Exploring the Heart of Mexico: A Geographic Overview of Central Mexico
Related Articles: Exploring the Heart of Mexico: A Geographic Overview of Central Mexico
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Heart of Mexico: A Geographic Overview of Central Mexico. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Heart of Mexico: A Geographic Overview of Central Mexico

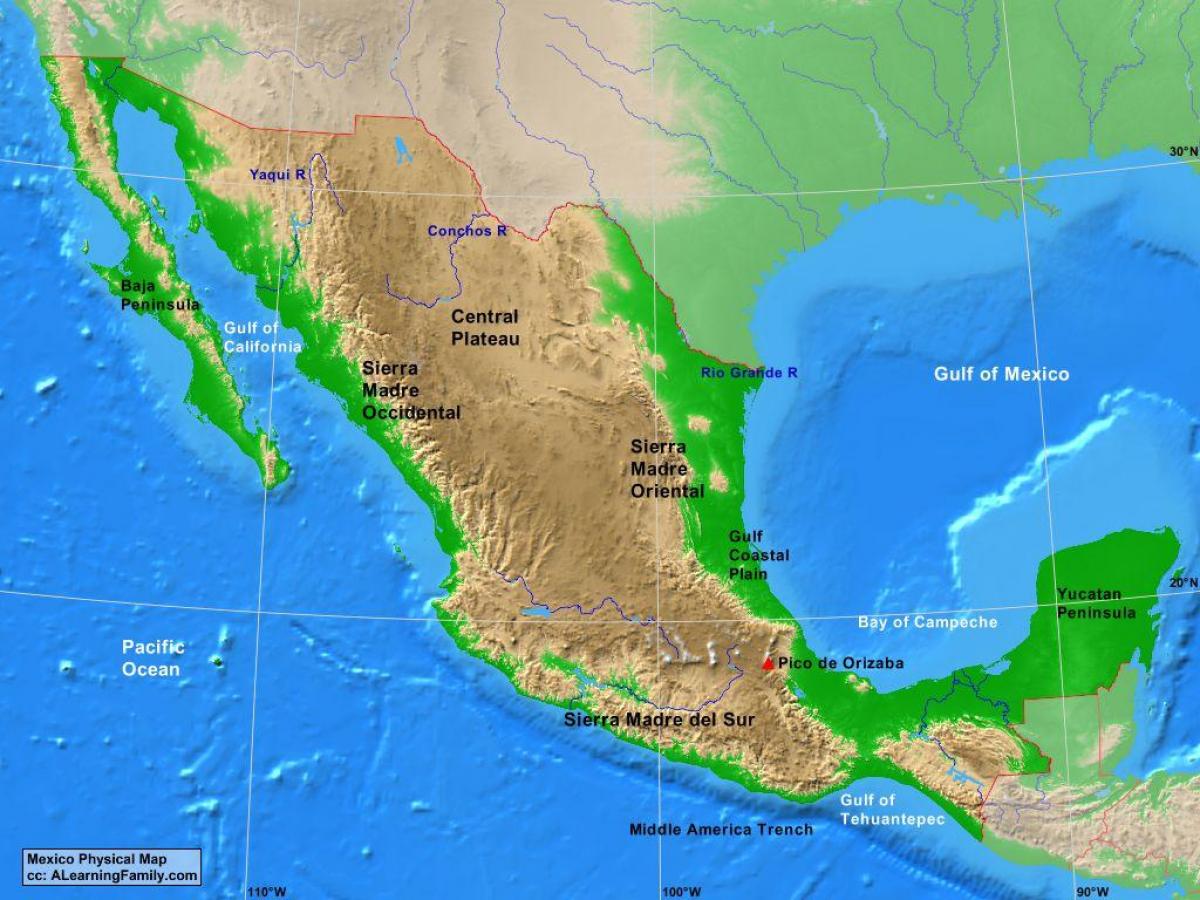
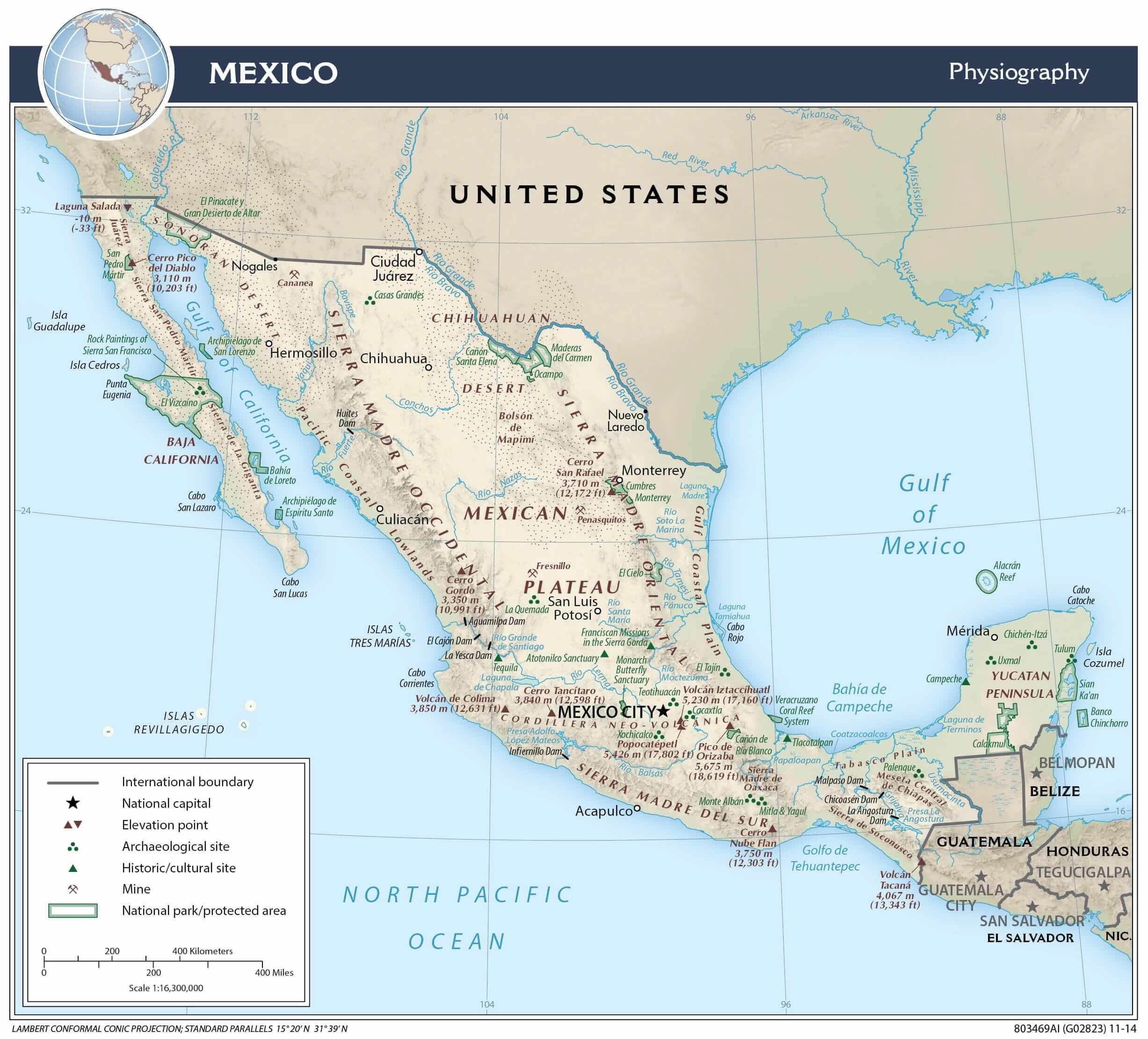
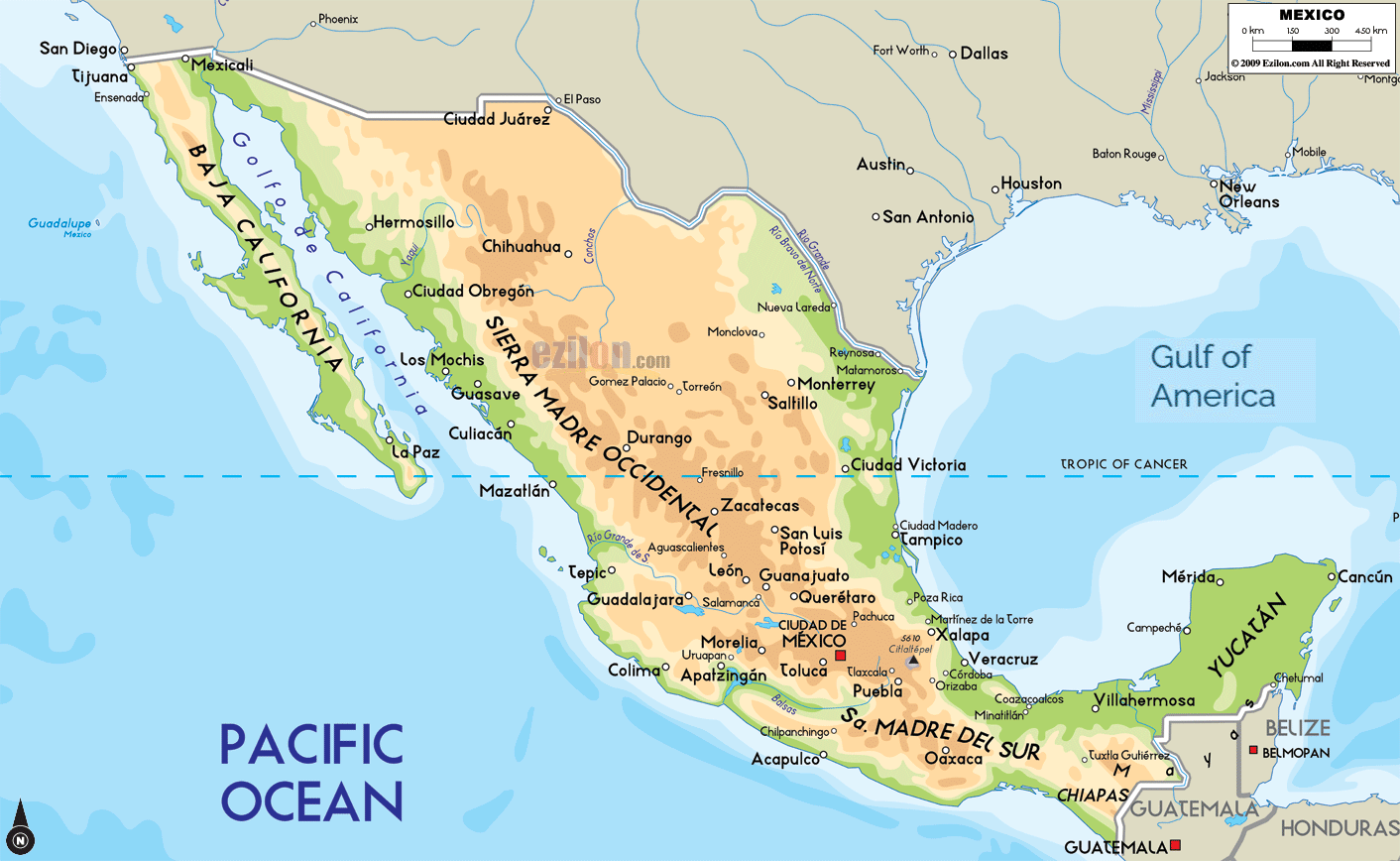
Central Mexico, a region encompassing the heartland of the country, holds a pivotal position in the nation’s history, culture, and economy. From the towering volcanoes of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt to the fertile valleys of the Bajío region, Central Mexico exhibits a diverse landscape that has shaped the lives of its inhabitants for centuries.
Defining the Region:
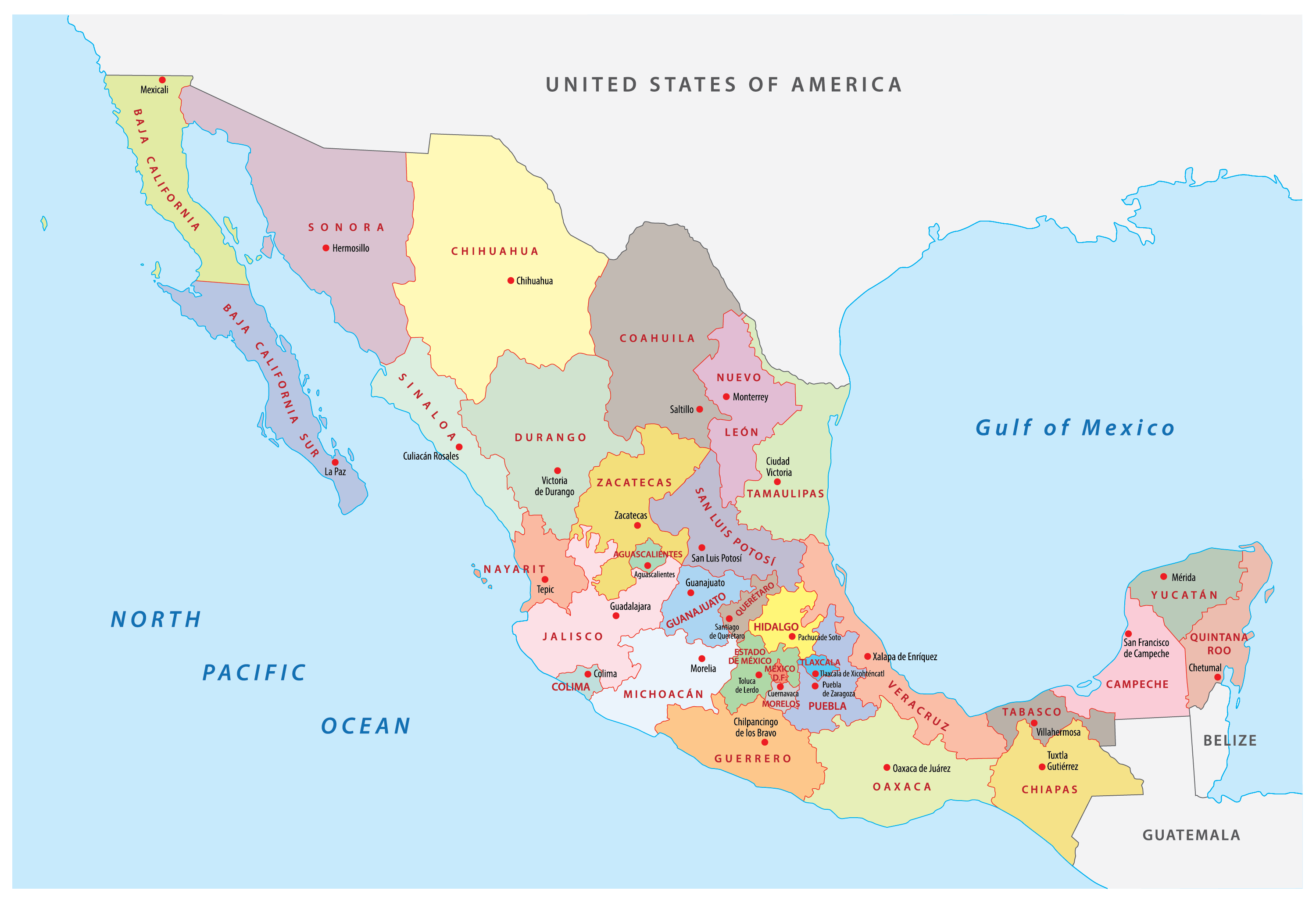
Central Mexico, often referred to as "Mesoamerica" in a broader historical context, is a loosely defined region encompassing several states. Generally, it includes:
- The Central Plateau: This area, characterized by high elevation and a semi-arid climate, is home to Mexico City, the nation’s capital, and surrounding states like Guanajuato, Querétaro, Hidalgo, and Morelos.
- The Bajío Region: This fertile valley region, renowned for its agricultural production, includes states like Michoacán, Jalisco, Aguascalientes, and Guanajuato.
- The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt: This volcanic mountain range, stretching across central Mexico, includes iconic peaks like Popocatépetl and Iztaccíhuatl, and encompasses states like Puebla, Tlaxcala, and Mexico City.
- The Gulf Coast Region: While geographically part of the Gulf Coast, states like Veracruz and Tabasco are often included in Central Mexico due to their close cultural and economic ties to the region.
A Tapestry of Landscapes and Cultures:
Central Mexico’s diverse landscape provides a rich tapestry of ecological zones, each with its unique characteristics:
- The Central Plateau: This region’s high elevation, ranging from 2,000 to 3,000 meters, results in a cooler climate with distinct dry and wet seasons. Its volcanic soils are fertile, supporting agriculture and supporting a diverse range of flora and fauna.
- The Bajío Region: Located within the Central Plateau, the Bajío is a fertile valley region characterized by its flat terrain and abundant water resources. This region is a major agricultural producer, known for its corn, wheat, and cattle production.
- The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt: This region, marked by towering volcanoes and rugged terrain, is home to a rich variety of ecosystems, from pine forests and alpine meadows to volcanic lakes and lava fields. This region is also a significant source of geothermal energy.
- The Gulf Coast Region: This region, with its humid climate and coastal plains, features a diverse array of flora and fauna, including mangrove forests, rainforests, and coastal lagoons.
This diverse landscape has given rise to a rich tapestry of cultures, each shaped by its environment and history. From the indigenous communities of the Central Plateau to the vibrant urban centers of the Bajío and the Gulf Coast, Central Mexico is a vibrant melting pot of traditions and languages.
Historical Significance:
Central Mexico holds immense historical significance, serving as the cradle of Mesoamerican civilizations. The region witnessed the rise and fall of empires like the Aztecs, Toltecs, and Teotihuacan, leaving behind a legacy of archaeological treasures and cultural traditions.
- Teotihuacan: This ancient city, located near present-day Mexico City, was one of the largest and most influential cities in Mesoamerica. Its impressive pyramids and temples are a testament to the advanced civilization that flourished there.
- The Aztec Empire: The Aztecs, a powerful empire that dominated Central Mexico for centuries, established their capital at Tenochtitlan, the site of present-day Mexico City. Their sophisticated culture, intricate art, and complex social structure left an indelible mark on the region.
- The Spanish Conquest: The arrival of the Spanish conquistadors in the 16th century marked a turning point in Central Mexico’s history. The Spanish conquest led to the fall of the Aztec Empire and the establishment of New Spain, a vast colonial empire that spanned much of North America.
Modern-Day Importance:
Central Mexico remains a vital region for Mexico’s economy and society. Its strategic location, abundant natural resources, and diverse population contribute significantly to the nation’s growth and development.
- Economic Hub: Mexico City, located in Central Mexico, is the country’s economic powerhouse, serving as a major center for finance, commerce, and industry. Other major cities in the region, such as Guadalajara and Monterrey, also play significant roles in the national economy.
- Agricultural Production: Central Mexico is a major agricultural producer, supplying food to the nation and contributing to its export market. The region’s fertile valleys and abundant water resources are ideal for growing a variety of crops, including corn, wheat, beans, and fruits.
- Tourism: Central Mexico’s rich history, diverse culture, and stunning landscapes attract millions of tourists each year. From the archaeological sites of Teotihuacan and Monte Albán to the colonial cities of Guanajuato and San Miguel de Allende, the region offers a wealth of attractions for visitors.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its significant contributions to Mexico’s development, Central Mexico faces several challenges:
- Overpopulation and Urbanization: The concentration of population in major cities like Mexico City has led to challenges such as overcrowding, pollution, and strain on infrastructure.
- Economic Inequality: Despite its economic importance, Central Mexico suffers from significant economic inequality. Poverty and unemployment persist in some areas, particularly in rural communities.
- Environmental Challenges: The region faces environmental challenges such as air pollution, water scarcity, and deforestation.
Despite these challenges, Central Mexico also presents significant opportunities for growth and development. The region’s diverse economy, rich cultural heritage, and strategic location offer potential for innovation, sustainability, and social progress.
FAQs about Central Mexico:
1. What are the major cities in Central Mexico?
Central Mexico is home to several major cities, including:
- Mexico City: The nation’s capital, a bustling metropolis with a rich history and diverse culture.
- Guadalajara: The second-largest city in Mexico, known for its colonial architecture, mariachi music, and vibrant nightlife.
- Monterrey: A major industrial center in northern Mexico, renowned for its modern architecture and dynamic economy.
- Puebla: A historic city with a strong culinary tradition, known for its Talavera pottery and its iconic mole sauce.
- Querétaro: A colonial city with a well-preserved historic center, known for its beautiful architecture and its role in the Mexican War of Independence.
2. What are the main industries in Central Mexico?
Central Mexico’s economy is diverse, with major industries including:
- Manufacturing: The region is a major manufacturing hub, producing a wide range of goods, from automobiles to electronics.
- Tourism: Central Mexico’s rich history, culture, and landscapes attract millions of tourists each year, contributing significantly to the region’s economy.
- Agriculture: The region’s fertile valleys and abundant water resources support a thriving agricultural sector, producing a variety of crops, including corn, wheat, and beans.
- Services: The region is also a major center for services, including finance, banking, and technology.
3. What are some of the major cultural attractions in Central Mexico?
Central Mexico offers a wealth of cultural attractions, including:
- Teotihuacan: This ancient city, located near present-day Mexico City, is one of the most important archaeological sites in Mesoamerica.
- Xochimilco: A network of canals and islands in Mexico City, offering a unique glimpse into the city’s history and culture.
- The Frida Kahlo Museum: A museum dedicated to the life and work of the iconic Mexican artist Frida Kahlo.
- The National Museum of Anthropology: A world-renowned museum showcasing the rich history and culture of Mexico’s indigenous peoples.
- The Zocalo: The main square in Mexico City, a bustling hub of activity and a historical landmark.
4. What are some of the environmental challenges facing Central Mexico?
Central Mexico faces several environmental challenges, including:
- Air pollution: The concentration of population and industry in major cities has led to significant air pollution problems.
- Water scarcity: The region is facing increasing water scarcity due to population growth, climate change, and unsustainable water management practices.
- Deforestation: Deforestation is a significant problem in Central Mexico, leading to soil erosion, habitat loss, and climate change.
Tips for Visiting Central Mexico:
- Learn some basic Spanish: While English is spoken in tourist areas, learning a few basic Spanish phrases will enhance your experience.
- Be prepared for altitude: The high elevation of Central Mexico can cause altitude sickness, so it’s important to acclimatize gradually and stay hydrated.
- Try the local cuisine: Central Mexico is known for its delicious food, so be sure to try some of the local specialties, such as tacos, mole, and pozole.
- Explore the historical sites: Central Mexico is home to numerous historical sites, from ancient pyramids to colonial cities, so take the time to explore these fascinating destinations.
- Be respectful of local customs: When visiting Central Mexico, it’s important to be respectful of local customs and traditions.
Conclusion:
Central Mexico, with its diverse landscape, rich history, and vibrant culture, plays a crucial role in Mexico’s development. The region’s strategic location, abundant natural resources, and diverse population contribute significantly to the nation’s economy and society. While facing challenges such as overpopulation, inequality, and environmental degradation, Central Mexico also presents opportunities for growth and progress. By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on its strengths, Central Mexico can continue to play a vital role in shaping Mexico’s future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Heart of Mexico: A Geographic Overview of Central Mexico. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!