Navigating the Tapestry of Germany: A Guide to its Regions
Related Articles: Navigating the Tapestry of Germany: A Guide to its Regions
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Tapestry of Germany: A Guide to its Regions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Tapestry of Germany: A Guide to its Regions
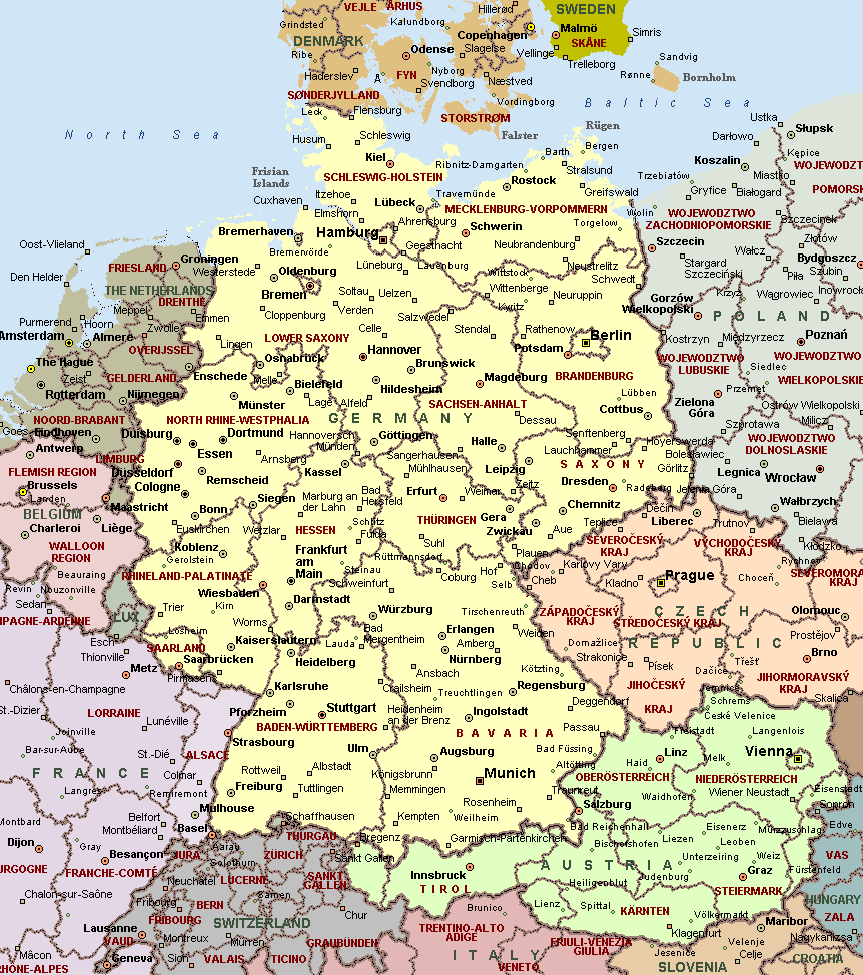
Germany, a nation of diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant culture, is often presented as a unified entity. However, a deeper understanding of the country reveals a mosaic of distinct regions, each with its unique character, traditions, and identity. Exploring these regions through a map provides a fascinating window into the country’s intricate tapestry.
A Framework for Understanding:
The map of German regions, while not an official administrative division, serves as a valuable tool for understanding the country’s geographical, cultural, and historical nuances. It broadly categorizes Germany into 16 states (Bundesländer), further grouped into larger regions based on shared characteristics such as:
- Geography: The North German Plain, the Central German Uplands, the Alps, and the Rhine Valley are all distinct geographical regions with their own landscapes, climates, and resources.
- History: Regions like Bavaria, Saxony, and Prussia have unique historical narratives, reflected in their architecture, traditions, and local dialects.
- Culture: From the beer gardens of Bavaria to the Hanseatic cities of the North, each region boasts a distinctive cultural identity, shaped by its history, traditions, and local customs.
Delving Deeper into the Regions:
Northern Germany:
- North German Plain: This vast, flat region stretches from the North Sea to the Baltic Sea, encompassing the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Hamburg, Bremen, and parts of Lower Saxony. Known for its fertile land, sandy beaches, and historic Hanseatic cities, this region boasts a maritime culture and a strong agricultural tradition.
- Lower Saxony: Located in the heart of Northern Germany, Lower Saxony is a diverse region encompassing the Lüneburg Heath, the Harz Mountains, and the North Sea coast. It is renowned for its picturesque landscapes, historic castles, and vibrant cities like Hanover and Braunschweig.
Central Germany:
- Central German Uplands: This region encompasses the states of Saxony, Thuringia, and Saxony-Anhalt. Characterized by rolling hills, forests, and historic cities, it is known for its rich cultural heritage, including the famed Romantic Road and the Bauhaus movement.
- Rhineland: Located along the Rhine River, this region comprises parts of North Rhine-Westphalia, Rhineland-Palatinate, and Hesse. It is renowned for its vineyards, historic castles, and bustling cities like Cologne, Bonn, and Frankfurt.
- Hesse: Situated in the heart of Germany, Hesse is a land of contrasts, featuring the rolling hills of the Taunus Mountains, the historic city of Frankfurt, and the picturesque Rhine Valley.
Southern Germany:
- Bavaria: The largest and most populous state in Germany, Bavaria is known for its stunning Alps, picturesque lakes, and traditional Bavarian culture. Munich, its capital, is renowned for its beer gardens, museums, and the Oktoberfest.
- Baden-Württemberg: This region in southwest Germany is renowned for its picturesque Black Forest, its automotive industry, and its vibrant cities like Stuttgart, Karlsruhe, and Freiburg.
- Swabia: A cultural region within Baden-Württemberg, Swabia is known for its traditional customs, its dialect, and its strong sense of regional identity.
Exploring the Benefits:
Understanding the regional map of Germany provides numerous benefits:
- Enhanced Travel Planning: By understanding the distinct characteristics of each region, travelers can tailor their itineraries to their interests, whether it be exploring the Alps, sampling local wines, or visiting historic castles.
- Cultural Appreciation: The map offers a framework for appreciating the diverse cultural tapestry of Germany, from traditional Bavarian folk music to the Bauhaus architecture of the Central German Uplands.
- Historical Context: By mapping the historical development of different regions, one can gain insights into the formation of modern Germany, its political landscape, and its societal values.
- Economic Understanding: The map highlights the economic strengths and weaknesses of different regions, revealing patterns of industrial development, agricultural production, and tourism.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are the official administrative divisions of Germany?
Germany is divided into 16 states (Bundesländer), each with its own government and parliament.
2. Are the regions on the map the same as the Bundesländer?
While the map broadly reflects the Bundesländer, it also groups them into larger regions based on shared characteristics, providing a more nuanced understanding of Germany’s diversity.
3. What are the main differences between the regions?
The regions differ in their geography, history, culture, and economic strengths. For example, Bavaria is known for its Alps and traditional culture, while the North German Plain is characterized by its flat landscape and maritime heritage.
4. How can I learn more about a specific region?
There are numerous resources available online and in libraries, including travel guides, historical accounts, and cultural publications.
5. Is there a specific region that is best for me to visit?
The best region for you to visit depends on your interests. If you enjoy hiking and outdoor activities, the Alps of Bavaria might be ideal. If you are interested in history and culture, the historic cities of the Central German Uplands might be more appealing.
Tips for Exploring German Regions:
- Embrace Local Culture: Immerse yourself in the local culture by trying regional cuisine, attending local festivals, and learning a few phrases in the local dialect.
- Explore Beyond the Major Cities: While major cities like Berlin, Munich, and Hamburg offer a wealth of attractions, venturing into smaller towns and villages can reveal hidden gems and provide a more authentic experience.
- Utilize Public Transportation: Germany boasts an extensive and efficient public transportation system, making it easy to explore different regions without relying on a car.
- Research Local Events: Many regions host festivals, markets, and other events throughout the year, offering unique opportunities to experience local culture and traditions.
Conclusion:
The map of German regions serves as a powerful tool for understanding the country’s multifaceted identity. It reveals a tapestry of diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant cultures, each contributing to the unique character of Germany as a whole. By exploring these regions, one gains a deeper appreciation for the country’s complexity and its enduring appeal as a destination for travel, study, and cultural exchange.


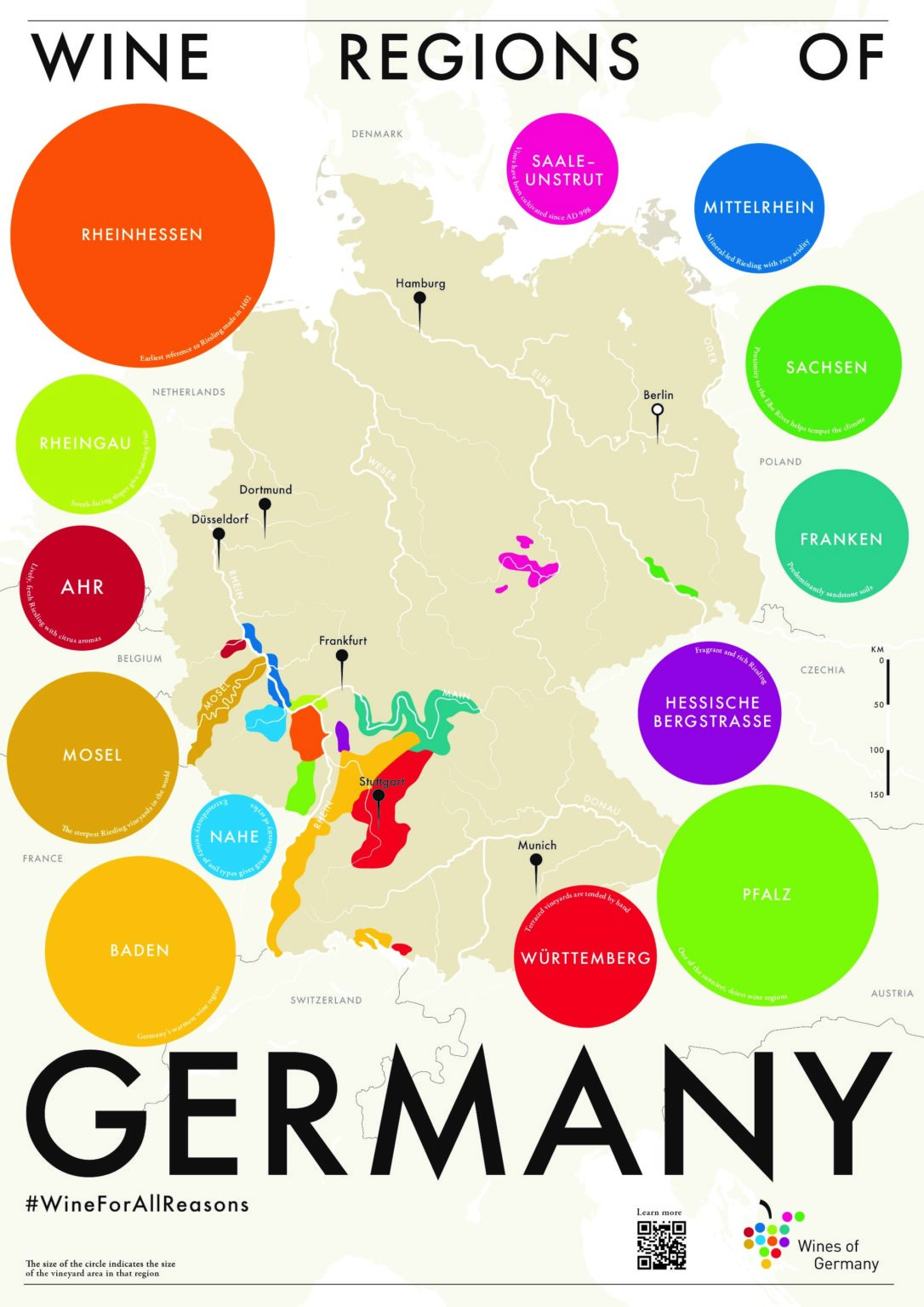

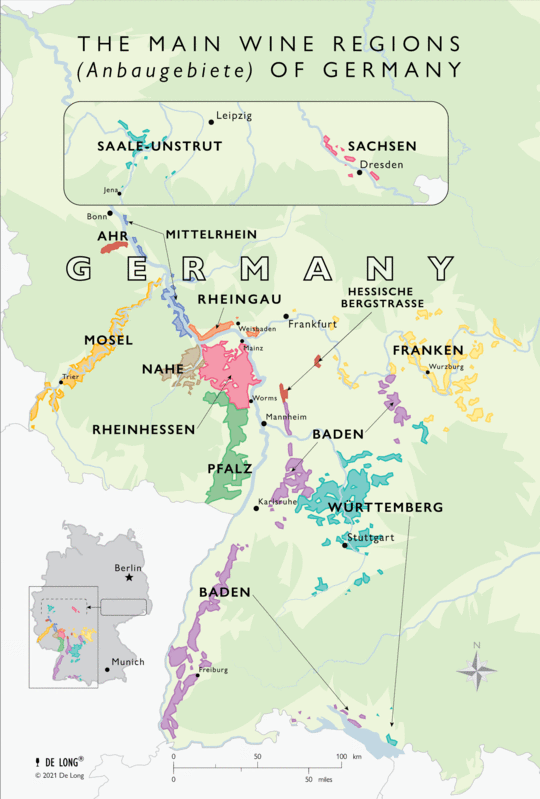



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Tapestry of Germany: A Guide to its Regions. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!