Deciphering Russia’s Administrative Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Provinces
Related Articles: Deciphering Russia’s Administrative Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Provinces
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Deciphering Russia’s Administrative Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Provinces. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering Russia’s Administrative Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Provinces

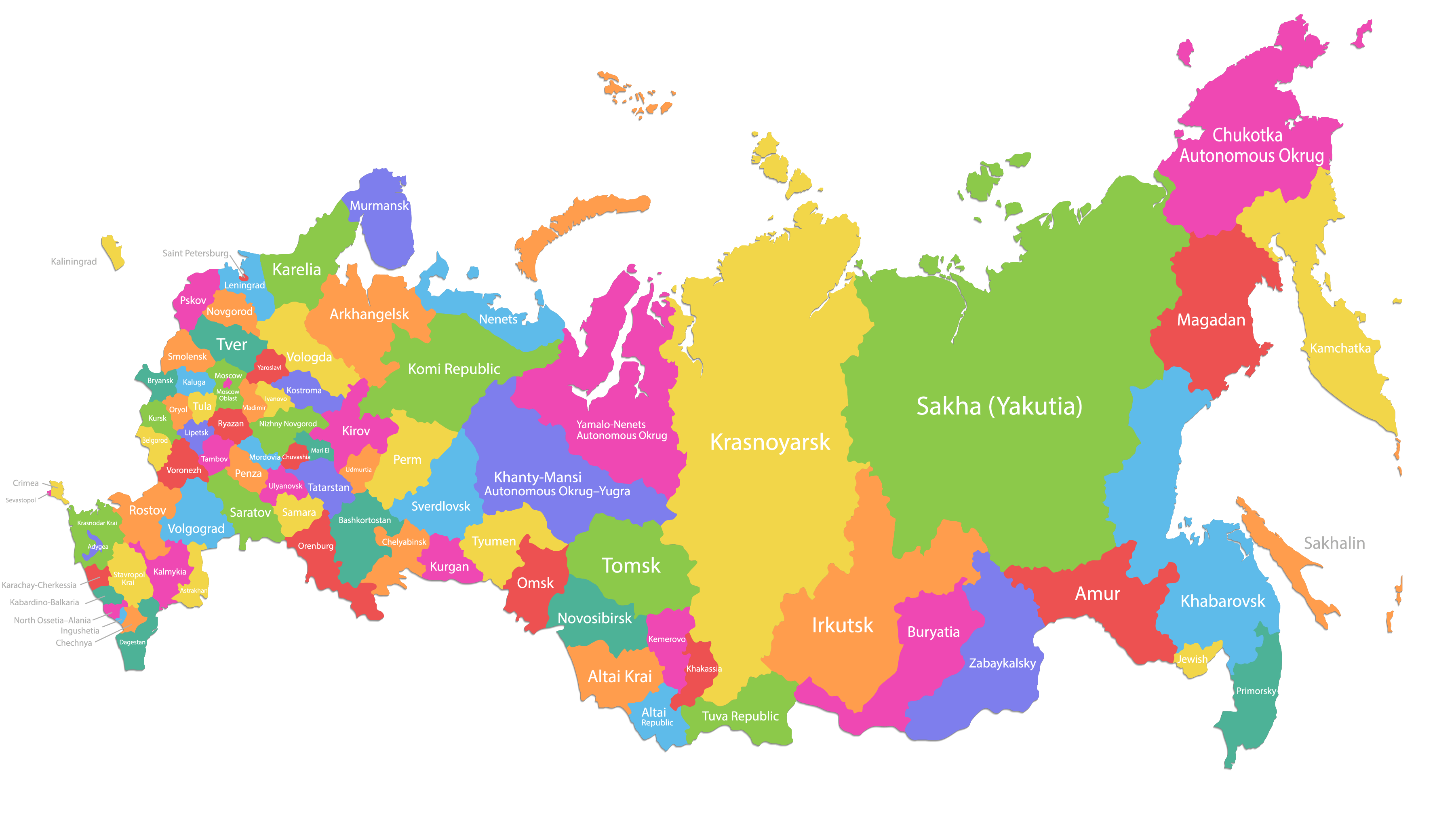
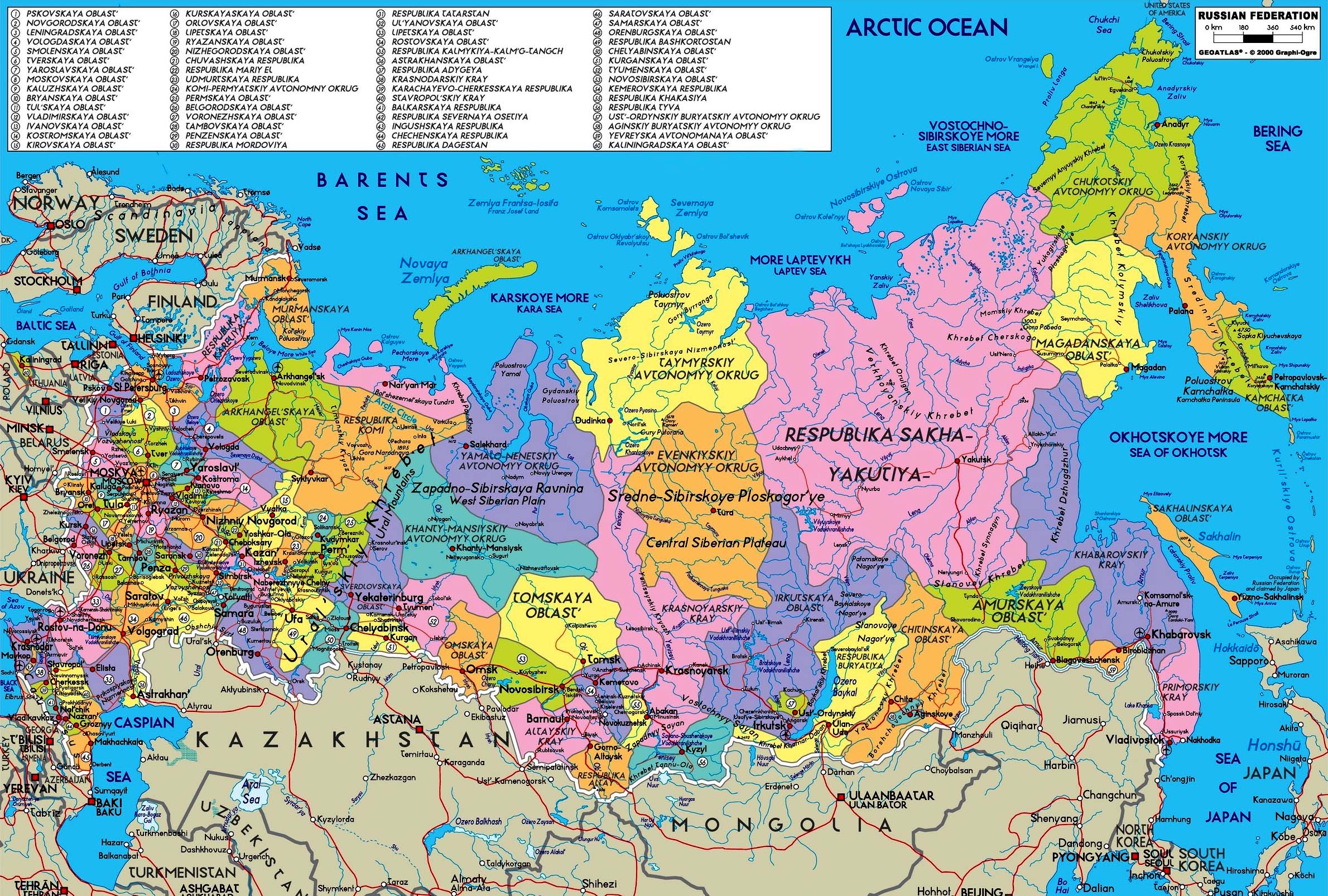
Russia, the largest country in the world by land area, is a vast and diverse nation spanning eleven time zones. Its administrative structure, a complex tapestry of regions, republics, and autonomous areas, reflects this vastness and diversity. Understanding the intricate map of Russia’s provinces is crucial for comprehending the country’s political, economic, and cultural landscape.
The Structure of Russian Provinces
Russia’s administrative divisions are hierarchical, with the federal government at the top and a series of sub-national entities below. The primary unit of administration is the subject of the Russian Federation, commonly referred to as a province. There are 85 subjects in total, each with its own government and legislature. These provinces are further categorized into:
- Republics: 22 republics, representing regions with significant ethnic and cultural autonomy. These republics often have their own constitutions and languages.
- Oblasts (Regions): 46 oblasts, representing geographically and culturally diverse areas.
- Krais (Territories): 9 krais, typically characterized by significant natural resources and industrial centers.
- Autonomous Okrugs: 4 autonomous okrugs, representing indigenous populations with special rights and autonomy.
- Federal Cities: 2 federal cities, Moscow and St. Petersburg, with a special status due to their political and economic importance.
Historical Context: From Tsardom to Federation
The current administrative structure of Russia has evolved over centuries. The Tsardom of Russia, stretching back to the 16th century, was initially divided into guberniyas (governorates), which were further subdivided into uyezds (districts). This system was replaced by the Soviet Union with a structure based on republics, oblasts, and krais. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia adopted a new constitution in 1993, establishing the current federal structure with its diverse provinces.
The Importance of Understanding Russia’s Provinces
Understanding Russia’s provinces is crucial for several reasons:
- Political Landscape: The provinces play a significant role in Russian politics. They have their own legislatures and governments, which are responsible for local affairs. The provinces also send representatives to the Federal Assembly, the bicameral legislature of the Russian Federation.
- Economic Development: Each province has its own unique economic profile, influenced by factors such as natural resources, industry, and agriculture. Understanding these differences is essential for businesses operating in Russia.
- Cultural Diversity: Russia is a nation of diverse cultures and ethnicities, and this diversity is reflected in its provinces. Each province has its own unique traditions, customs, and languages. Understanding this cultural richness is crucial for promoting understanding and tolerance.
- Foreign Policy: Russia’s provinces play a role in its foreign policy, particularly in regions bordering other countries. Understanding the dynamics within these provinces is essential for navigating the complexities of Russia’s international relations.
Exploring the Provinces: A Glimpse into Russia’s Diversity
Each province of Russia holds a unique story, offering a glimpse into the country’s vast cultural and geographical diversity.
- The European Heart: Moscow and St. Petersburg
Moscow, the capital, is a sprawling metropolis, a center of finance, culture, and politics. St. Petersburg, a former imperial capital, boasts stunning architecture and a vibrant cultural scene.
- The Ural Mountains: A Region of Transition
The Ural Mountains, a natural boundary between Europe and Asia, are home to diverse provinces like Chelyabinsk Oblast, known for its steel industry, and Sverdlovsk Oblast, with its rich history of mining and heavy industry.
- The Siberian Frontier: Land of Vastness and Resources
Siberia, a vast region stretching across northern Asia, is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, and timber. Provinces like Krasnoyarsk Krai and Irkutsk Oblast are home to sprawling forests, towering mountains, and vast lakes.
- The Far East: A Gateway to Asia
The Russian Far East, bordering China, North Korea, and Japan, is a region of strategic importance. Provinces like Primorsky Krai and Khabarovsk Krai are vital for trade and economic development with Asia.
- The Caucasus: A Region of Cultural Crossroads
The Caucasus region, with its diverse ethnicities and languages, is home to republics like Chechnya, Dagestan, and Ingushetia. This region has experienced significant political and social challenges in recent decades.
FAQs: Demystifying the Russian Provinces
Q: What is the difference between an oblast and a krai?
A: Both oblasts and krais are administrative divisions of Russia. Oblasts are typically smaller and less populous than krais. Krais often have more autonomy and control over their resources.
Q: What is the significance of the autonomous okrugs?
A: Autonomous okrugs are special administrative divisions created to protect the rights of indigenous populations. They have their own legislative bodies and governments.
Q: How are the provinces governed?
A: Each province has its own governor, elected by the population, and a legislative body, which is responsible for passing laws. The provinces are also represented in the Federal Assembly, the bicameral legislature of the Russian Federation.
Q: What are some of the challenges facing the Russian provinces?
A: The provinces face a range of challenges, including economic disparity, social inequality, and environmental degradation. These challenges are often exacerbated by the vast size of Russia and the geographical isolation of some regions.
Tips for Understanding Russia’s Provinces
- Consult Maps: Use detailed maps to visualize the geographic locations and borders of the provinces.
- Explore Online Resources: Websites of the Russian government and independent organizations provide valuable information about each province.
- Read Books and Articles: Explore books and articles about Russia’s history, culture, and politics to gain a deeper understanding of the provinces.
- Engage with Russian Media: Follow Russian news outlets and media to gain insights into the current affairs and perspectives of the provinces.
- Travel to Russia: If possible, visit different provinces to experience their unique culture, landscapes, and people firsthand.
Conclusion: A Nation of Diverse Provinces
Russia’s map of provinces is a testament to the country’s vastness and diversity. Understanding this administrative landscape is crucial for comprehending the country’s political, economic, and cultural dynamics. From the bustling metropolises of Moscow and St. Petersburg to the remote reaches of Siberia and the Caucasus, each province holds a unique story, contributing to the rich tapestry of Russia’s national identity. By understanding the nuances of Russia’s provinces, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of this vast and fascinating nation.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering Russia’s Administrative Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Provinces. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!