Navigating the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Threat Mapping
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Threat Mapping
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Threat Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Threat Mapping
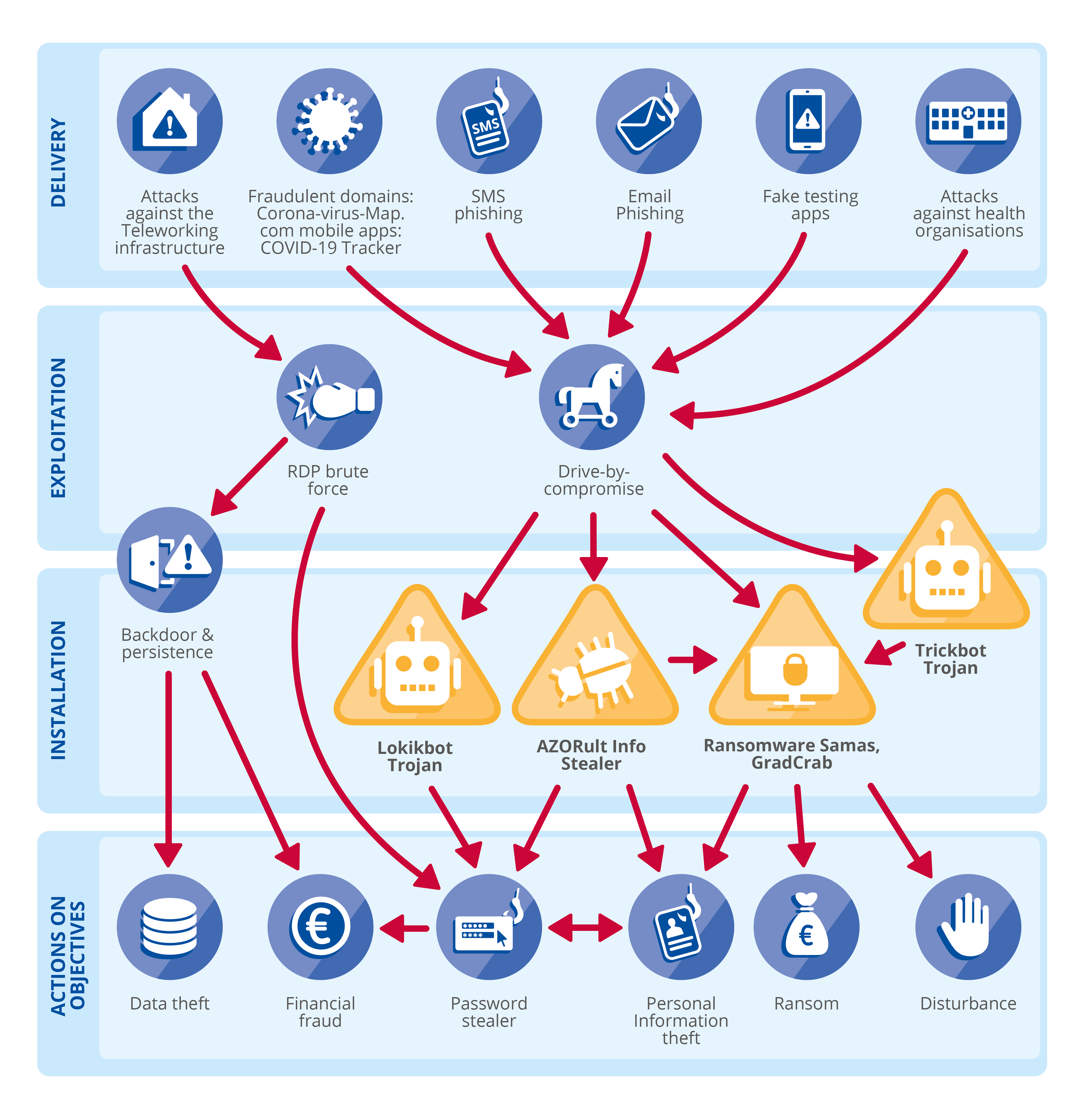
In today’s interconnected and increasingly complex world, organizations face a multitude of potential threats that can disrupt operations, compromise sensitive data, and damage reputation. To effectively mitigate these risks, a proactive and structured approach is essential. This is where threat mapping emerges as a powerful tool for understanding and managing vulnerabilities.
Defining Threat Mapping: A Visual Representation of Risk
Threat mapping is a visual representation of potential threats to an organization, its assets, and its operations. It serves as a roadmap for identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing risks, enabling organizations to develop targeted mitigation strategies. This methodology goes beyond simply listing potential threats; it provides a holistic view of the attack surface, encompassing potential attack vectors, vulnerabilities, and potential consequences.
Components of a Threat Map
A comprehensive threat map typically consists of the following components:
- Assets: These are the organization’s valuable resources, including physical assets (e.g., infrastructure, equipment), digital assets (e.g., data, systems, applications), and intangible assets (e.g., intellectual property, brand reputation).
- Threats: These are the potential dangers that could harm the organization’s assets. They can be internal (e.g., disgruntled employees) or external (e.g., cybercriminals, natural disasters).
- Vulnerabilities: These are weaknesses in the organization’s systems, processes, or personnel that could be exploited by threats.
- Attack Vectors: These are the pathways that attackers could use to exploit vulnerabilities and gain access to assets.
- Impact: This refers to the potential consequences of a successful attack, ranging from financial loss to reputational damage.
Benefits of Threat Mapping
Implementing threat mapping offers numerous benefits for organizations of all sizes:
- Improved Risk Awareness: By visualizing potential threats, organizations gain a clearer understanding of their overall risk landscape, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Prioritization of Resources: Threat mapping helps organizations prioritize resources by focusing on the most critical vulnerabilities and threats.
- Enhanced Security Posture: The process of creating a threat map encourages organizations to identify and address vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
- Improved Communication and Collaboration: Threat mapping fosters communication and collaboration between different departments, ensuring a unified approach to security.
- Proactive Risk Management: By proactively identifying and addressing potential threats, organizations can reduce the likelihood of costly incidents.
Creating a Threat Map: A Step-by-Step Guide
The process of creating a threat map typically involves the following steps:
- Identify Assets: Begin by identifying all critical assets, including their value and sensitivity.
- Identify Threats: Brainstorm potential threats, considering both internal and external sources.
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Analyze the organization’s systems, processes, and personnel to identify weaknesses that could be exploited.
- Identify Attack Vectors: Determine how attackers could exploit vulnerabilities to access assets.
- Assess Impact: Evaluate the potential consequences of a successful attack, including financial loss, reputational damage, and legal liabilities.
- Prioritize Risks: Rank threats based on their likelihood and impact, focusing on the most significant risks.
- Develop Mitigation Strategies: Create a plan to address the identified vulnerabilities and threats.
- Implement and Monitor: Implement the mitigation strategies and continuously monitor the effectiveness of the threat map.
Threat Mapping Tools and Techniques
Various tools and techniques can assist in creating and managing threat maps:
- Threat Modeling Tools: Software applications designed to facilitate threat modeling and mapping.
- Whiteboard Sessions: Collaborative brainstorming sessions involving stakeholders from different departments.
- Threat Intelligence Feeds: External sources of information on emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Vulnerability Scanning Tools: Automated tools that scan systems and applications for known vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing: Simulated attacks designed to identify and exploit vulnerabilities.
FAQs about Threat Mapping
Q: Who should be involved in creating a threat map?
A: Creating a threat map requires input from various stakeholders, including security professionals, IT personnel, business leaders, and legal representatives.
Q: How often should a threat map be updated?
A: Threat maps should be updated regularly, ideally on a quarterly or semi-annual basis, to reflect changes in the threat landscape, organizational priorities, and vulnerabilities.
Q: What are some common threats that should be considered?
A: Common threats include cyberattacks, data breaches, natural disasters, insider threats, and regulatory non-compliance.
Q: How can threat mapping be used to improve security awareness?
A: By visualizing potential threats, threat mapping can raise awareness among employees about the importance of security practices and the potential consequences of security breaches.
Tips for Effective Threat Mapping
- Focus on the most critical assets: Prioritize assets based on their value and sensitivity.
- Involve stakeholders from all relevant departments: Ensure that the threat map reflects a holistic view of the organization’s risk landscape.
- Keep the threat map updated: Regularly review and update the threat map to reflect changes in the threat landscape and organizational priorities.
- Use clear and concise language: Ensure that the threat map is easy to understand and interpret.
- Make the threat map visually appealing: Use diagrams, charts, and other visual elements to make the threat map engaging and informative.
Conclusion: A Foundation for Proactive Risk Management
Threat mapping is a valuable tool for organizations seeking to proactively identify, analyze, and mitigate risks. By providing a comprehensive and visual representation of potential threats, vulnerabilities, and attack vectors, threat mapping enables organizations to make informed decisions about their security posture and allocate resources effectively. By integrating threat mapping into their risk management processes, organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to threats and build a more resilient and secure environment.






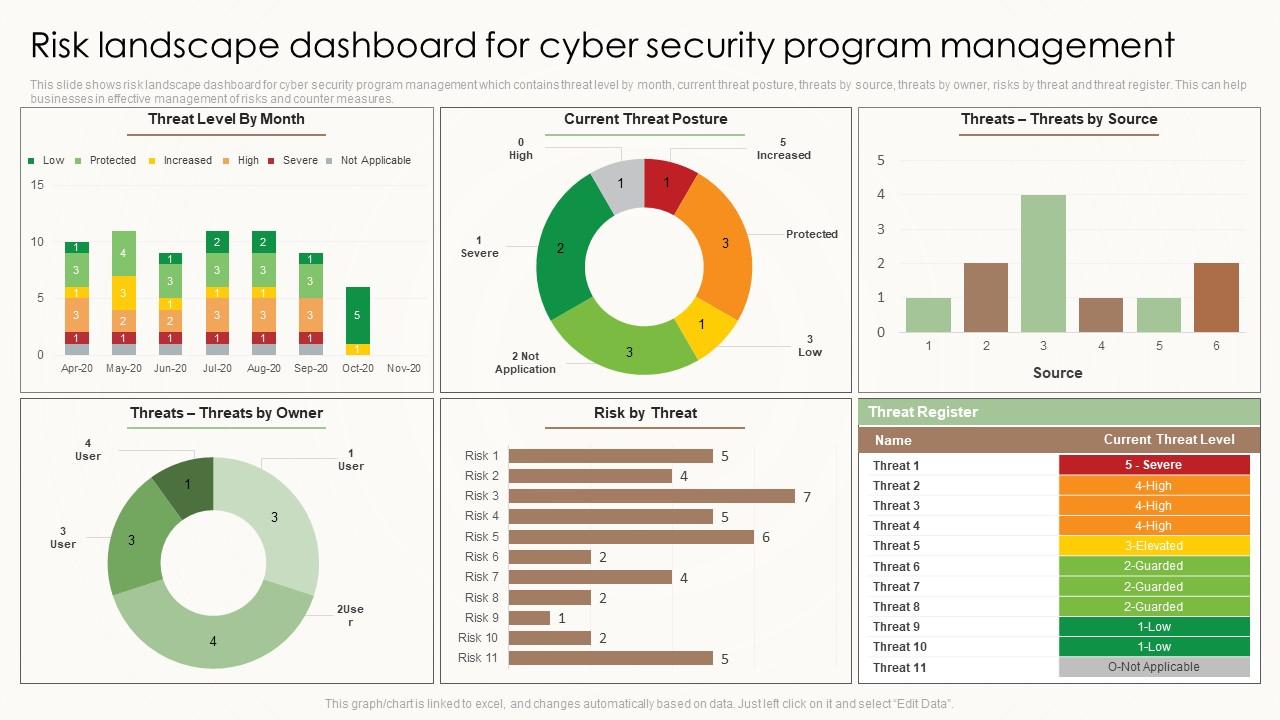
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape of Risk: A Comprehensive Guide to Threat Mapping. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!