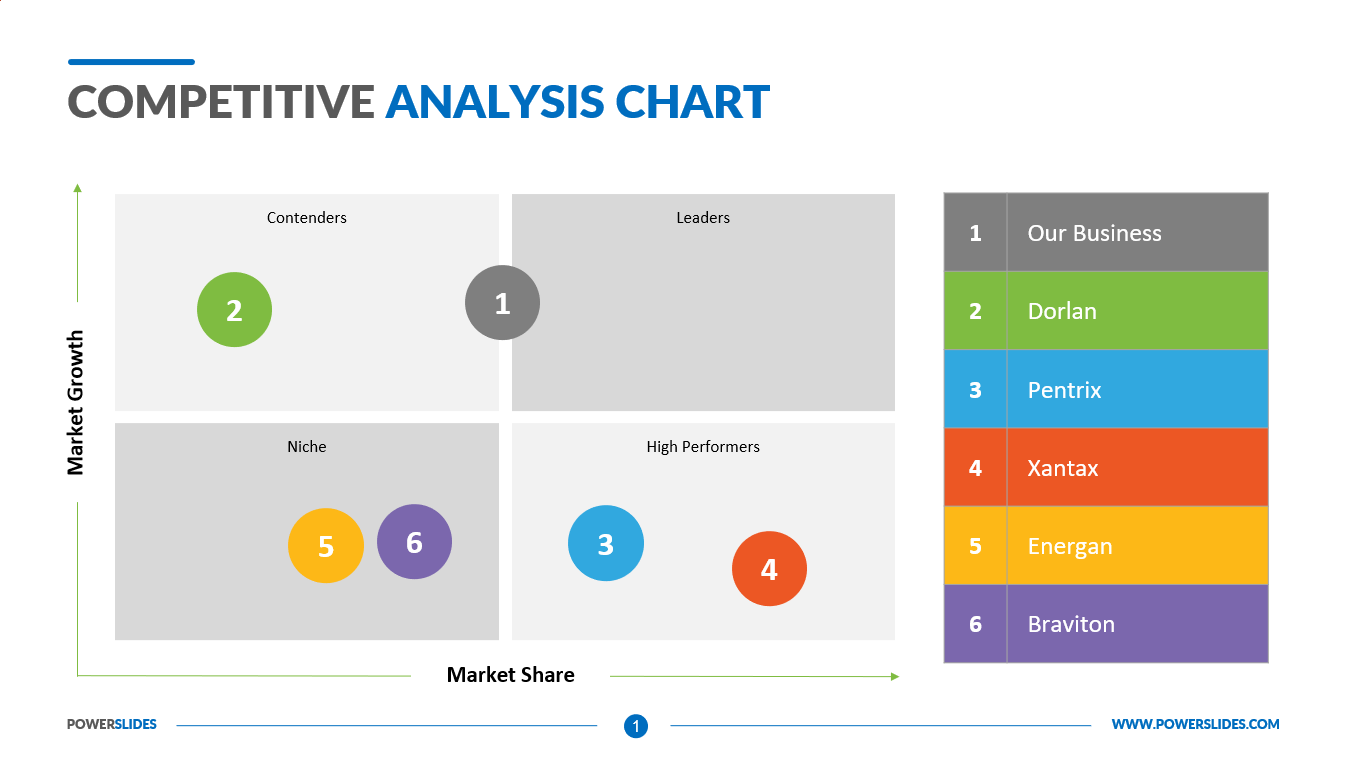
In the dynamic world of business, understanding your place within the market is paramount. A product positioning map, also known as a perceptual map, serves as a visual representation of how consumers perceive different products in relation to each other. By meticulously mapping out the competitive landscape, businesses gain valuable insights into their target audience, identify potential market gaps, and strategize effectively to optimize their product offerings.
Deconstructing the Map:
A product positioning map typically employs two key axes, each representing a distinct attribute or dimension crucial to consumer perception. These axes could encompass:
- Price: Reflecting the cost of the product, ranging from budget-friendly to premium.
- Quality: Encompassing factors like durability, craftsmanship, and overall performance.
- Features: Highlighting specific functionalities or attributes that differentiate products.
- Benefits: Emphasizing the value proposition, such as convenience, efficiency, or exclusivity.
- Target Audience: Segmenting the market based on demographics, psychographics, or lifestyle choices.
The choice of axes depends entirely on the specific industry and the competitive landscape. For example, a map for smartphones might use price and features as axes, while a map for luxury cars could prioritize brand image and performance.
Visualizing Consumer Perception:
Once the axes are defined, each competing product is plotted on the map based on its perceived position in relation to those attributes. This placement is determined through market research, surveys, focus groups, and analysis of consumer reviews and online discussions. The resulting visual representation provides a clear picture of how consumers perceive the products in terms of their relative strengths and weaknesses.
Unveiling Key Insights:
A well-constructed product positioning map offers a wealth of information, enabling businesses to:
- Identify Market Gaps: By pinpointing areas on the map where few or no products exist, businesses can identify potential opportunities for new product development or market expansion.
- Understand Competitive Positioning: The map reveals how a product stacks up against competitors, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses in comparison.
- Target the Right Audience: By analyzing the position of competing products and the demographics of their target audiences, businesses can refine their own target market and tailor their marketing efforts accordingly.
- Develop Effective Positioning Strategies: The map provides a foundation for crafting a compelling value proposition, differentiating the product from competitors, and communicating its unique selling points to the target audience.
- Monitor Market Dynamics: As the market evolves, the map can be updated to reflect changes in consumer perception, competitor strategies, and emerging trends.
Beyond the Basics:
While traditional product positioning maps use two axes, more complex versions can incorporate additional dimensions, such as:
- Brand Image: Reflecting the perceived personality, values, and reputation of a brand.
- Distribution Channels: Highlighting the availability of products through different retail outlets or online platforms.
- Customer Service: Evaluating the level of support and responsiveness offered by a company.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
1. What are the limitations of product positioning maps?
While valuable tools, product positioning maps are not without limitations. They are based on subjective consumer perceptions, which can be influenced by factors like individual preferences, brand loyalty, and marketing campaigns. Additionally, they may not capture the full complexity of product offerings or account for emerging trends.
2. How can I create an effective product positioning map?
Start by defining your target market and identifying key attributes relevant to consumer decision-making. Conduct thorough market research to gather data on consumer perceptions and competitor positioning. Utilize appropriate visualization tools to create a clear and informative map.
3. How frequently should I update my product positioning map?
The frequency of updates depends on the dynamism of the market. For industries experiencing rapid change, regular updates (quarterly or even monthly) are recommended. For more stable markets, annual updates may suffice.
4. How can I use a product positioning map to inform marketing strategies?
The map provides insights into the target audience, competitor positioning, and key product attributes. This information can be leveraged to develop compelling marketing messages, select appropriate channels, and tailor content to resonate with the desired audience.
5. What are some examples of successful product positioning maps?
Numerous companies have successfully employed product positioning maps to achieve strategic goals. For instance, Apple’s positioning of its iPhone as a premium device with a user-friendly interface and sleek design has been highly effective. Similarly, Southwest Airlines’ positioning as a low-cost carrier with a focus on customer service has been instrumental in its success.
Tips for Effective Product Positioning Mapping:
- Focus on Key Attributes: Select axes that are relevant to your target audience and accurately reflect the competitive landscape.
- Utilize Reliable Data: Conduct thorough market research to ensure accurate and reliable information for plotting products on the map.
- Visualize Clearly: Choose a clear and intuitive design that effectively communicates the positioning of products and identifies key insights.
- Regularly Update: Monitor market trends and competitor strategies to ensure the map remains relevant and informative.
- Link to Marketing Strategies: Utilize the insights gained from the map to inform marketing campaigns, messaging, and target audience selection.
Conclusion:
Product positioning maps are invaluable tools for businesses seeking to navigate the complexities of the marketplace. By visualizing consumer perceptions, identifying market gaps, and understanding competitive positioning, businesses can develop effective strategies to differentiate their products, target the right audience, and ultimately achieve success. As the business landscape continues to evolve, the ability to effectively map and understand product positioning will remain a critical factor in achieving sustainable growth and market leadership.
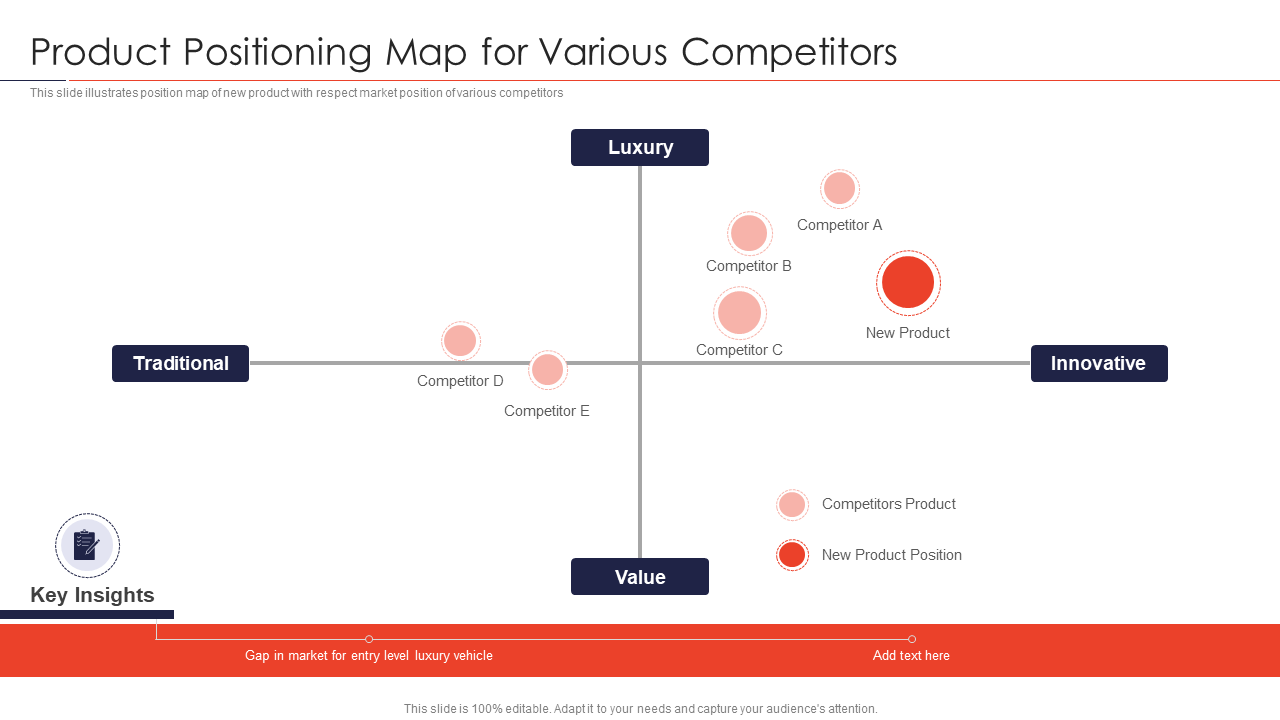


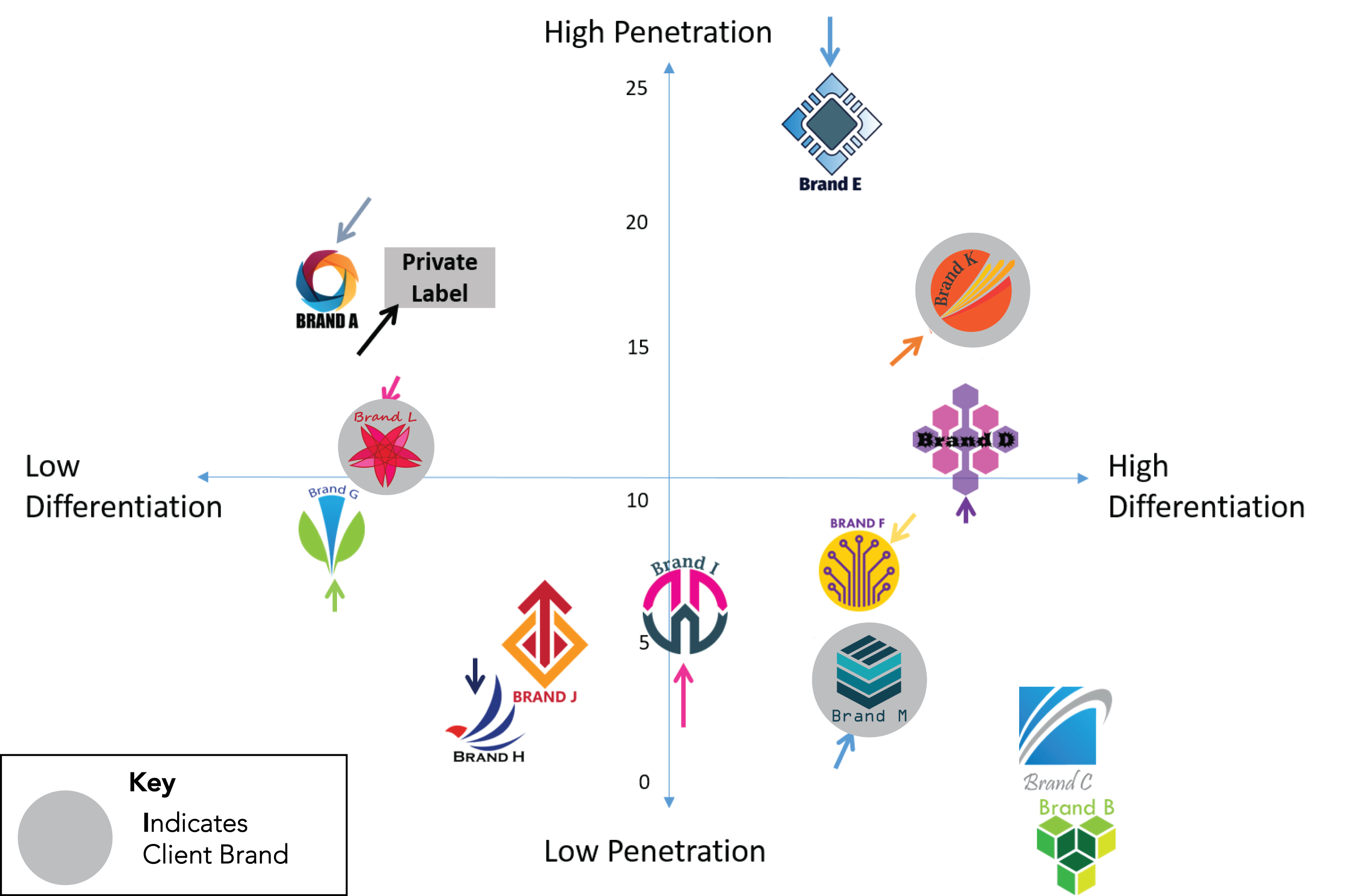

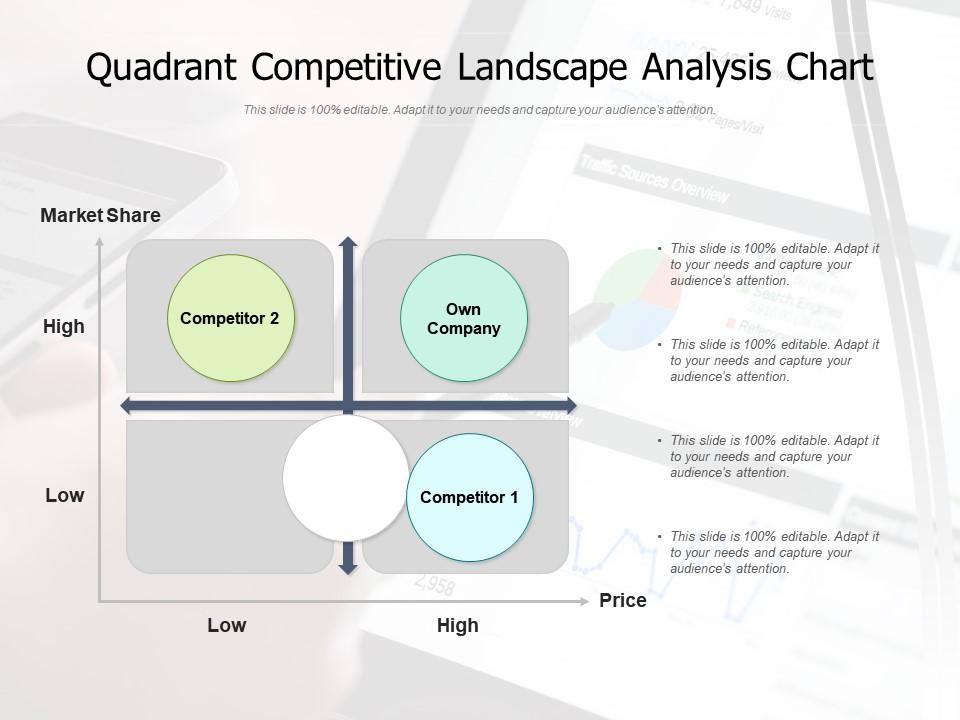
.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Competitive Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Product Positioning Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!