Navigating the Complexities of the Human Brain: An Exploration of the Samford Map
Related Articles: Navigating the Complexities of the Human Brain: An Exploration of the Samford Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Complexities of the Human Brain: An Exploration of the Samford Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Complexities of the Human Brain: An Exploration of the Samford Map
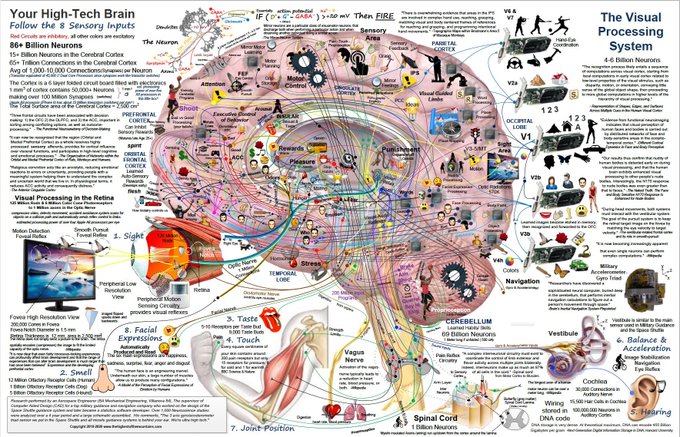
The human brain, a marvel of biological engineering, remains a complex and fascinating frontier for scientific exploration. Understanding its intricate structure and function is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of cognition, behavior, and disease. One approach to this challenging task is through the use of anatomical maps, detailed representations that depict the brain’s various regions and their interconnections. Among these, the Samford Map stands out as a significant tool, offering a novel perspective on brain organization and its potential implications for neuroscience research.
A Fresh Perspective on Brain Organization
The Samford Map, developed by Dr. Michael Samford and his team at the University of Queensland, presents a unique framework for understanding the human brain. It departs from traditional anatomical maps by emphasizing the interconnectedness of brain regions rather than solely focusing on their physical boundaries. This approach recognizes that the brain functions as a complex network, with information flowing seamlessly between different areas.
The map utilizes a color-coded system to represent different functional networks within the brain. These networks, identified through advanced neuroimaging techniques, encompass various cognitive functions, including language, memory, attention, and motor control. By visualizing these networks, the Samford Map reveals how different brain regions collaborate to perform complex tasks. This interconnectedness, often overlooked in traditional maps, offers a more comprehensive understanding of brain function.
Beyond Traditional Anatomical Maps
Traditional anatomical maps, often based on gross anatomical features, can be limited in their ability to capture the dynamic nature of brain function. They often fail to adequately represent the intricate interplay between different brain regions, leading to a fragmented view of brain activity.
The Samford Map, in contrast, transcends these limitations by providing a more holistic representation of brain function. It highlights the interconnected nature of brain networks, emphasizing their dynamic interactions and influence on cognitive processes. This approach offers a more nuanced understanding of the brain’s functional architecture, paving the way for new discoveries in neuroscience.
Applications and Potential Benefits
The Samford Map holds significant potential for various applications in neuroscience research, clinical practice, and education.
1. Neuroscience Research:
- Understanding Brain Disorders: The map’s focus on brain networks offers a valuable framework for investigating the neural underpinnings of various brain disorders, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and autism spectrum disorder. By identifying disruptions in specific networks, researchers can gain insights into the mechanisms underlying these conditions and develop targeted therapies.
- Developing Novel Interventions: The map’s detailed representation of brain connectivity can guide the development of novel interventions, such as brain stimulation therapies, aimed at enhancing specific cognitive functions or mitigating the effects of neurological disorders.
- Personalized Medicine: By understanding the unique network configurations of individual brains, the Samford Map can contribute to the development of personalized medicine approaches, tailoring treatments to individual needs and maximizing their effectiveness.
2. Clinical Practice:
- Diagnosis and Treatment: The map can assist clinicians in diagnosing and treating neurological disorders by providing a more comprehensive understanding of the affected brain regions and their interconnectedness.
- Rehabilitation: The map’s insights into brain plasticity and network reorganization can guide rehabilitation programs for patients recovering from brain injuries or strokes, promoting optimal recovery and functional improvement.
- Mental Health: The map’s emphasis on brain networks can aid in understanding the neural mechanisms underlying mental health disorders, leading to more targeted and effective treatment strategies.
3. Education:
- Neuroscience Education: The Samford Map can be a powerful tool for teaching neuroscience, providing a visually engaging and accessible way to convey complex concepts about brain structure and function.
- Public Awareness: The map can help educate the public about the intricacies of the human brain, fostering greater appreciation for its complexity and promoting brain health awareness.
Addressing Common Questions about the Samford Map
1. How is the Samford Map different from other brain maps?
The Samford Map distinguishes itself from traditional anatomical maps by emphasizing the interconnectedness of brain regions within functional networks. It provides a more holistic view of brain function, going beyond the physical boundaries of individual brain structures.
2. What are the limitations of the Samford Map?
The Samford Map is a relatively new tool, and its limitations are still being explored. It is based on current neuroimaging techniques, which may not fully capture the complexity of all brain functions. Further research is needed to refine and validate the map’s accuracy and applicability across various contexts.
3. How is the Samford Map developed?
The map is developed using advanced neuroimaging techniques, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). These techniques allow researchers to identify and map the connections between different brain regions, revealing the underlying functional networks.
4. What are the potential ethical considerations surrounding the Samford Map?
As with any scientific advancement, there are ethical considerations surrounding the development and application of the Samford Map. These include ensuring data privacy, protecting against potential misuse, and promoting responsible research practices.
Tips for Understanding and Utilizing the Samford Map
- Familiarize yourself with the basics of brain anatomy and function.
- Study the map’s color-coding system and the functional networks it represents.
- Explore the map’s online resources and accompanying publications.
- Engage in discussions with experts in the field to gain a deeper understanding.
- Consider the map’s potential applications in your own field of interest.
Conclusion
The Samford Map represents a significant advancement in our understanding of the human brain. By highlighting the interconnectedness of brain networks, it provides a more comprehensive and dynamic representation of brain function. This novel approach has the potential to revolutionize neuroscience research, clinical practice, and education, opening new avenues for understanding the brain and its complexities. As research continues to refine and validate the map, it promises to become an invaluable tool for unraveling the mysteries of the human mind and improving human health.




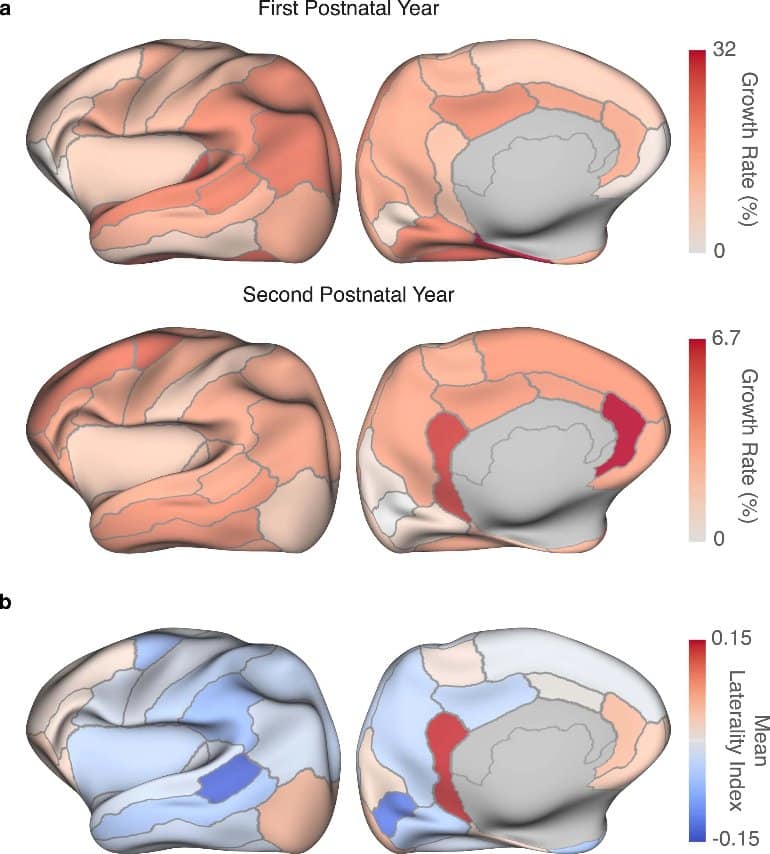


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Complexities of the Human Brain: An Exploration of the Samford Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!