Navigating the Appalachian Heart: A Geographical Exploration of West Virginia and its Neighbors
Related Articles: Navigating the Appalachian Heart: A Geographical Exploration of West Virginia and its Neighbors
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Appalachian Heart: A Geographical Exploration of West Virginia and its Neighbors. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Appalachian Heart: A Geographical Exploration of West Virginia and its Neighbors

West Virginia, the "Mountain State," sits nestled within the Appalachian Mountains, a region renowned for its rugged beauty and rich history. Its geographic position, surrounded by a constellation of states, plays a pivotal role in shaping its culture, economy, and overall identity. Understanding the map of West Virginia and its surrounding states reveals a fascinating tapestry of interconnected landscapes, cultural influences, and historical events.
A Geographic Crossroads:
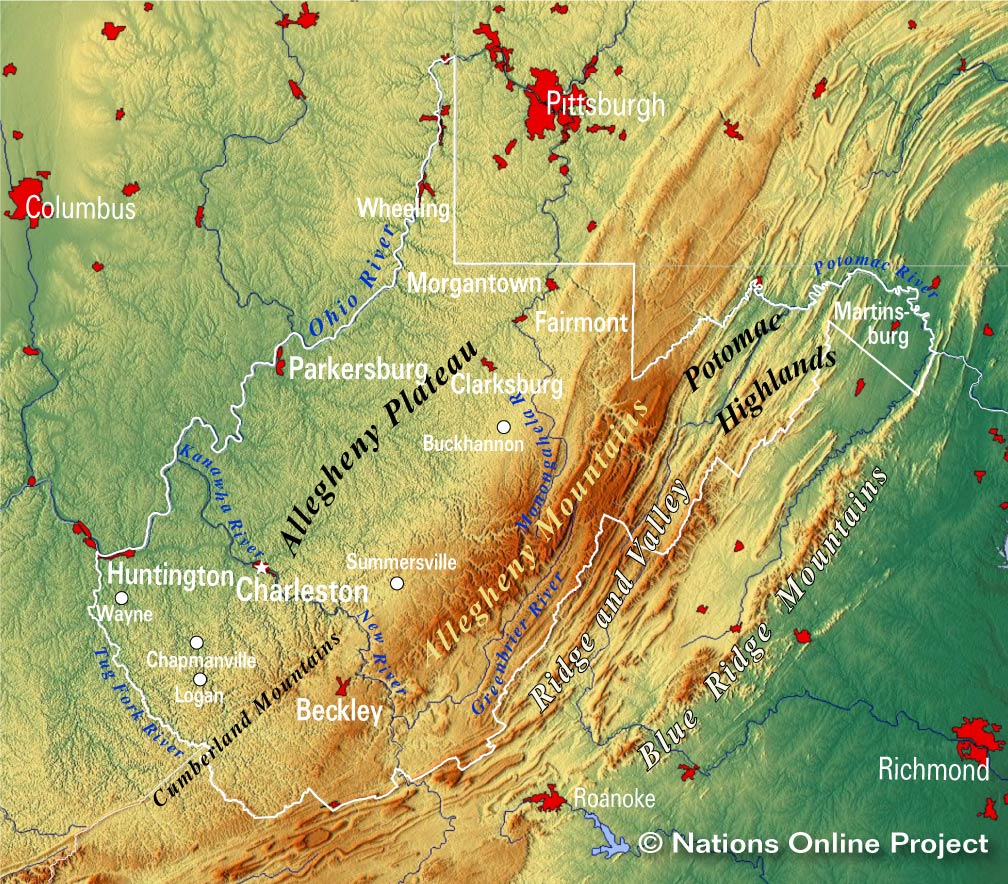
West Virginia’s unique geographical location, bordered by Virginia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Ohio, and Kentucky, makes it a true crossroads of the Eastern United States. This proximity to major metropolitan areas like Washington D.C., Pittsburgh, and Baltimore, coupled with its own diverse topography, has had a profound impact on the state’s development.
The Appalachian Spine:
The Appalachian Mountains, a dominant feature in the region, carve a dramatic path through West Virginia, creating a diverse landscape of rolling hills, steep valleys, and towering peaks. This mountainous terrain has historically shaped the state’s economy, with coal mining and timber industries playing a significant role. The Appalachian Mountains also influence the state’s climate, creating a humid subtropical climate in the lowlands and a humid continental climate in the higher elevations.
Waterways and Transportation:
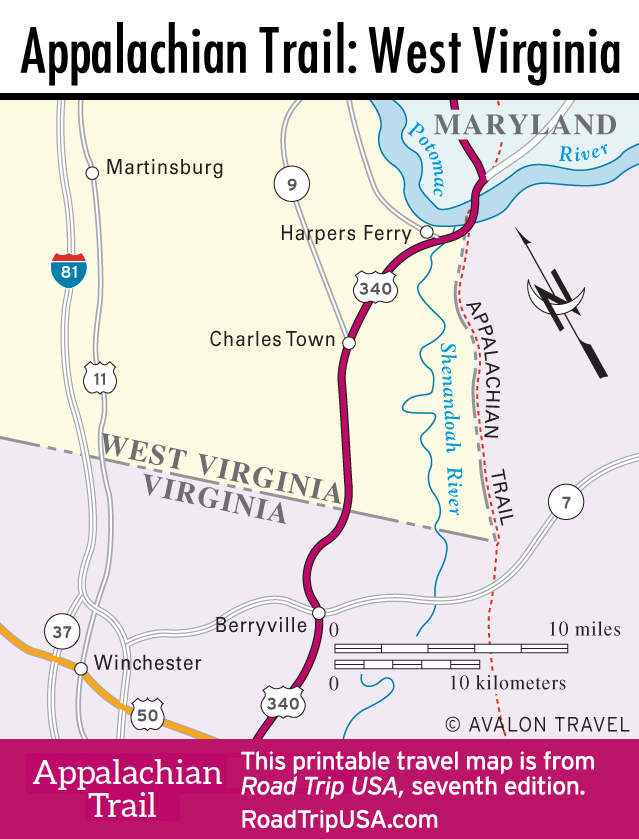
West Virginia’s geography is further defined by its numerous rivers and streams, including the Ohio River, the Potomac River, and the Monongahela River. These waterways have historically served as vital transportation routes, facilitating trade and commerce. The state’s position along the I-77 and I-64 corridors also makes it a key transportation hub, connecting major cities and facilitating the movement of goods and people.
Surrounding States: A Mosaic of Influences:
Each of West Virginia’s neighboring states contributes to the state’s cultural and economic landscape. Virginia, with its rich history and diverse cultural heritage, shares a close bond with West Virginia, particularly in the areas of music, folklore, and language. Maryland, known for its vibrant cities and coastal landscapes, provides a contrasting backdrop, influencing West Virginia’s urban development and cultural exchanges.
Pennsylvania, with its industrial heritage and strong ties to the coal mining industry, has historically shared a close economic relationship with West Virginia. Ohio, a state with a strong manufacturing base and a vibrant agricultural sector, has also played a role in shaping West Virginia’s economic landscape. Finally, Kentucky, with its shared Appalachian heritage and strong cultural ties, continues to influence West Virginia’s artistic expressions and musical traditions.
The Importance of Understanding the Map:
A thorough understanding of the map of West Virginia and its surrounding states reveals the intricate web of connections that have shaped the state’s history, culture, and economy. This geographical knowledge allows for a deeper appreciation of the state’s unique identity and its place within the broader context of the Eastern United States.
Understanding the Map: Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the major geographical features of West Virginia?
West Virginia is characterized by the Appalachian Mountains, which create a diverse landscape of hills, valleys, and peaks. The state is also crisscrossed by numerous rivers and streams, including the Ohio River, the Potomac River, and the Monongahela River.
2. How has West Virginia’s geography influenced its economy?
The state’s mountainous terrain and abundant natural resources have historically shaped its economy, with coal mining, timber, and agriculture playing significant roles. The presence of waterways has facilitated transportation and trade, contributing to the state’s economic development.
3. How do the surrounding states influence West Virginia’s culture?
West Virginia’s neighboring states, with their diverse cultural heritage, have influenced the state’s music, folklore, language, and artistic expressions. The proximity to major metropolitan areas has also shaped West Virginia’s urban development and cultural exchanges.
4. What is the significance of West Virginia’s location within the Appalachian region?
West Virginia’s position within the Appalachian Mountains has shaped its physical environment, its economic development, and its cultural identity. The region’s history of coal mining, timber harvesting, and rural life has left an enduring mark on the state’s character.
5. How has West Virginia’s geography impacted its transportation infrastructure?
The state’s mountainous terrain and river systems have influenced its transportation infrastructure. The development of highways, railways, and waterways has played a crucial role in connecting West Virginia to the rest of the country.
Tips for Navigating the Map:
1. Use a detailed map: Employing a map that showcases both physical features and political boundaries will provide a comprehensive understanding of West Virginia’s geography and its relationship with surrounding states.
2. Explore regional distinctions: Pay attention to the differences in elevation, landforms, and vegetation patterns across the state and its neighboring regions. This will reveal the diverse geographical influences that shape the region.
3. Trace historical routes: Examine the paths of major rivers, railroads, and highways to understand how transportation has shaped the region’s development and connections.
4. Consider cultural influences: Analyze the distribution of cultural landmarks, historical sites, and population centers to appreciate how surrounding states have influenced West Virginia’s cultural landscape.
5. Connect the dots: By understanding the interconnectedness of geographical features, cultural influences, and historical events, a deeper appreciation for the complexities of West Virginia and its surrounding states can be achieved.
Conclusion:
The map of West Virginia and its surrounding states is a powerful tool for understanding the region’s unique character. By examining the interplay of geography, history, and culture, a comprehensive picture emerges, revealing the interconnectedness of this diverse landscape and its profound impact on the lives of its inhabitants. This geographical knowledge fosters a deeper appreciation for the region’s rich heritage and its place within the larger context of the Eastern United States.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Appalachian Heart: A Geographical Exploration of West Virginia and its Neighbors. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!