Measuring the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Area Calculation Using Maps
Related Articles: Measuring the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Area Calculation Using Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Measuring the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Area Calculation Using Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Measuring the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Area Calculation Using Maps
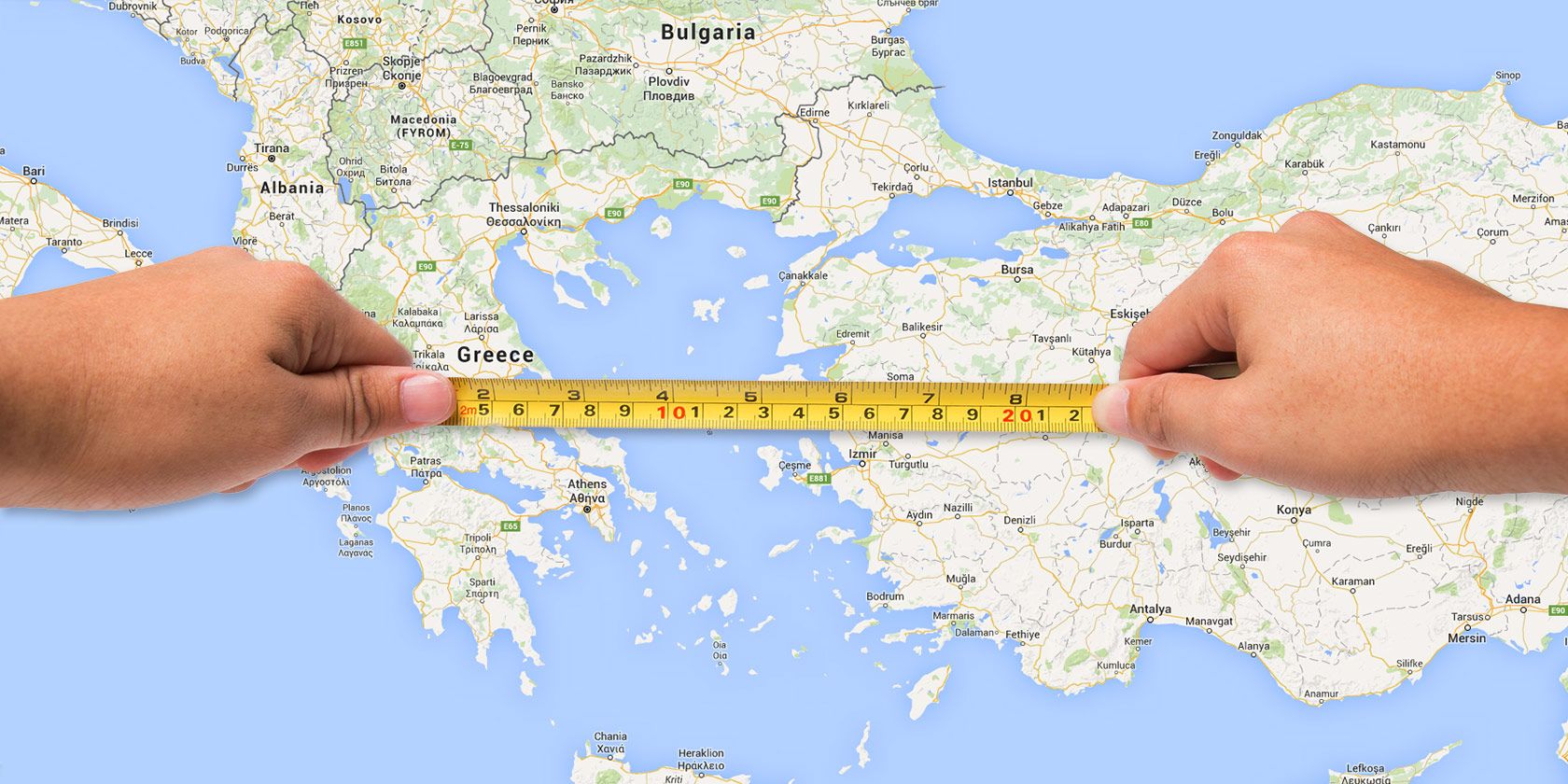

Maps, ubiquitous tools for navigation and spatial understanding, possess a hidden power: the ability to accurately calculate the area of regions, be it a small garden, a vast forest, or even an entire country. This capacity, often overlooked, is crucial for diverse applications, from land management and urban planning to environmental monitoring and resource allocation.
This article delves into the intricate world of area measurement using maps, exploring its underlying principles, methods, and applications. We will navigate through the historical evolution of this technique, discuss the crucial role of scale and projection, and highlight the significance of various measurement methods.
The Genesis of Area Measurement on Maps
The concept of measuring area on maps finds its roots in the ancient world. Early civilizations, driven by the need to manage land and resources, developed rudimentary methods for calculating area. The Egyptians, renowned for their advanced surveying techniques, employed a system based on squares and rectangles to estimate land size. The Greeks, with their emphasis on geometry, further refined these methods, introducing the concept of area calculation using geometric formulas.
However, the true revolution in area measurement arrived with the advent of map projections. These mathematical transformations enabled the representation of the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane, facilitating accurate area calculation. The development of various map projections, each with its unique properties and distortions, opened new avenues for area measurement, catering to specific needs and applications.
Scale: The Key to Accuracy
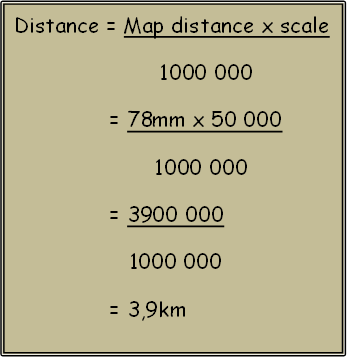
The cornerstone of any area measurement using maps is the concept of scale. Scale represents the ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. This fundamental principle dictates the accuracy of area calculations. A large-scale map, with a smaller ratio, provides a more detailed representation and allows for more precise area determination, particularly for smaller regions. Conversely, a small-scale map, with a larger ratio, offers a broader overview, suitable for measuring larger areas, but with less precision.
Projection: Shaping the World
The choice of map projection significantly influences area measurement. Different projections distort the Earth’s surface in distinct ways, affecting the accuracy of area calculations. For instance, a cylindrical projection, often used for world maps, tends to exaggerate areas near the poles while compressing areas closer to the equator. Conversely, a conic projection, commonly used for regional maps, generally maintains area accuracy within a specific zone.
Methods of Area Measurement
The actual process of calculating area from maps involves various methods, each with its own advantages and limitations:
1. Grid Method: This method, often used for irregular shapes, involves overlaying a grid of squares onto the map. The area of each square is known, and by counting the squares within the region of interest, an estimate of the total area can be obtained. The accuracy of this method depends on the grid size and the complexity of the shape.
2. Planimeter Method: This mechanical device, resembling a compass, utilizes a tracing wheel to measure the area of irregular shapes. The planimeter operates based on the principle of integrating the area enclosed by a closed curve. While providing accurate results, the planimeter is a specialized tool requiring expertise to operate.
3. Digital Area Measurement: With the advent of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and digital maps, area calculation has become highly efficient and accurate. GIS software utilizes advanced algorithms to calculate area with precision, allowing for complex calculations and analysis.
4. Geometric Formulas: For regular shapes like squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles, the use of geometric formulas provides a precise and straightforward method for area calculation. This method relies on readily available formulas and requires accurate measurements of relevant dimensions from the map.
Applications of Area Measurement on Maps
The ability to measure area using maps finds diverse applications across various fields:
1. Land Management: Land surveyors and property owners rely on area calculations to determine property boundaries, calculate land values, and manage land resources efficiently.
2. Urban Planning: City planners utilize area measurements to assess the size of neighborhoods, parks, and infrastructure projects, facilitating informed decisions regarding urban development and resource allocation.
3. Environmental Monitoring: Ecologists and environmental scientists use area measurements to track changes in forest cover, monitor the spread of invasive species, and assess the impact of environmental changes on ecosystems.
4. Resource Management: Governments and organizations rely on area measurements to estimate the availability of natural resources like water, minerals, and timber, facilitating sustainable resource management and allocation.
5. Disaster Response: Area calculations play a crucial role in disaster response, enabling efficient allocation of resources and personnel to affected regions.
FAQs on Area Measurement Using Maps
Q: What are the limitations of area measurement using maps?
A: The accuracy of area measurement using maps is influenced by various factors, including the scale of the map, the projection used, and the complexity of the shape being measured. Distortions introduced by map projections can lead to inaccuracies, particularly for larger areas or regions with complex shapes.
Q: How do I choose the right map for area measurement?
A: The choice of map depends on the specific application and the desired level of accuracy. For small-scale projects, a large-scale map with a smaller ratio is preferred. For larger areas, a small-scale map with a larger ratio may be sufficient. Consider the projection used and its potential distortions.
Q: What are the benefits of using digital maps for area measurement?
A: Digital maps, integrated with GIS software, offer numerous advantages: high accuracy, automated calculations, efficient data management, and the ability to integrate with other data sources for complex analysis.
Tips for Accurate Area Measurement Using Maps
1. Choose the appropriate map scale: Select a map scale that provides sufficient detail for the specific application and desired accuracy.
2. Understand the map projection: Be aware of the projection used and its potential distortions, and consider how they might affect area calculations.
3. Utilize appropriate measurement methods: Choose the method that best suits the shape and complexity of the region being measured.
4. Calibrate the map: If using a physical map, ensure it is properly calibrated to ensure accurate measurements.
5. Use a ruler or grid: For accurate measurements, use a ruler or grid to measure distances on the map.
Conclusion
Area measurement using maps, a seemingly simple concept, holds immense power for various applications, influencing decisions related to land management, urban planning, environmental monitoring, and resource allocation. Understanding the principles of scale, projection, and the various measurement methods empowers individuals and organizations to harness the potential of maps for accurate area calculations. As technology continues to advance, digital maps and GIS software are poised to revolutionize area measurement, offering unprecedented accuracy and efficiency, further solidifying the role of maps in shaping our understanding and management of the world around us.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/85210081-58b5973d5f9b58604675bafc.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Measuring the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Area Calculation Using Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!