Mapping the Landscape of Law Enforcement: Understanding Police Maps and Their Significance
Related Articles: Mapping the Landscape of Law Enforcement: Understanding Police Maps and Their Significance
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Landscape of Law Enforcement: Understanding Police Maps and Their Significance. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Mapping the Landscape of Law Enforcement: Understanding Police Maps and Their Significance
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Mapping the Landscape of Law Enforcement: Understanding Police Maps and Their Significance
- 3.1 Demystifying Police Maps: A Deeper Dive into Their Components and Functionality
- 3.2 Beyond Visualization: The Power of Analysis and Insight
- 3.3 Beyond Traditional Mapping: Embracing Technological Advancements
- 3.4 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Police Maps
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Use of Police Maps
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Police Maps
- 4 Closure
Mapping the Landscape of Law Enforcement: Understanding Police Maps and Their Significance
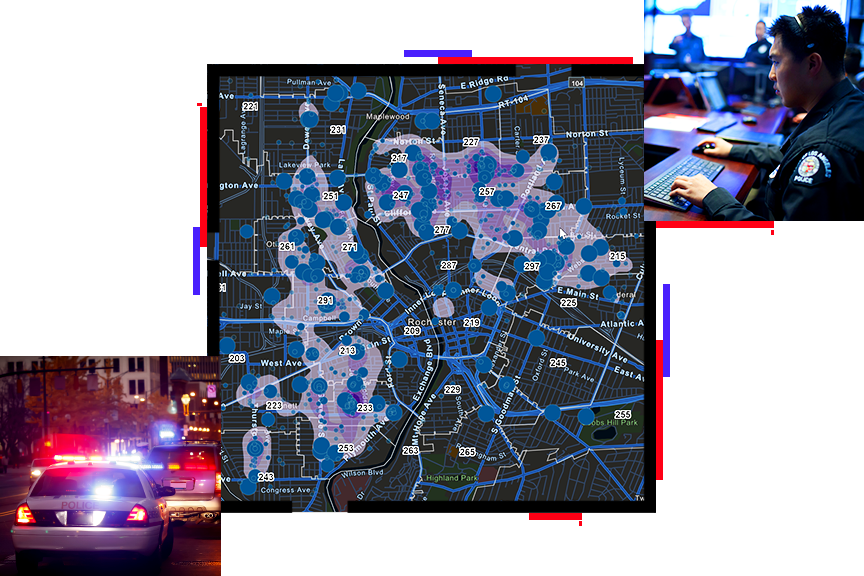
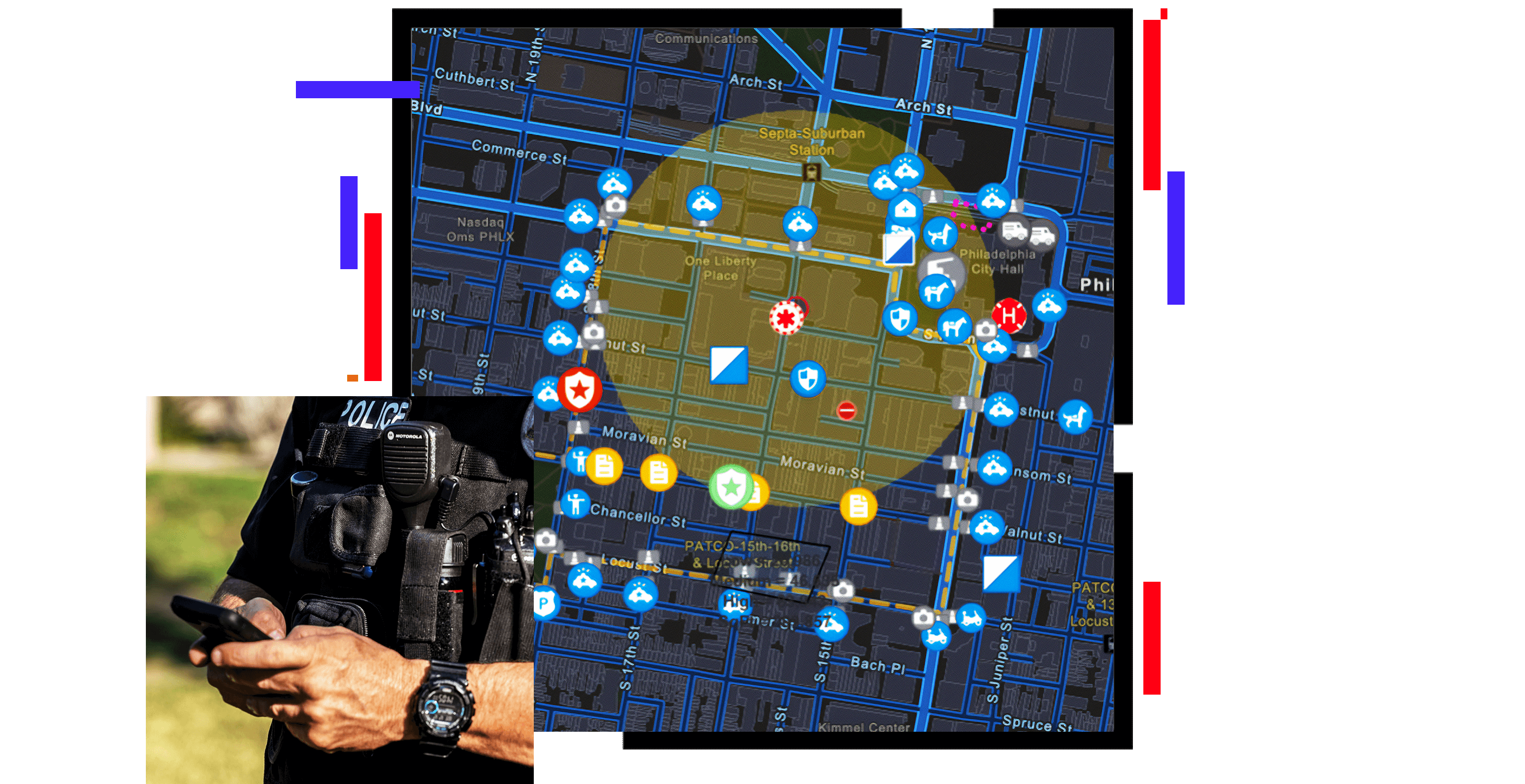
Police maps, often referred to as crime maps, are powerful tools utilized by law enforcement agencies to visualize and analyze crime data. These maps serve as visual representations of criminal activity, offering insights into patterns, trends, and hotspots within a specific jurisdiction. By harnessing the power of spatial analysis, police maps provide a comprehensive understanding of the crime landscape, aiding in resource allocation, crime prevention strategies, and the development of targeted interventions.
Demystifying Police Maps: A Deeper Dive into Their Components and Functionality
At their core, police maps are visual representations of geographic data overlaid with information about criminal incidents. This information typically includes:
- Location: The precise coordinates of the crime, often pinpointed on a street-level map.
- Date and Time: The specific date and time when the crime occurred, providing temporal context for analysis.
- Crime Type: The classification of the crime, such as theft, assault, or drug offenses, allowing for categorization and identification of crime patterns.
- Other Relevant Information: Additional details can be incorporated, such as victim demographics, suspect descriptions, or associated property information.
The data used to populate these maps originates from various sources, including:
- Police Reports: Detailed records of reported crimes provide the foundation for mapping.
- Incident Management Systems: Modern law enforcement agencies utilize sophisticated software systems that automatically collect and organize crime data.
- Citizen Reporting: Community engagement initiatives, such as mobile apps or online platforms, allow citizens to report suspicious activity or incidents directly.
By combining these data sources, police maps offer a dynamic and comprehensive overview of crime within a defined area.
Beyond Visualization: The Power of Analysis and Insight
The true value of police maps lies in their ability to facilitate analysis and generate actionable insights. By analyzing the spatial distribution of crime, law enforcement can identify:
- Crime Hotspots: Areas with an unusually high concentration of criminal activity, indicating potential targets for increased patrols or targeted interventions.
- Crime Clusters: Groups of similar offenses occurring in close proximity, suggesting potential links between crimes or criminal networks.
- Temporal Patterns: Recurring crime trends over time, highlighting periods of increased criminal activity or specific days of the week with higher incident rates.
This information allows law enforcement agencies to:
- Optimize Resource Allocation: Deploying personnel and resources to areas with the highest crime rates, maximizing their effectiveness.
- Develop Targeted Prevention Strategies: Identifying specific areas or crime types that require focused interventions, such as community policing initiatives or specialized task forces.
- Improve Crime Prediction: Utilizing historical crime data to anticipate potential future crime trends, enabling proactive measures to deter crime.
- Evaluate the Effectiveness of Interventions: Tracking crime trends over time to assess the impact of various crime prevention strategies.
Beyond Traditional Mapping: Embracing Technological Advancements
The landscape of police mapping is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and the increasing availability of data. Modern crime mapping tools utilize:
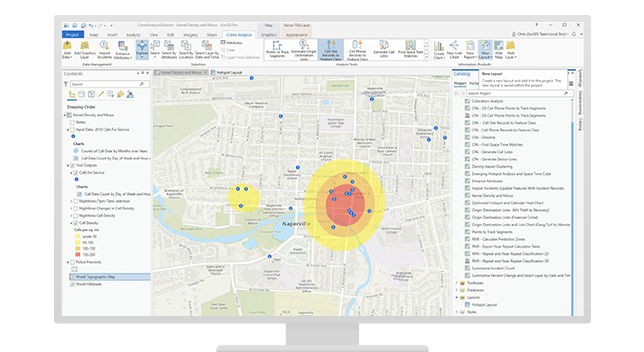
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Powerful software platforms that enable the integration and analysis of geospatial data, providing sophisticated visualization and analytical capabilities.
- Real-Time Data Integration: Connecting crime maps to live data feeds, such as incident reports or emergency calls, offering near real-time updates on criminal activity.
- Predictive Analytics: Utilizing algorithms and machine learning to identify potential crime patterns and predict future crime hotspots, enabling proactive crime prevention.
- Data Visualization Techniques: Employing interactive dashboards and infographics to present crime data in a clear and engaging manner, facilitating communication and collaboration among law enforcement agencies and the community.
These advancements enhance the capabilities of police maps, allowing for more effective analysis, proactive crime prevention, and improved communication within the law enforcement community.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Police Maps
1. What are the benefits of using police maps?
Police maps offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Crime Prevention: By identifying crime hotspots and patterns, law enforcement can allocate resources effectively and develop targeted prevention strategies.
- Enhanced Resource Allocation: Focusing resources on areas with the highest crime rates, maximizing efficiency and effectiveness.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Providing evidence-based insights to guide law enforcement strategies and resource allocation.
- Improved Community Engagement: Sharing crime data with the public can foster transparency and encourage community involvement in crime prevention.
2. What are the limitations of police maps?
While powerful tools, police maps have certain limitations:
- Data Bias: Crime data may reflect reporting biases, with certain crimes being underreported or overrepresented.
- Lack of Context: Maps alone do not capture the full complexity of crime, neglecting social and economic factors that contribute to criminal activity.
- Oversimplification: Maps can potentially lead to oversimplification of crime patterns, neglecting individual circumstances and motivations.
3. How can police maps be used to improve community safety?
Police maps play a crucial role in enhancing community safety by:
- Identifying Areas of Concern: Highlighting high-crime areas, allowing for increased patrols and community engagement initiatives.
- Facilitating Targeted Interventions: Focusing resources on specific crime types or hotspots to address specific community concerns.
- Promoting Transparency and Collaboration: Sharing crime data with the community fosters trust and encourages collaboration in crime prevention efforts.
4. What are the ethical considerations related to police maps?
The use of police maps raises ethical concerns, including:
- Privacy Concerns: The potential for misuse of personal data associated with crime incidents.
- Discrimination: The risk of perpetuating biases or discrimination based on race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status.
- Transparency and Public Access: The balance between sharing crime data for public safety and protecting individual privacy.
5. What is the future of police mapping?
The future of police mapping is likely to be driven by:
- Advanced Analytics: Integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance crime prediction and pattern recognition.
- Real-Time Data Integration: Utilizing live data feeds to provide near real-time insights into criminal activity.
- Interactive Visualization: Developing user-friendly interfaces and dashboards for effective data communication and collaboration.
- Community Engagement: Fostering public participation in crime mapping and analysis to enhance community safety.
Tips for Effective Use of Police Maps
- Data Quality: Ensure the accuracy and reliability of the data used for mapping, addressing potential biases and inconsistencies.
- Contextual Analysis: Consider social, economic, and environmental factors that may contribute to crime patterns.
- Collaboration and Communication: Share crime data and insights with relevant stakeholders, including community members, law enforcement agencies, and researchers.
- Ethical Considerations: Prioritize privacy, fairness, and transparency in the collection, analysis, and dissemination of crime data.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of police maps and adjust strategies based on data analysis and feedback.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Police Maps
Police maps have evolved from simple visual representations of crime data to sophisticated analytical tools that empower law enforcement agencies to understand, predict, and prevent crime. By harnessing the power of spatial analysis and embracing technological advancements, police maps play a critical role in enhancing public safety, allocating resources effectively, and fostering collaboration between law enforcement and the community. As technology continues to advance, police maps will likely play an even greater role in shaping the future of law enforcement, contributing to safer and more secure communities.
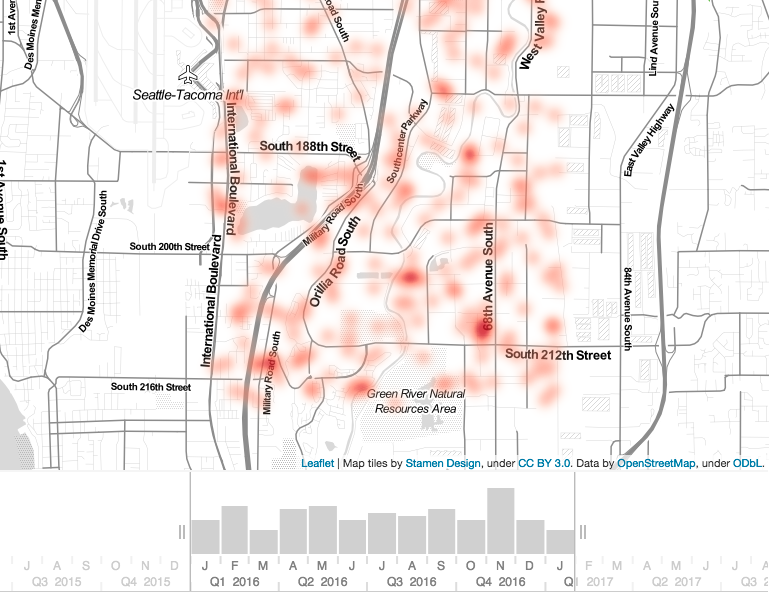

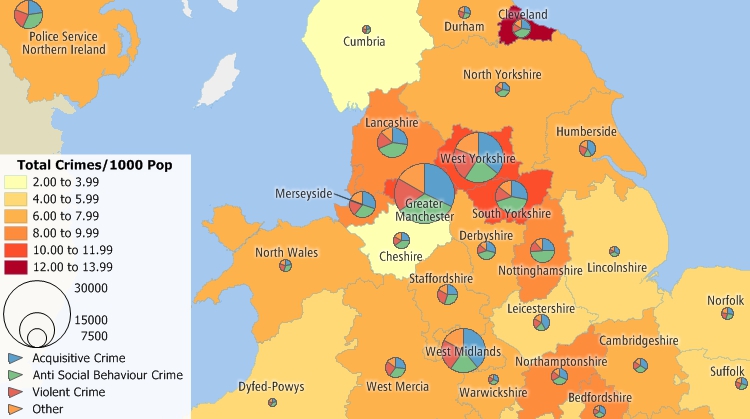

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Landscape of Law Enforcement: Understanding Police Maps and Their Significance. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!