Navigating Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to In and Out Maps
Related Articles: Navigating Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to In and Out Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Navigating Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to In and Out Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to In and Out Maps

In the realm of data visualization and analysis, understanding complex systems and processes often necessitates a structured approach. This is where "in and out" maps, also known as "flow maps" or "process maps," emerge as a powerful tool. These visual representations, often depicted as diagrams, provide a clear and concise overview of how information, materials, or even people move through a system.
This article delves into the intricacies of in and out maps, exploring their structure, applications, benefits, and limitations. By understanding the fundamental principles of these maps, individuals and organizations can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of their operations, leading to improved decision-making, process optimization, and ultimately, enhanced efficiency.
Understanding the Structure of In and Out Maps
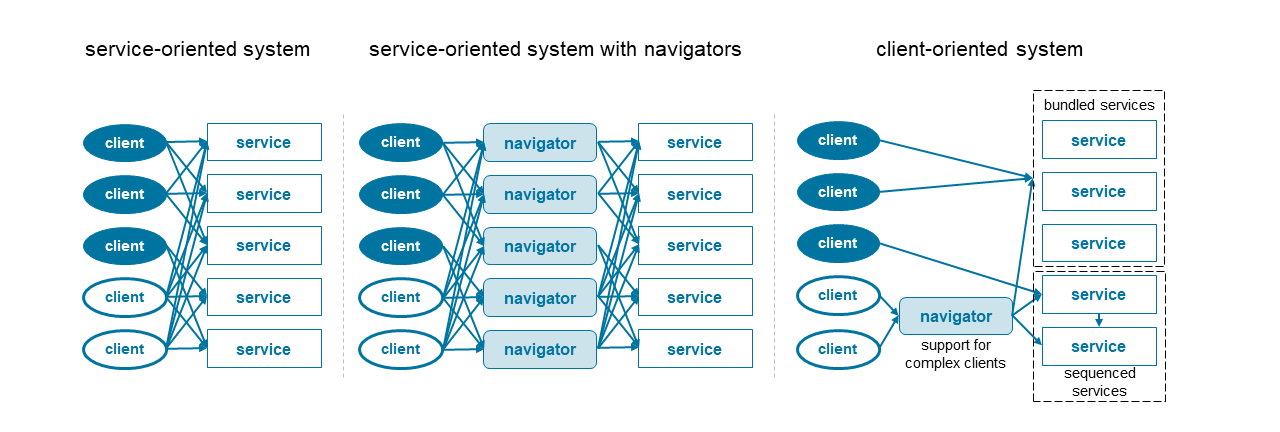
At its core, an in and out map consists of interconnected nodes and arrows. The nodes represent various stages, activities, or entities within a system, while the arrows depict the flow of information, materials, or resources between them.
Nodes: These can be represented as boxes, circles, or other shapes, each containing a label that clearly identifies the specific stage or entity it represents. For example, in a manufacturing process, a node might represent "Raw Material Procurement," "Assembly," or "Quality Control."
Arrows: These indicate the direction of flow between nodes. They can be labeled with descriptive information such as the type of material being transferred, the process involved, or the time it takes to complete the transition.
Types of In and Out Maps
In and out maps are adaptable and can be tailored to represent a wide range of systems and processes. Here are some common types:
- Process Flow Maps: These maps illustrate the sequence of activities within a specific process, highlighting the steps involved and the flow of information or materials between them. They are commonly used in manufacturing, service industries, and project management.
- Data Flow Maps: These maps depict the movement of data through a system, showing how information is collected, processed, stored, and disseminated. They are crucial for understanding data management processes and ensuring data integrity.
- Value Stream Maps: These maps focus on the flow of value through a process, identifying areas of waste and inefficiency. They are commonly used in lean manufacturing and process improvement initiatives.
- System Dynamics Maps: These maps represent the interconnectedness of various elements within a complex system, highlighting feedback loops and the impact of changes on different parts of the system. They are often used in strategic planning and policy analysis.
Benefits of Using In and Out Maps
The application of in and out maps offers numerous advantages, including:
- Enhanced Visualization: By presenting complex information in a visually intuitive format, these maps facilitate a clear understanding of the system’s structure and dynamics.
- Improved Communication: In and out maps provide a common language for discussing processes and systems, fostering collaboration and ensuring everyone is on the same page.
- Process Optimization: By identifying bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas for improvement, in and out maps enable organizations to streamline their processes and increase efficiency.
- Risk Identification: These maps can help identify potential risks and vulnerabilities within a system, enabling proactive mitigation strategies.
- Decision Support: In and out maps provide a comprehensive overview of a system, facilitating informed decision-making based on a clear understanding of the flow of information and resources.
Limitations of In and Out Maps
While in and out maps offer significant benefits, it’s important to recognize their limitations:
- Oversimplification: In and out maps can sometimes oversimplify complex systems, potentially overlooking important details or nuances.
- Static Representation: These maps capture a snapshot of a system at a specific point in time, failing to account for dynamic changes and fluctuations.
- Limited Scope: In and out maps typically focus on a specific process or system, neglecting the broader context and potential interdependencies with other systems.
- Subjectivity: The interpretation of in and out maps can be subjective, potentially leading to different perspectives and conclusions.
FAQs about In and Out Maps
Q: What are some common software tools used for creating in and out maps?
A: Popular software tools for creating in and out maps include Microsoft Visio, Lucidchart, Draw.io, and Google Drawings. These tools offer a range of features for designing visually appealing and interactive maps.
Q: How can in and out maps be used in different industries?
A: In and out maps find applications across various industries, including:
- Manufacturing: Process mapping, value stream mapping, and supply chain optimization.
- Healthcare: Patient flow analysis, workflow optimization, and risk management.
- Finance: Financial transaction analysis, regulatory compliance mapping, and risk assessment.
- IT: Network architecture diagrams, software development process mapping, and data flow analysis.
- Education: Curriculum mapping, learning process analysis, and student flow optimization.
Q: How can I ensure my in and out map is effective?
A: To ensure your in and out map is effective, consider the following:
- Clear and concise labeling: Use clear and descriptive labels for nodes and arrows.
- Visual clarity: Use colors, shapes, and arrows to differentiate between different elements and flows.
- Appropriate level of detail: Strike a balance between providing sufficient detail and avoiding overwhelming complexity.
- User-friendliness: Ensure the map is easy to understand and navigate.
Tips for Creating Effective In and Out Maps
- Start with a clear objective: Define the purpose of the map and the specific information you aim to convey.
- Gather relevant data: Collect all necessary information about the system or process being mapped.
- Use a structured approach: Employ a standardized format and symbols to ensure consistency and clarity.
- Involve stakeholders: Seek input from individuals involved in the system or process to ensure accuracy and buy-in.
- Iterate and refine: Continuously review and update the map as the system or process evolves.
Conclusion
In and out maps serve as valuable tools for visualizing, analyzing, and understanding complex systems and processes. By providing a clear and concise representation of information flow, these maps facilitate improved communication, process optimization, and informed decision-making. While they are not without limitations, their benefits outweigh the drawbacks, making them an essential resource for individuals and organizations seeking to navigate the complexities of their operations. As organizations continue to embrace data-driven decision-making, in and out maps will play an increasingly vital role in optimizing processes, mitigating risks, and achieving strategic goals.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Complexity: A Comprehensive Guide to In and Out Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!