The Ottoman Empire in the Great War: A Geographical Perspective
Related Articles: The Ottoman Empire in the Great War: A Geographical Perspective
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Ottoman Empire in the Great War: A Geographical Perspective. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Ottoman Empire in the Great War: A Geographical Perspective

The Ottoman Empire, a sprawling and diverse entity that spanned three continents, entered World War I in 1914, marking a pivotal moment in its long and complex history. The war’s impact on the empire’s geography was profound, reshaping its borders, altering its internal dynamics, and ultimately contributing to its demise. Understanding the Ottoman Empire’s geographical context during the war provides crucial insights into the conflict’s unfolding, its consequences, and the legacy it left behind.
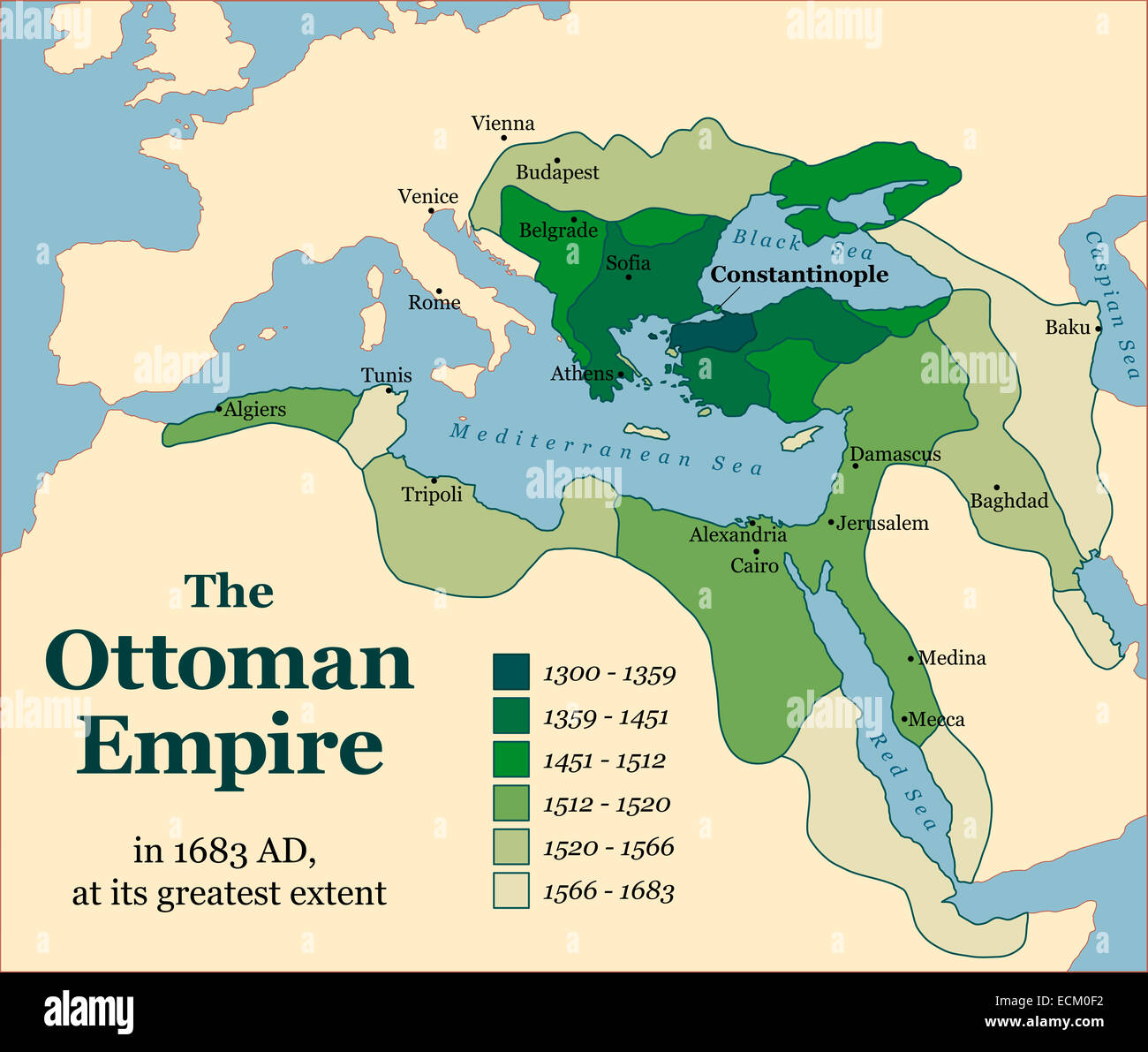
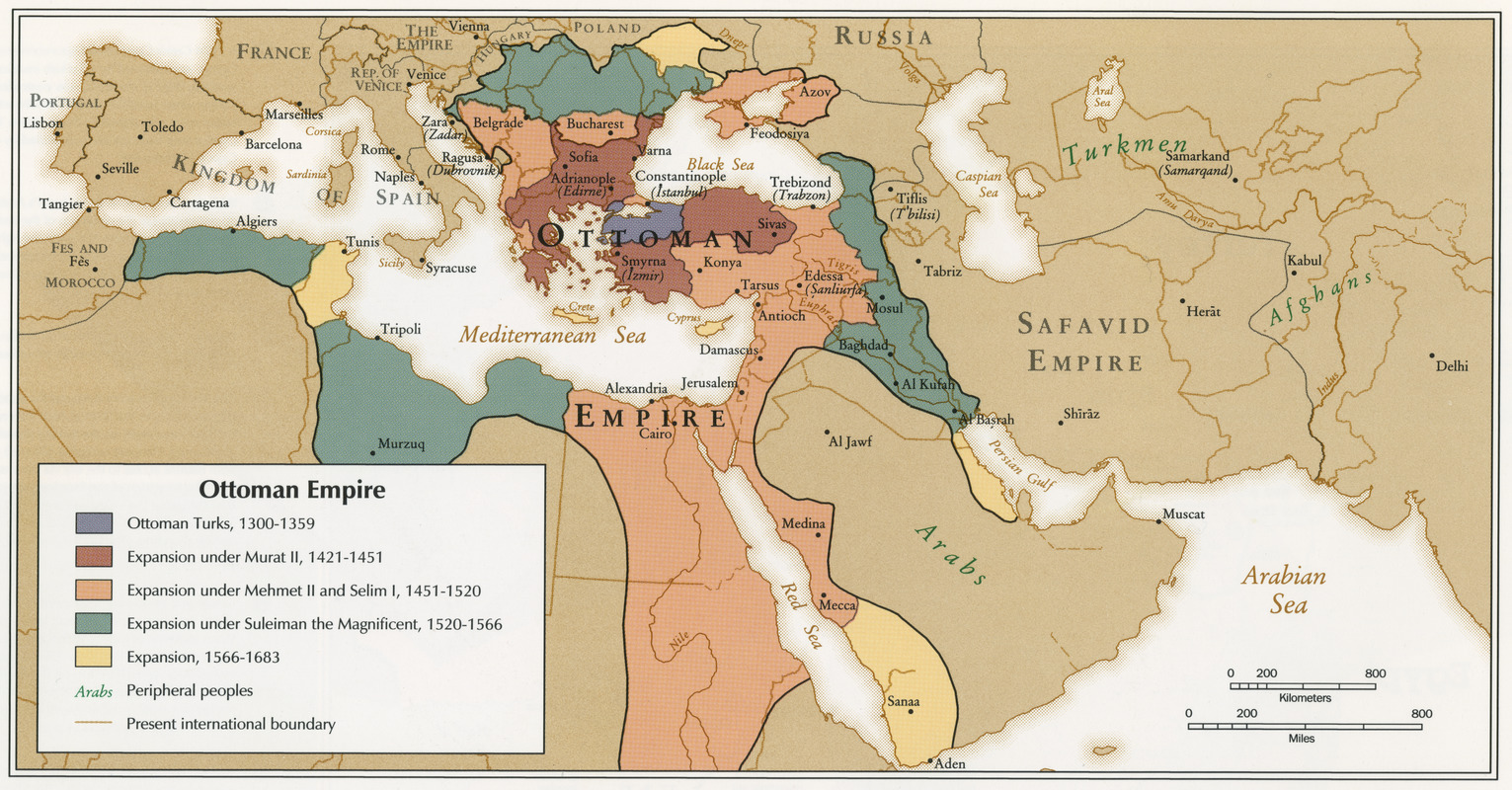
The Ottoman Empire in 1914: A Vast and Fragile State
At the outbreak of World War I, the Ottoman Empire was a vast and geographically diverse entity, encompassing the territories of modern-day Turkey, Greece, Bulgaria, Romania, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Iraq, Kuwait, parts of Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Yemen. Its vastness, however, was a double-edged sword. While providing access to strategic locations and diverse resources, it also presented immense challenges in terms of administration, communication, and defense. The empire’s internal structure was characterized by a complex mix of ethnicities, religions, and languages, often leading to tensions and conflicts.
Strategic Location and Geopolitical Significance
The Ottoman Empire’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa made it a critical player in global power politics. Its control over the Dardanelles Strait, the sole passage connecting the Black Sea to the Mediterranean, gave it immense power to control maritime traffic and influence regional affairs. Furthermore, the empire’s vast landmass provided access to valuable resources, including agricultural products, minerals, and manpower. This strategic significance made the Ottomans a coveted ally for both the Central Powers and the Entente.
The Entanglement in the Great War
The Ottoman Empire’s entry into World War I on the side of the Central Powers was a consequence of a complex interplay of factors. The empire’s leadership, under the rule of Sultan Mehmed V, felt increasingly threatened by the growing influence of Russia in the Balkans. The perceived threat to its territorial integrity, coupled with the perceived threat to its Muslim populations in the region, prompted the Ottomans to seek an alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary.
The War’s Impact on the Ottoman Empire’s Geography
The Ottoman Empire’s involvement in the Great War had a profound impact on its geography, leading to significant changes in its borders, internal dynamics, and overall territorial integrity.
1. The Front Lines and the War’s Devastation:
The Ottoman Empire’s geographic position placed it on the front lines of the war. The Gallipoli Campaign, the Caucasus Campaign, and the Mesopotamian Campaign were all fought on Ottoman soil, causing widespread devastation and displacement of populations. The war’s destructive forces decimated infrastructure, disrupted trade routes, and caused severe economic hardship.
2. The Rise of Nationalism and Ethnic Tensions:
The war’s impact on the Ottoman Empire’s geography was exacerbated by the rise of nationalist movements among its diverse ethnic groups. The war provided a platform for these movements to gain momentum, leading to demands for autonomy and independence. These movements, often fueled by wartime grievances and the promise of self-determination, further destabilized the empire’s internal structure.
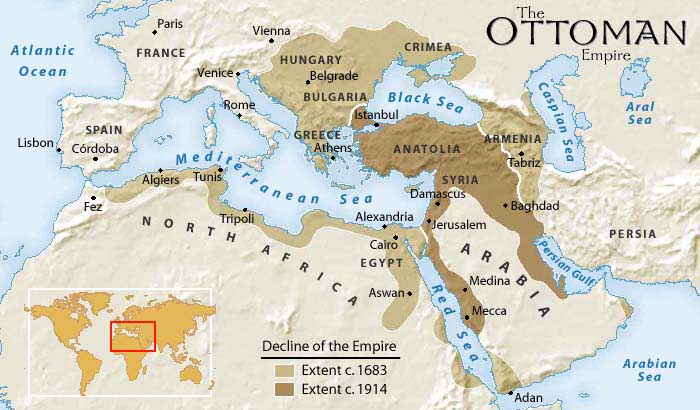
3. The Treaty of Lausanne and the Post-War Realignment:
The Ottoman Empire’s defeat in World War I led to the Treaty of Lausanne in 1923, which formally ended the war and resulted in the empire’s dissolution. The treaty significantly reduced Ottoman territory, carving out new nation-states from its former possessions. The empire’s defeat and the subsequent redrawing of its borders had a profound impact on the region’s demographics and geopolitical landscape, leading to the emergence of new states and the redrawing of ethnic and religious boundaries.
4. The Rise of Turkey and the Legacy of the Ottoman Empire:
The Ottoman Empire’s demise paved the way for the creation of the Republic of Turkey, led by Mustafa Kemal Atatürk. The new republic, founded on principles of secularism and modernization, embarked on a path of nation-building, striving to create a unified and modern Turkish state. The legacy of the Ottoman Empire, however, continued to shape the region’s political, social, and cultural landscape, influencing the development of new nations and the ongoing dynamics of regional affairs.
FAQs about the Ottoman Empire in World War I
1. Why did the Ottoman Empire join World War I?
The Ottoman Empire entered World War I on the side of the Central Powers due to a complex interplay of factors, including a perceived threat from Russia in the Balkans, a desire to protect its Muslim populations in the region, and strategic considerations related to its alliance with Germany and Austria-Hungary.
2. What were the key battles fought on Ottoman territory?
The Ottoman Empire was the site of several major battles during World War I, including the Gallipoli Campaign, the Caucasus Campaign, and the Mesopotamian Campaign. These battles resulted in significant losses for both sides, highlighting the war’s destructive impact on the empire’s geography.
3. How did the war affect the Ottoman Empire’s internal structure?
The war exacerbated existing ethnic tensions and contributed to the rise of nationalist movements within the Ottoman Empire. The war’s devastation and the promise of self-determination further destabilized the empire’s internal structure, ultimately contributing to its demise.
4. What was the Treaty of Lausanne and what were its implications?
The Treaty of Lausanne, signed in 1923, formally ended the war and resulted in the Ottoman Empire’s dissolution. The treaty significantly reduced Ottoman territory, carving out new nation-states from its former possessions, and reshaping the region’s geopolitical landscape.
5. How did the Ottoman Empire’s defeat impact the region’s demographics and geopolitical landscape?
The Ottoman Empire’s defeat led to the emergence of new nation-states, the redrawing of ethnic and religious boundaries, and the creation of new political structures. The region’s demographics and geopolitical landscape were significantly altered, shaping the political and social dynamics of the Middle East for decades to come.
Tips for Understanding the Ottoman Empire in World War I
1. Focus on the Geographic Context:
Understanding the Ottoman Empire’s vast and diverse geography is crucial for grasping the war’s impact. Maps, historical accounts, and visual representations can be valuable tools for understanding the empire’s territorial extent, internal dynamics, and strategic locations.
2. Explore the Impact on Different Regions:
The war’s impact varied across different regions of the Ottoman Empire. Examining the experiences of individual regions, such as the Balkans, the Middle East, and Anatolia, can provide a more nuanced understanding of the war’s consequences.
3. Analyze the Role of Nationalism and Ethnic Tensions:
The rise of nationalist movements and ethnic tensions played a significant role in the Ottoman Empire’s demise. Exploring these dynamics can shed light on the internal conflicts that contributed to the empire’s fragmentation and the emergence of new nation-states.
4. Consider the Long-Term Consequences:
The Ottoman Empire’s defeat in World War I had lasting consequences for the region. Examining the geopolitical and demographic changes that followed the war can provide valuable insights into the region’s contemporary political landscape.
Conclusion
The Ottoman Empire’s involvement in World War I had a profound impact on its geography, leading to significant changes in its borders, internal dynamics, and ultimately its demise. The war’s devastation, the rise of nationalism, and the subsequent treaty settlements reshaped the region’s political, social, and cultural landscape, leaving a lasting legacy that continues to shape the Middle East today. Understanding the Ottoman Empire’s geographical context during the war provides crucial insights into the conflict’s unfolding, its consequences, and the enduring impact it has had on the region’s history and development.


![The Ottoman Empire 1798 - 1923 [1590x1773] Ottoman empire, Ottomans](https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/originals/de/6b/62/de6b62455c0af32310c08ee65d0b35f2.jpg)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Ottoman Empire in the Great War: A Geographical Perspective. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!