The Appalachian Mountains: A Geographical and Cultural Tapestry
Related Articles: The Appalachian Mountains: A Geographical and Cultural Tapestry
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Appalachian Mountains: A Geographical and Cultural Tapestry. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Appalachian Mountains: A Geographical and Cultural Tapestry
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-573798635-58b59b293df78cdcd8712fb2.jpg)
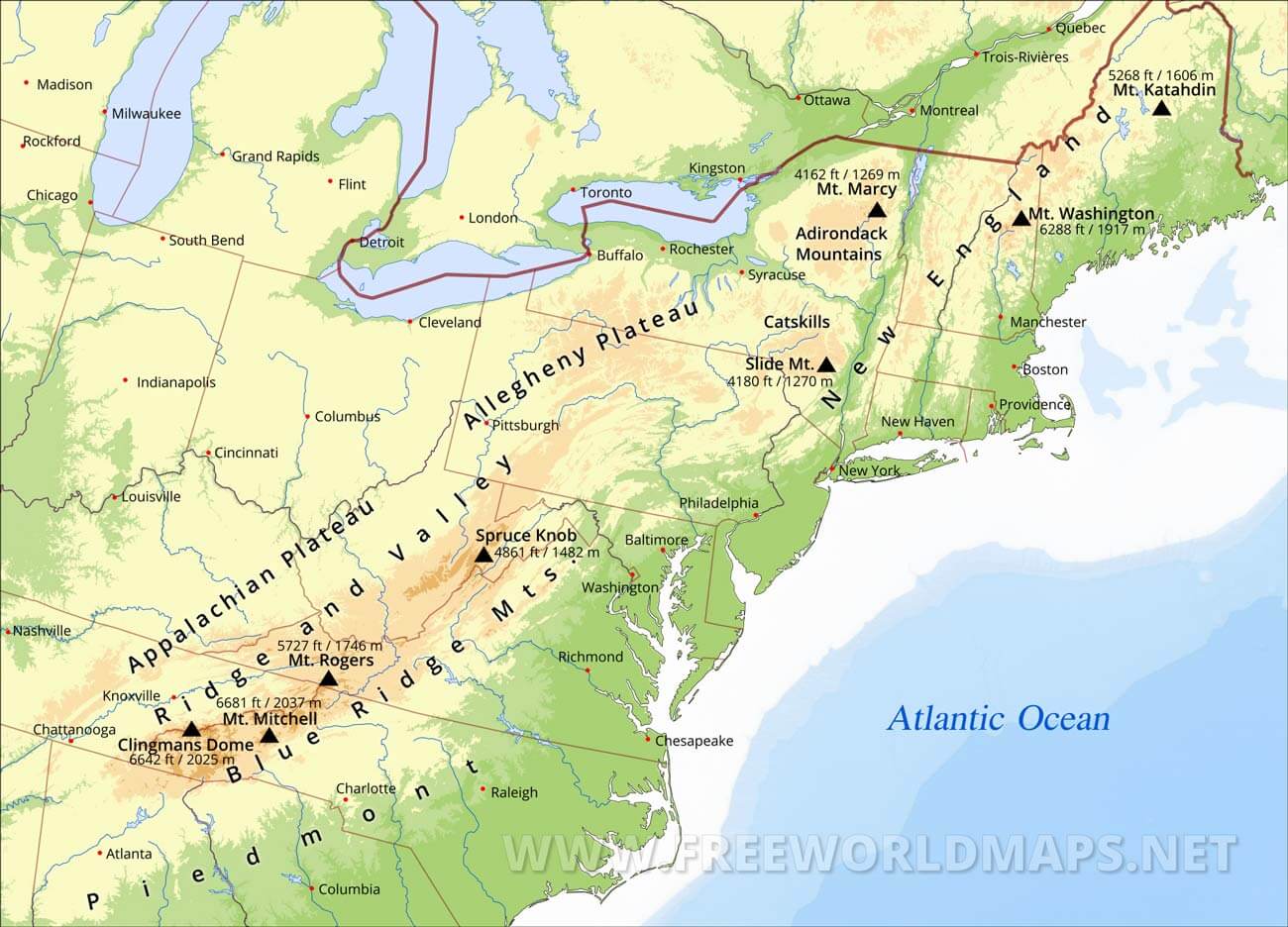
The Appalachian Mountains, a majestic range stretching over 1,500 miles from the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador to Alabama in the southeastern United States, are a defining feature of the eastern North American landscape. This ancient mountain chain, formed over millions of years, serves as a geological backbone, influencing the region’s climate, ecosystems, and human history.
Locating the Appalachians on a Map:
To understand the vastness and significance of the Appalachians, it’s crucial to visualize their location on a map. They run in a southwest-to-northeast direction, forming a distinct arc across the eastern United States.
-
Northern Appalachian Plateau: This region, characterized by rolling hills and plateaus, encompasses portions of New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, West Virginia, and Kentucky. It’s known for its rich coal deposits and the dramatic landscapes carved by glaciers during the last Ice Age.
-
Central Appalachians: The heart of the range, this region is dominated by the Blue Ridge Mountains, known for their high peaks and stunning vistas. It includes parts of Virginia, North Carolina, and Tennessee, and is home to iconic peaks like Mount Mitchell, the highest point east of the Mississippi River.
-
Southern Appalachians: This region, encompassing portions of Georgia, Alabama, and North Carolina, features the Great Smoky Mountains, renowned for their biodiversity and the iconic Great Smoky Mountains National Park. This area is also known for its unique cultural heritage, exemplified by the Appalachian folk music and storytelling traditions.
Beyond the Map: Unveiling the Importance of the Appalachians
The Appalachian Mountains are more than just a geographical feature; they are a cultural, economic, and ecological force shaping the region and its inhabitants.
1. A Cradle of Biodiversity:
The diverse terrain and elevations of the Appalachians have fostered a remarkable array of ecosystems, supporting a vast and varied biodiversity. From the dense forests of the Blue Ridge to the high-altitude meadows of the Great Smokies, the mountains provide habitat for countless species of plants, animals, and fungi. This rich biodiversity is not only essential for the health of the ecosystem but also for scientific research and conservation efforts.
2. A Source of Natural Resources:
The Appalachians have been a vital source of natural resources for centuries. The region’s rich coal deposits fueled the Industrial Revolution and continue to play a significant role in the energy sector. Forests provide timber and other products, while rivers and streams offer hydroelectric power and recreational opportunities. However, the extraction of these resources has also come at a cost, leading to environmental challenges and debates about sustainability.
3. A Cultural Tapestry:
The Appalachian Mountains have shaped the culture and identity of the people who live there. The region’s distinctive folk music, storytelling traditions, and crafts reflect a rich cultural heritage passed down through generations. The Appalachian way of life, characterized by resilience, self-reliance, and a strong sense of community, is deeply intertwined with the landscape and its challenges.
4. A Landscape for Recreation and Tourism:
The Appalachians offer a diverse range of recreational opportunities, attracting outdoor enthusiasts from around the world. Hiking, backpacking, camping, fishing, and whitewater rafting are just a few of the activities enjoyed in the mountains. The region’s scenic beauty, diverse ecosystems, and historic sites also draw millions of tourists each year, contributing significantly to the local economy.
5. A Landscape of Challenges:
Despite their beauty and importance, the Appalachians also face significant challenges. Poverty, unemployment, and a lack of access to healthcare are persistent issues in many Appalachian communities. Environmental degradation, caused by mining, logging, and pollution, threatens the region’s ecosystems and the health of its inhabitants.
FAQs:
-
What is the highest peak in the Appalachian Mountains? Mount Mitchell in North Carolina, with an elevation of 6,684 feet, is the highest point east of the Mississippi River.
-
What are the major rivers that flow through the Appalachian Mountains? The major rivers flowing through the Appalachians include the Ohio River, the Tennessee River, the Potomac River, the Susquehanna River, and the James River.
-
What are some of the most popular national parks in the Appalachian Mountains? The most popular national parks in the Appalachians include Great Smoky Mountains National Park, Shenandoah National Park, and Mammoth Cave National Park.
-
What are some of the unique plant and animal species found in the Appalachian Mountains? The Appalachians are home to a variety of unique species, including the red spruce, the black bear, the white-tailed deer, and the Appalachian brook trout.
-
What are some of the cultural traditions associated with the Appalachian Mountains? Appalachian culture is known for its folk music, storytelling, crafts, and a strong sense of community.
Tips for Exploring the Appalachians:
-
Plan your trip in advance: Research the different regions and choose the activities that best suit your interests.
-
Pack for all types of weather: The Appalachians can experience a wide range of temperatures and weather conditions.
-
Be aware of the dangers of hiking: Always hike with a partner, let someone know your itinerary, and be prepared for emergencies.
-
Respect the environment: Leave no trace of your visit and be mindful of the delicate ecosystems.
-
Engage with the local culture: Learn about the history and traditions of the Appalachian people and support local businesses.
Conclusion:
The Appalachian Mountains are a testament to the power of nature and the resilience of the human spirit. From their majestic peaks to their diverse ecosystems, the mountains offer a rich tapestry of experiences, challenging us to understand the delicate balance between human activity and the natural world. By recognizing the importance of the Appalachians and addressing the challenges they face, we can ensure that this iconic landscape continues to inspire and enrich generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Appalachian Mountains: A Geographical and Cultural Tapestry. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!