Navigating the Red Sea: A Geographical Exploration of a Unique Body of Water
Related Articles: Navigating the Red Sea: A Geographical Exploration of a Unique Body of Water
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Red Sea: A Geographical Exploration of a Unique Body of Water. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Red Sea: A Geographical Exploration of a Unique Body of Water
The Red Sea, a vibrant ribbon of blue stretching between Africa and Asia, holds a captivating allure for explorers, historians, and travelers alike. Its name, derived from the reddish hue of the water at times due to the presence of certain algae, hints at its unique character. But where exactly is this fascinating body of water located on the map?
A Sea of Significance: Geographical Location and Surrounding Regions
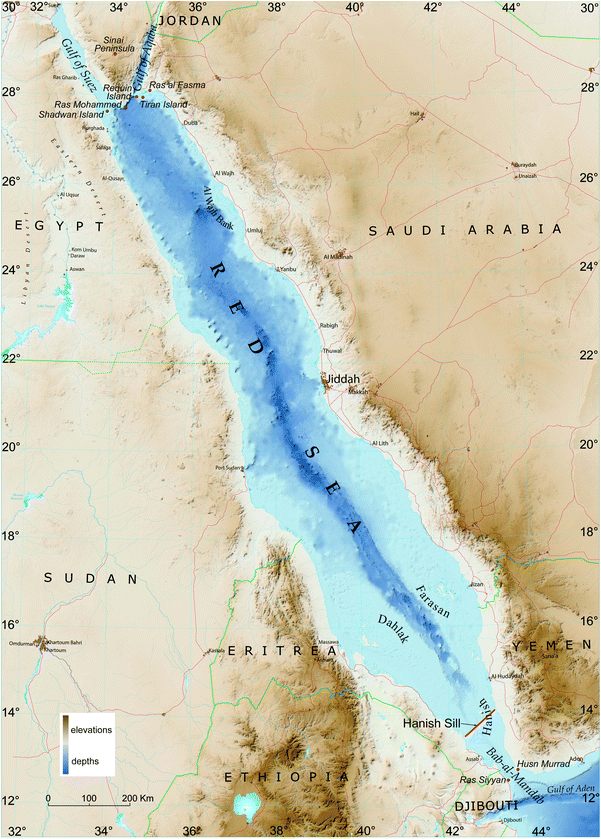
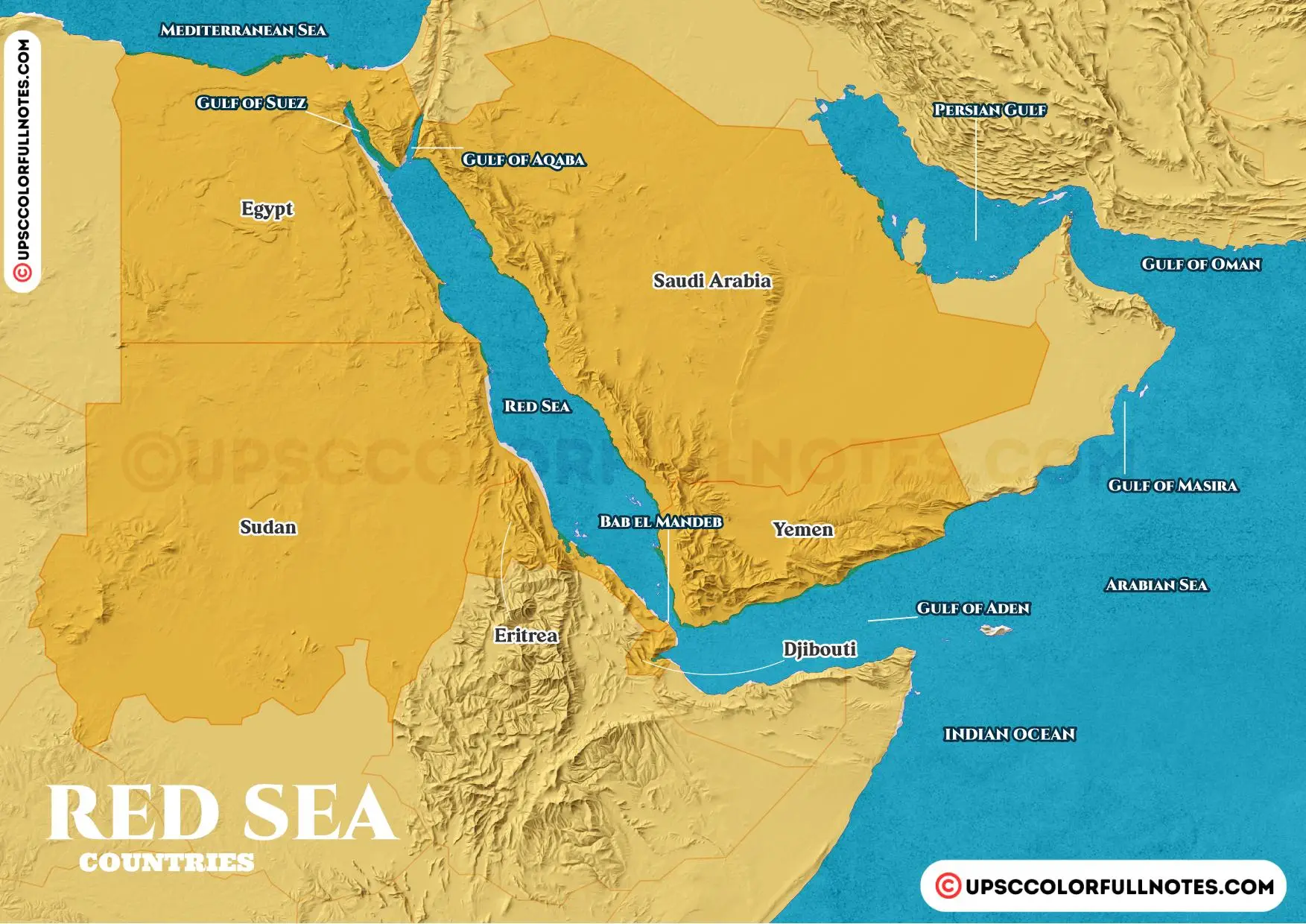
The Red Sea is a narrow, elongated sea situated in the northeastern part of Africa. It is a part of the Indian Ocean, connected to it through the Gulf of Aden at its southern end. Its northernmost point lies in the Sinai Peninsula, where it forms the Gulf of Suez, a vital waterway linking the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea.
The Red Sea is bordered by several countries, each contributing to its unique cultural and geographical tapestry:
- On the African side: Egypt, Sudan, Eritrea, Djibouti, and Somalia.
- On the Asian side: Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Israel (through the Gulf of Aqaba).
Understanding the Red Sea’s Formation and Geological Significance
The Red Sea’s formation is a fascinating testament to the dynamic nature of the Earth’s crust. It is a rift valley, a geological feature created by the separation of tectonic plates. The African and Arabian plates are slowly moving apart, creating a gap that is gradually widening. This separation has led to the formation of the Red Sea, a unique geological feature that continues to evolve.
The Red Sea’s geological history is not merely a matter of scientific curiosity; it holds immense economic and strategic significance. The region is rich in natural resources, including oil and gas deposits, and the Red Sea is a crucial shipping route connecting East and West.
A World of Marine Wonders: Exploring the Red Sea’s Diverse Ecosystem
The Red Sea’s unique geological formation has resulted in a vibrant and diverse marine ecosystem. Its warm, clear waters are home to a remarkable array of coral reefs, teeming with life. The coral reefs are a haven for over 1,200 species of fish, hundreds of coral species, and numerous other marine organisms.
The Red Sea’s diverse ecosystem is a testament to its isolation and its unique environmental conditions. The high salinity, warm temperatures, and limited freshwater input create a challenging environment for marine life. Yet, the Red Sea’s inhabitants have adapted remarkably, showcasing a vibrant tapestry of life.
Navigating the Red Sea: Historical Significance and Modern-Day Importance
The Red Sea has played a crucial role in human history for millennia. Its strategic location has made it a vital trade route connecting Africa, Asia, and Europe. Ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans, utilized the Red Sea for trade and exploration.
In modern times, the Red Sea remains a vital shipping route, connecting the Suez Canal to the Indian Ocean. This waterway provides a crucial link for global trade, facilitating the movement of goods and resources between continents.
The Red Sea: A Tourist Destination and a Fragile Ecosystem
The Red Sea’s natural beauty and diverse marine life have made it a popular destination for tourists worldwide. Its crystal-clear waters, vibrant coral reefs, and rich marine life offer a breathtaking underwater experience. Diving and snorkeling are popular activities, allowing visitors to explore the wonders of the Red Sea’s ecosystem.
However, the Red Sea’s fragile ecosystem faces threats from pollution, overfishing, and climate change. Rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification pose significant challenges to the health of coral reefs, impacting the entire marine ecosystem.
FAQs: Exploring the Red Sea’s Mysteries
Q: What is the average depth of the Red Sea?
A: The average depth of the Red Sea is approximately 490 meters (1,608 feet). However, it reaches depths of over 2,200 meters (7,218 feet) in some areas.
Q: What is the Red Sea’s temperature range?
A: The Red Sea’s temperature varies depending on the season and location. It generally ranges from 20°C (68°F) in the winter to 30°C (86°F) in the summer.
Q: What are the main threats to the Red Sea’s ecosystem?
A: The Red Sea’s ecosystem faces threats from pollution, overfishing, and climate change. Rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification pose significant challenges to the health of coral reefs.
Q: What are some of the unique features of the Red Sea?
A: The Red Sea is known for its high salinity, warm temperatures, and limited freshwater input. It is also home to a unique and diverse marine ecosystem, including over 1,200 species of fish and hundreds of coral species.
Q: What are some of the best places to visit in the Red Sea region?
A: Popular tourist destinations in the Red Sea region include Hurghada, Sharm El-Sheikh, and Dahab in Egypt; Aqaba in Jordan; and Jeddah and Yanbu in Saudi Arabia.
Tips for Exploring the Red Sea:
- Respect the environment: Avoid touching or damaging coral reefs and marine life.
- Choose responsible tourism operators: Opt for companies that prioritize sustainable practices and environmental conservation.
- Learn about the local culture: Respect local customs and traditions.
- Be aware of potential hazards: Be cautious of strong currents and marine life.
- Plan your trip in advance: Book accommodations and activities in advance, especially during peak season.
Conclusion: A Sea of Wonders and Challenges
The Red Sea, a geographical marvel and a vibrant ecosystem, holds a unique place in the world’s map. Its geological significance, its diverse marine life, and its historical importance continue to attract explorers, scientists, and travelers alike. However, the Red Sea faces significant challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change. Sustainable tourism and responsible environmental practices are crucial to preserving this remarkable body of water for future generations. By understanding the Red Sea’s unique characteristics and the challenges it faces, we can contribute to its preservation and continue to marvel at its beauty and significance for years to come.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Red Sea: A Geographical Exploration of a Unique Body of Water. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!