Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen Bullet Train Map
Related Articles: Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen Bullet Train Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen Bullet Train Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen Bullet Train Map
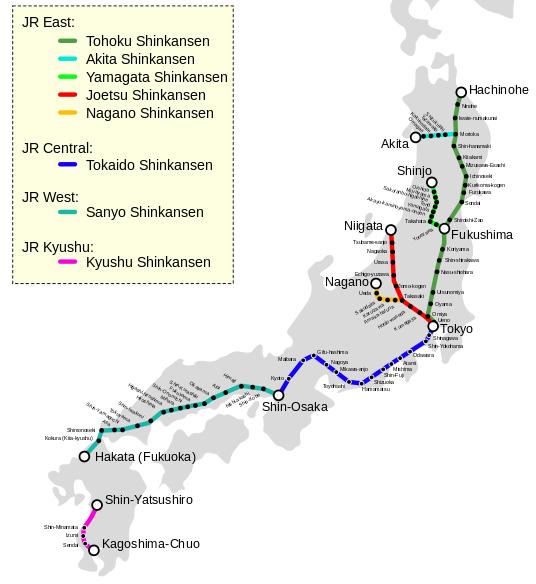
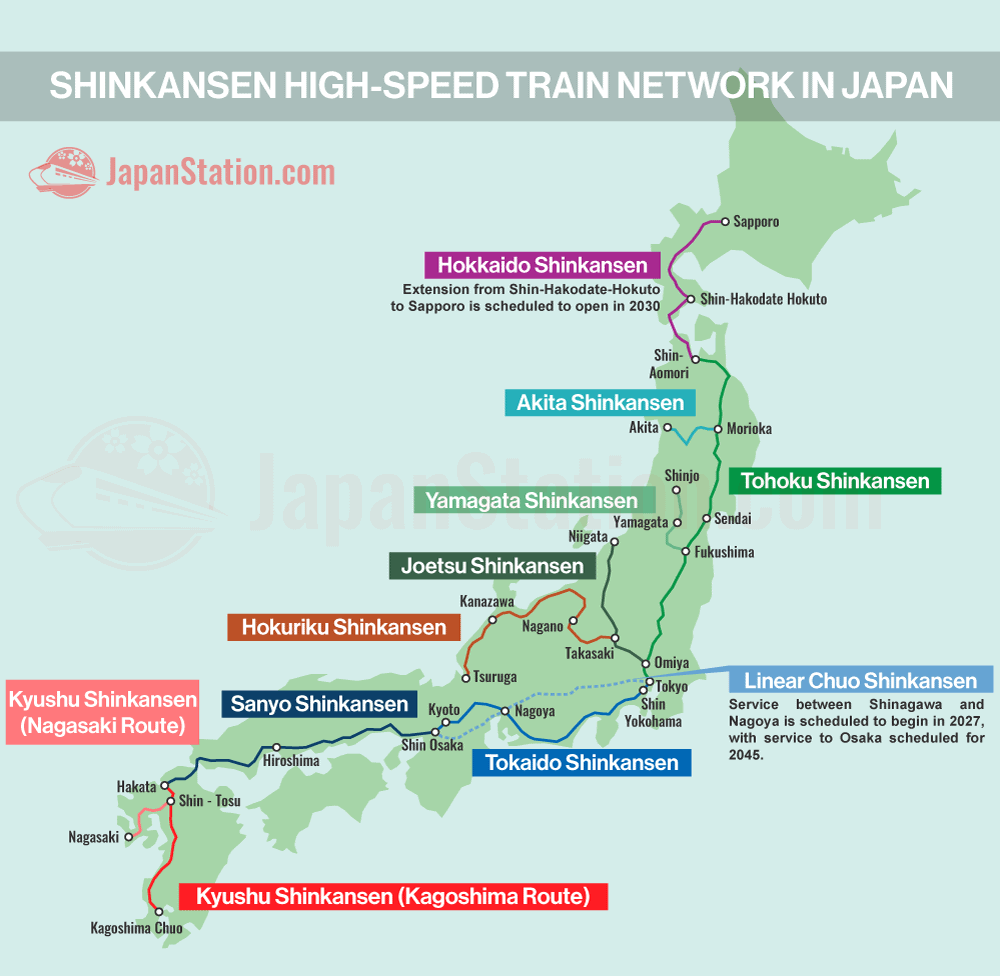
Japan’s Shinkansen, or bullet train, network is a marvel of modern engineering and a testament to the country’s dedication to efficient transportation. This intricate web of high-speed lines crisscrosses the archipelago, connecting major cities and offering a seamless, comfortable, and time-saving mode of travel. Understanding the Shinkansen map is crucial for any traveler seeking to maximize their experience in Japan.
Understanding the Network:
The Shinkansen network, operated by Japan Railways (JR), comprises several distinct lines, each distinguished by color and route. Some lines operate under specific names, such as the Tokaido Shinkansen, while others are simply identified by their color, like the "Green Shinkansen."
- Tokaido Shinkansen: This is the original and most prominent Shinkansen line, connecting Tokyo to Osaka via Nagoya. It is the busiest high-speed rail line in the world and serves as the backbone of the network.
- Sanyo Shinkansen: This line extends the Tokaido Shinkansen westward, connecting Osaka to Hakata (Fukuoka) in Kyushu.
- Tohoku Shinkansen: This line runs north from Tokyo, reaching Sendai and Morioka, and eventually extending to Aomori in northern Honshu.
- Hokkaido Shinkansen: This line connects Aomori with Hakodate in Hokkaido, Japan’s northernmost island.
- Joetsu Shinkansen: This line runs parallel to the Tohoku Shinkansen, connecting Tokyo to Niigata on the Sea of Japan coast.
- Nagano Shinkansen: This line connects Tokyo to Nagano, the site of the 1998 Winter Olympics.
Reading the Map:
The Shinkansen map is remarkably simple to navigate. Key elements to understand include:
- Lines: Different colored lines represent distinct Shinkansen routes.
- Stations: Major stations are clearly marked with their names and symbols.
- Transfer Points: Stations where lines intersect allow for easy connections between different routes.
- Direction of Travel: Arrows indicate the direction of travel along each line.
- Speed: The Shinkansen’s average speed is around 270 km/h, making it incredibly efficient for long-distance travel.
Benefits of the Shinkansen:
- Speed and Efficiency: The Shinkansen’s high speed significantly reduces travel time between major cities.
- Comfort and Convenience: Comfortable seating, spacious cabins, and on-board amenities make for a pleasant journey.
- Reliability: The Shinkansen system is known for its punctuality and reliability, making it a dependable travel option.
- Accessibility: The Shinkansen network connects major cities and tourist destinations, making it easy to explore Japan.
- Environmental Sustainability: High-speed rail is a more environmentally friendly mode of transportation compared to air travel.
Planning Your Journey:
- Choose Your Destination: Identify the cities you wish to visit and their corresponding Shinkansen stations.
- Select Your Route: Refer to the Shinkansen map to identify the most efficient route between your chosen destinations.
- Book Tickets: Tickets can be purchased online, at station ticket machines, or through travel agencies.
- Consider Travel Passes: For frequent travelers, Japan Rail Pass offers unlimited travel on the Shinkansen and other JR lines.
- Check Schedules: Be sure to check the latest schedules and make necessary reservations in advance.
FAQs:
- What is the average speed of the Shinkansen? The average speed of the Shinkansen is around 270 km/h.
- How often do trains run on the Shinkansen? Train frequency varies depending on the line and time of day. However, trains generally run every 15-30 minutes during peak hours.
- Are there different classes of seating on the Shinkansen? Yes, most Shinkansen lines offer different seating classes, including standard, green car (first class), and reserved seating.
- Can I bring luggage on the Shinkansen? Yes, luggage is permitted on the Shinkansen, but there may be size restrictions for larger items.
- What about food and drinks on the Shinkansen? Food and drinks are available for purchase on most Shinkansen trains.
Tips:
- Purchase tickets in advance, especially during peak season.
- Consider purchasing a Japan Rail Pass if you plan to travel extensively by train.
- Arrive at the station early to allow ample time for check-in and boarding.
- Be mindful of the different seating classes and choose the option that best suits your needs.
- Utilize the free Wi-Fi available on most Shinkansen trains.
Conclusion:
The Shinkansen bullet train network is an integral part of Japan’s transportation infrastructure, offering a convenient, efficient, and comfortable mode of travel. Its extensive network connects major cities and tourist destinations, making it a vital tool for exploring the diverse landscapes and cultural offerings of Japan. By understanding the Shinkansen map and its intricacies, travelers can maximize their journey and experience the best that Japan has to offer.
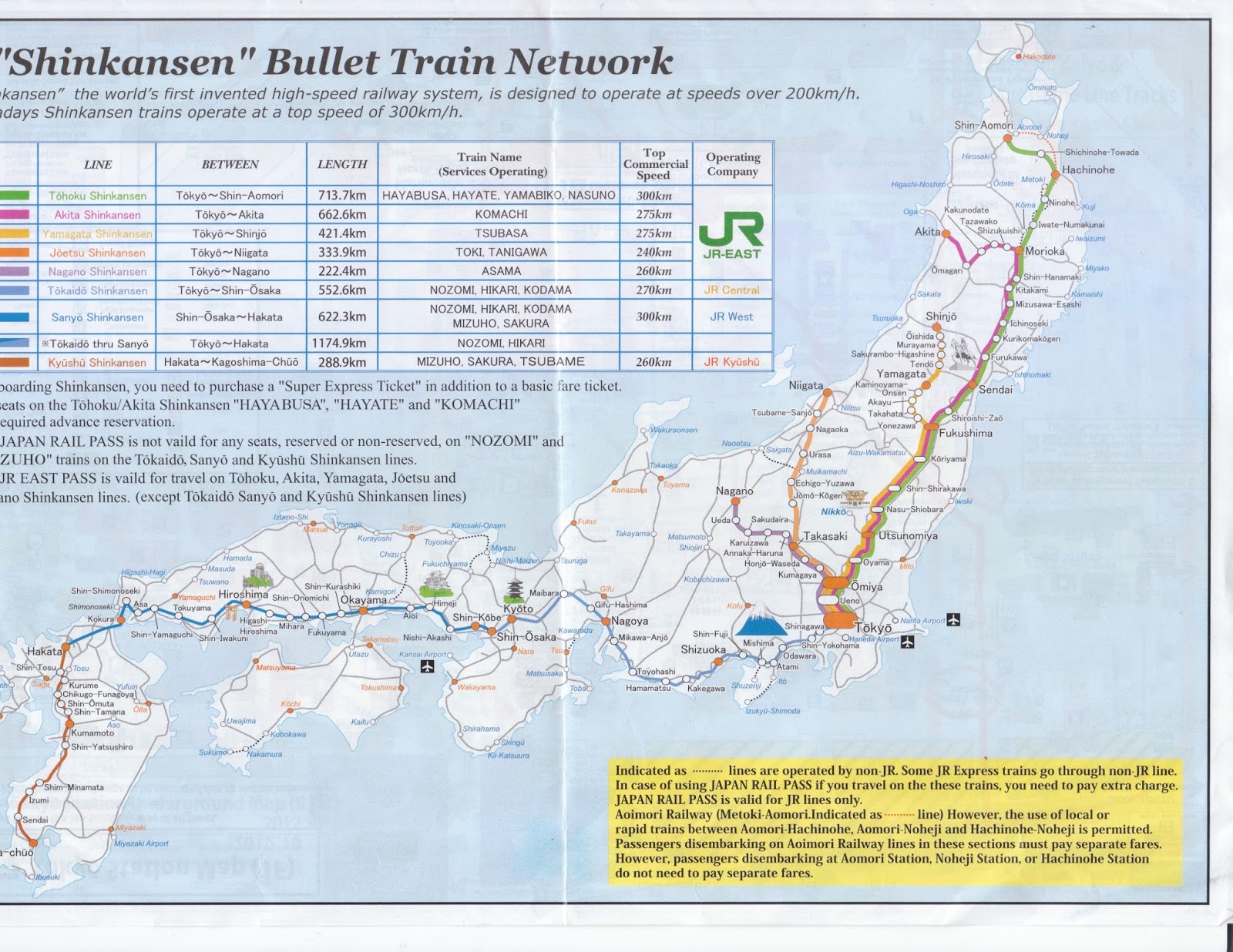

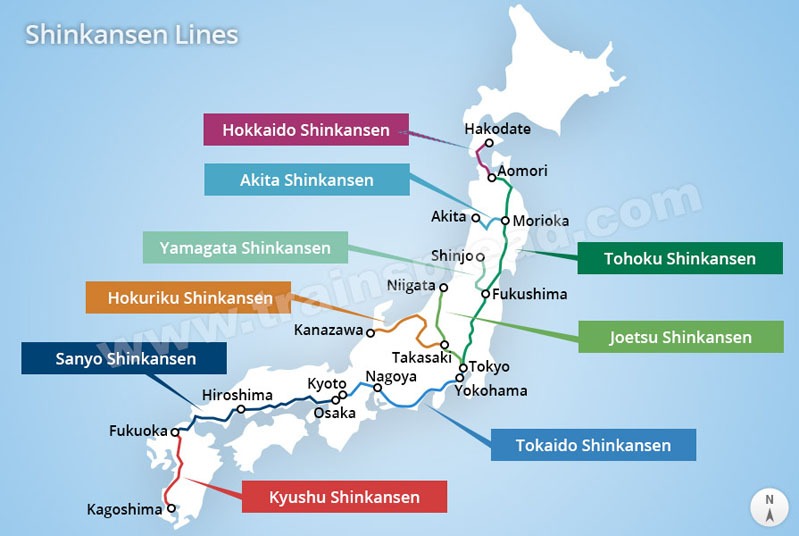
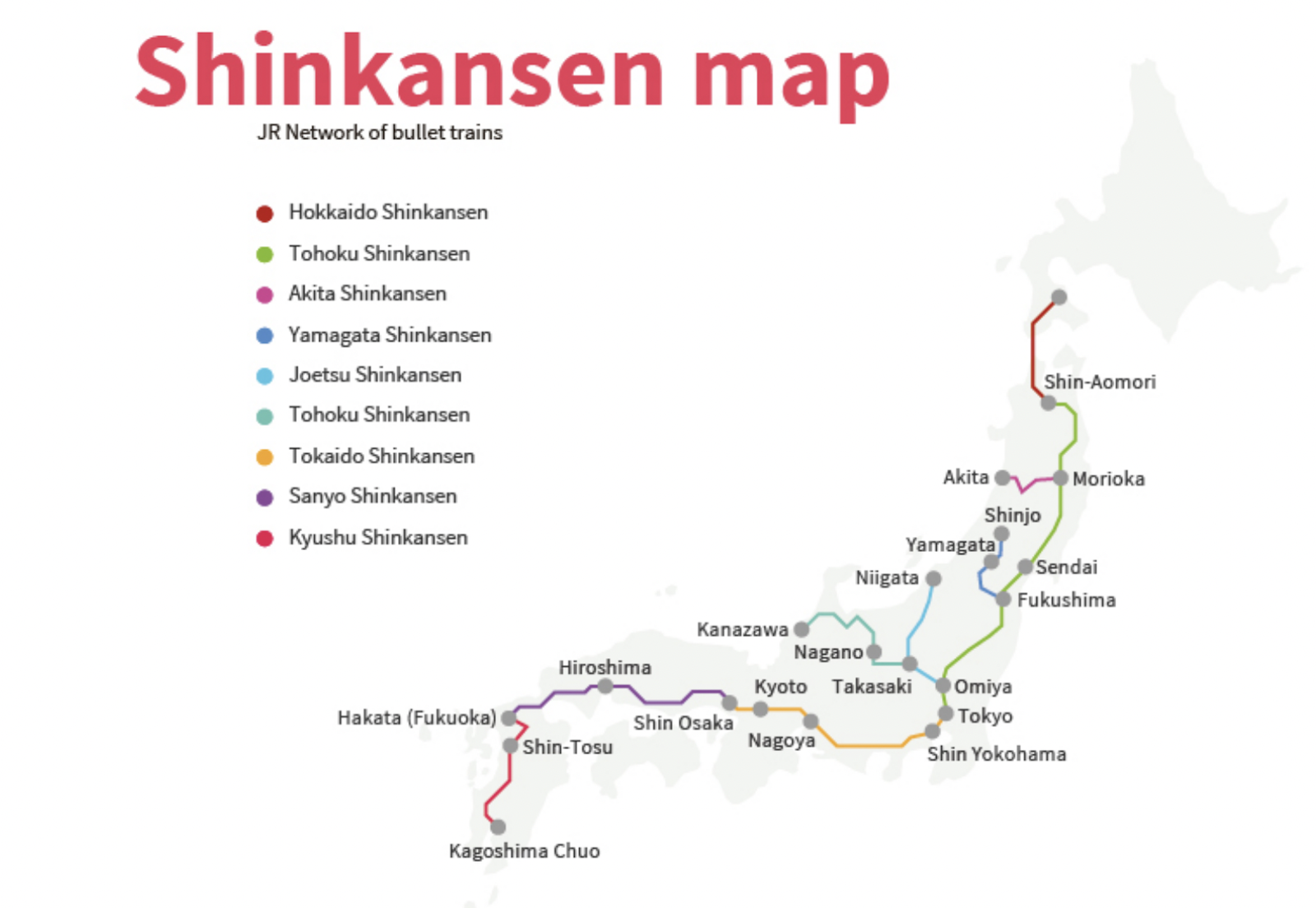



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Japan’s High-Speed Network: A Comprehensive Guide to the Shinkansen Bullet Train Map. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!