Measuring the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Area Measurement Maps
Related Articles: Measuring the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Area Measurement Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Measuring the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Area Measurement Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Measuring the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Area Measurement Maps

Area measurement maps, often referred to as area maps, are specialized cartographic representations that go beyond simply depicting geographical features. They serve as powerful tools for quantifying and analyzing the spatial extent of specific regions, providing crucial insights for a wide range of applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of area measurement maps, exploring their construction, uses, and importance in various fields.
The Foundation of Area Measurement: Understanding the Basics
At the heart of area measurement maps lies the concept of geospatial data. This data, often gathered through satellite imagery, aerial photography, or ground surveys, provides detailed information about the Earth’s surface. It includes features like elevation, land cover, and boundaries, forming the basis for constructing accurate area measurements.
Creating Area Measurement Maps: A Multi-Step Process
The creation of an area measurement map involves a series of meticulous steps:
-
Data Acquisition: This stage involves collecting the necessary geospatial data using appropriate methods. The choice of data source depends on the specific application and desired level of accuracy.
-
Data Processing: Raw data is cleaned, transformed, and prepared for analysis. This may include correcting for distortions, aligning multiple datasets, and ensuring consistency in units.
-
Defining the Area of Interest: The specific region or feature to be measured is clearly defined. This may involve delineating boundaries, identifying specific land cover types, or focusing on particular features.
-
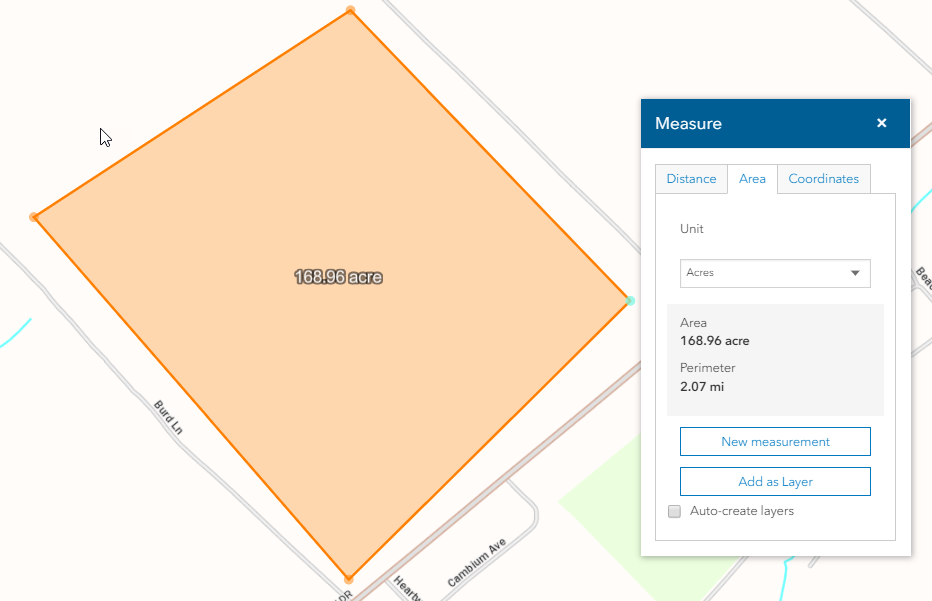
Area Calculation: Utilizing specialized software, the defined area is calculated using various techniques. These can include:
- Georeferenced polygons: Defining the area using closed shapes with coordinates.
- Pixel counting: Counting the number of pixels representing the area within the defined boundaries.
- Raster analysis: Analyzing the spatial distribution of data values to determine area.
-
Visualization and Presentation: The calculated area measurements are displayed on the map, often using different colors, symbols, or patterns to represent different zones or categories.
Applications of Area Measurement Maps: A Wide Range of Uses
Area measurement maps find applications in a vast array of fields, playing a vital role in:
- Land Management and Planning: Assessing land use, identifying suitable areas for development, and planning infrastructure projects.
- Environmental Monitoring: Mapping deforestation, tracking changes in land cover, and assessing the impact of natural disasters.
- Agriculture and Forestry: Measuring crop yields, monitoring forest health, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Urban Planning and Development: Analyzing urban sprawl, identifying areas for green spaces, and planning efficient transportation systems.
- Disaster Management: Assessing the impact of floods, earthquakes, and other disasters, and guiding relief efforts.
- Resource Management: Identifying and quantifying natural resources like water, minerals, and timber.
- Legal and Boundary Disputes: Resolving land ownership disputes, determining property boundaries, and supporting legal proceedings.
- Research and Analysis: Providing data for scientific research, environmental studies, and social impact assessments.
Benefits of Area Measurement Maps: Empowering Informed Decisions
The use of area measurement maps offers numerous benefits, enabling:
- Accurate and Reliable Data: Providing precise measurements of spatial extents, reducing the risk of errors and inaccuracies.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Supporting informed decisions based on quantifiable data, promoting efficiency and effectiveness.
- Improved Planning and Management: Facilitating better resource allocation, optimizing operations, and minimizing environmental impact.
- Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: Providing a common platform for sharing information and collaborating on projects.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability: Enabling clear documentation of data and methods, fostering trust and accountability.
Frequently Asked Questions about Area Measurement Maps
Q: What are the different types of area measurement maps?
A: Area measurement maps can be classified based on their purpose, scale, and the data they represent. Some common types include:
- Land use maps: Depicting different land uses within a specific region.
- Forest cover maps: Showing the extent and distribution of forest areas.
- Agricultural land maps: Illustrating the distribution of different crops and agricultural practices.
- Urban planning maps: Representing urban development patterns and zoning regulations.
- Disaster risk maps: Identifying areas vulnerable to natural hazards.
Q: What are the challenges associated with creating area measurement maps?
A: Several challenges can arise during the creation of area measurement maps, including:
- Data Availability and Quality: Ensuring access to accurate and up-to-date geospatial data can be challenging, especially in remote areas.
- Data Processing and Analysis: Processing large datasets, handling complex spatial relationships, and ensuring accuracy requires specialized skills and software.
- Uncertainty and Error: Data collection and analysis methods can introduce uncertainties and errors, requiring careful evaluation and mitigation strategies.
- Cost and Time: Creating high-quality area measurement maps can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy of area measurements?
A: Several factors contribute to the accuracy of area measurements:
- Data Source Quality: Using high-resolution and accurate geospatial data is crucial.
- Data Processing Techniques: Employing appropriate data processing methods and quality control measures.
- Validation and Verification: Regularly validating the measurements against ground truth data or other reliable sources.
- Error Estimation: Quantifying and reporting the potential errors associated with the measurements.
Tips for Using Area Measurement Maps Effectively
- Define the Purpose: Clearly articulate the specific objectives of the area measurement map before starting.
- Choose the Right Data: Select the appropriate data source and resolution based on the intended use.
- Use Reliable Software: Employ specialized software designed for geospatial analysis and area measurement.
- Validate the Results: Ensure the accuracy of the measurements by comparing them with known data or conducting field verification.
- Communicate Effectively: Present the results in a clear and concise manner, using appropriate visualizations and legends.
Conclusion: Empowering Informed Decision-Making with Area Measurement Maps
Area measurement maps play a pivotal role in understanding and quantifying the spatial extent of various regions. By providing accurate data and insights, they empower informed decision-making in a wide range of fields, from land management and environmental monitoring to urban planning and disaster response. As technology continues to advance, area measurement maps will undoubtedly become even more powerful tools for analyzing and managing our planet’s resources. The ability to measure and understand the spatial distribution of features is crucial for addressing the challenges of a rapidly changing world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Measuring the World: A Comprehensive Guide to Area Measurement Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!