The Political Landscape of Eastern Europe: A Shifting Mosaic
Related Articles: The Political Landscape of Eastern Europe: A Shifting Mosaic
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Political Landscape of Eastern Europe: A Shifting Mosaic. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Political Landscape of Eastern Europe: A Shifting Mosaic
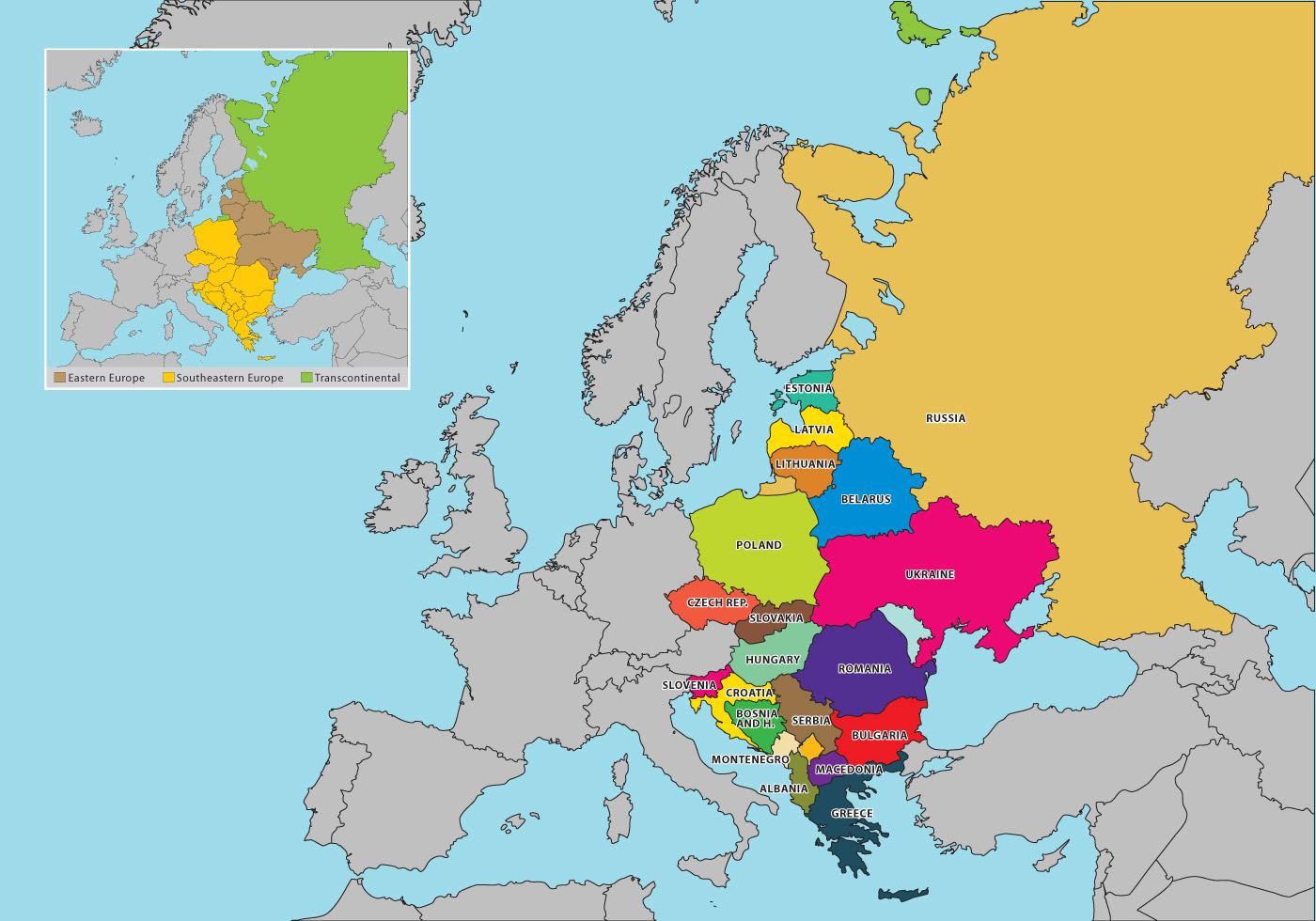
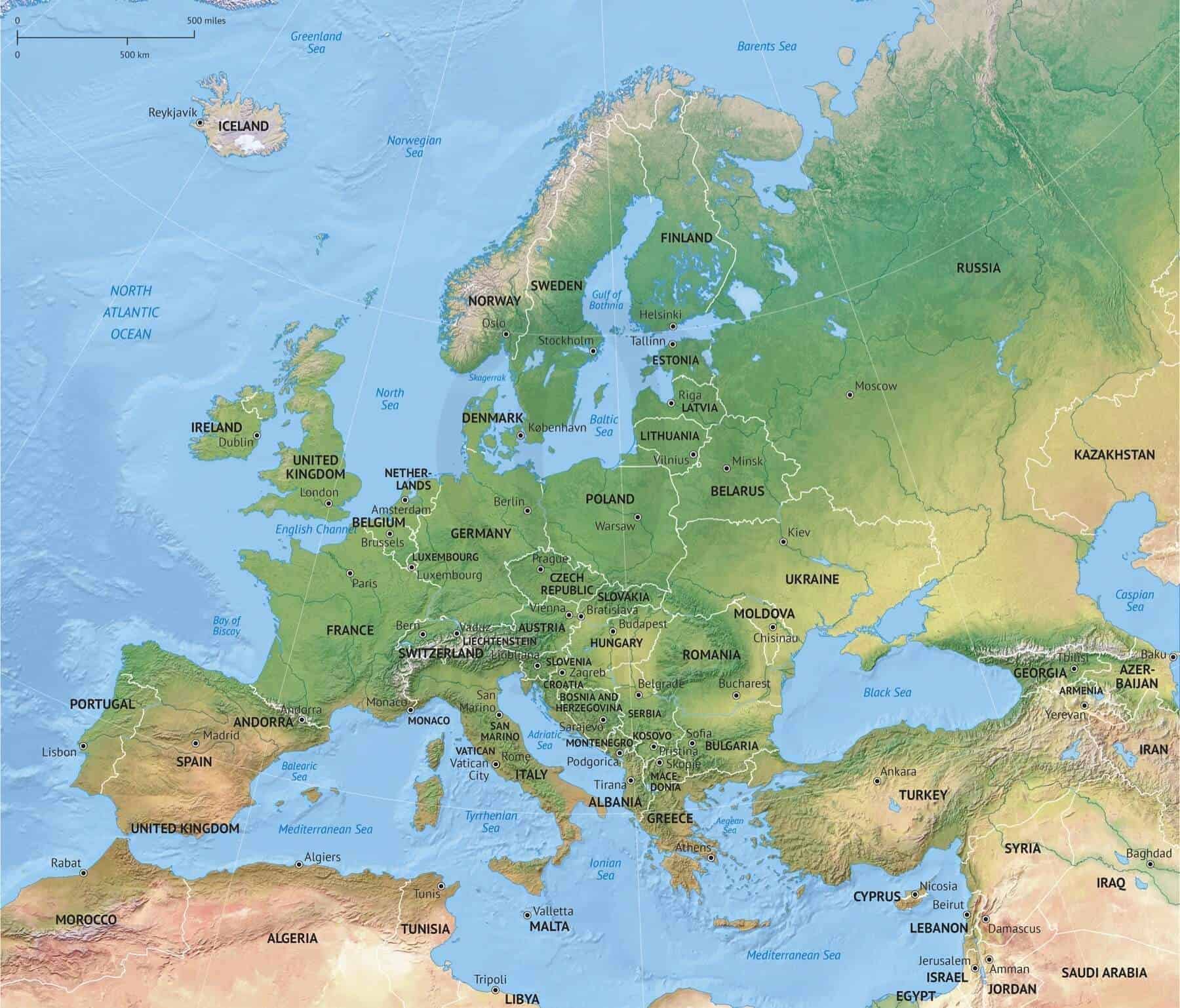
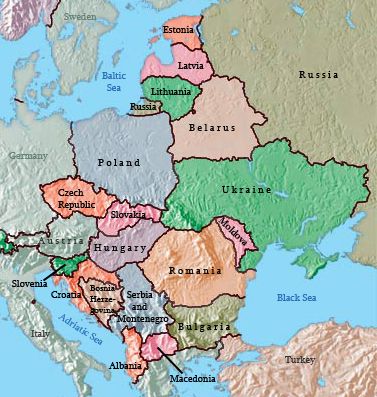
Eastern Europe, a region encompassing a diverse array of nations, presents a complex and dynamic political map. This region has witnessed significant transformations throughout history, from the fall of the Soviet Union to the rise of new democracies, each shaping its current political landscape. Understanding the political map of Eastern Europe is crucial for comprehending the region’s history, its present challenges, and its potential for future development.
A Historical Overview:
The political map of Eastern Europe has been profoundly influenced by historical events. For centuries, the region was dominated by powerful empires, including the Russian Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and the Ottoman Empire. The 20th century witnessed a period of significant upheaval, with the rise of communism, the Cold War, and the eventual collapse of the Soviet Union. The fall of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to the emergence of new independent states, dramatically altering the political map of Eastern Europe.
The Diversity of Political Systems:
Eastern Europe is characterized by a diverse range of political systems, reflecting the region’s historical and cultural complexities. While many countries have embraced democratic principles and multi-party systems, others have opted for more authoritarian models.
-
Democratic Republics: The majority of Eastern European countries are democratic republics, with parliamentary or presidential systems of government. These countries hold regular elections, uphold the rule of law, and guarantee fundamental rights and freedoms for their citizens. Examples include Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Estonia.
-
Semi-Presidential Republics: Some countries in Eastern Europe, such as Ukraine and Belarus, operate under semi-presidential systems, combining elements of parliamentary and presidential models. These systems often feature a strong president and a parliament with significant legislative powers.
-
Authoritarian Regimes: While less prevalent, some countries in Eastern Europe maintain authoritarian regimes, characterized by limited political freedoms, suppression of dissent, and centralized control. Examples include Belarus and Russia, where political power is concentrated in the hands of a single party or individual.
Challenges and Opportunities:
The political map of Eastern Europe is not static. It continues to evolve, facing a range of challenges and opportunities.
-
Economic Development: Many Eastern European countries are striving to achieve economic stability and prosperity. While some have achieved significant economic growth, others continue to face challenges such as poverty, unemployment, and corruption.
-
EU Integration: The European Union (EU) has played a significant role in shaping the political landscape of Eastern Europe. Many countries have joined the EU, seeking economic benefits, political stability, and closer ties with Western Europe. However, EU membership has also brought challenges, including economic adjustments and political pressure to align with EU standards.
-
Russia’s Influence: Russia remains a significant power in the region, wielding political and economic influence over its neighbors. This influence has been a source of tension and instability, particularly in countries like Ukraine, Georgia, and Moldova, where Russia has sought to maintain its sphere of influence.
-
Nationalism and Identity: The rise of nationalism and identity politics has also impacted the political landscape of Eastern Europe. In some countries, nationalist movements have gained traction, challenging existing political structures and promoting policies that emphasize national identity and cultural homogeneity.
The Importance of Understanding the Political Map:
Understanding the political map of Eastern Europe is crucial for several reasons:
-
International Relations: The region plays a vital role in global politics, impacting international relations, security, and trade. Understanding the political dynamics within Eastern Europe is essential for navigating complex geopolitical issues.
-
Economic Development: The region offers significant economic opportunities for investors and businesses. Understanding the political landscape is crucial for assessing investment risks and identifying potential areas for growth.
-
Human Rights and Democracy: The political map of Eastern Europe reflects the struggle for human rights and democracy. Understanding the region’s political dynamics is essential for advocating for democratic values and promoting respect for human rights.
FAQs about the Political Map of Eastern Europe:
-
What is the most common form of government in Eastern Europe?
- The majority of Eastern European countries are democratic republics with parliamentary or presidential systems of government.
-
How has the collapse of the Soviet Union impacted the political map of Eastern Europe?
- The fall of the Soviet Union led to the emergence of new independent states, dramatically altering the political map and creating a more diverse range of political systems.
-
What are some of the challenges facing Eastern European countries?
- Challenges include economic development, EU integration, Russia’s influence, and the rise of nationalism and identity politics.
-
What are some of the opportunities for Eastern European countries?
- Opportunities include economic growth, access to EU markets, and the potential for regional cooperation and integration.
-
How does the political map of Eastern Europe impact international relations?
- The region plays a vital role in global politics, impacting international relations, security, and trade. Understanding the political dynamics within Eastern Europe is essential for navigating complex geopolitical issues.
Tips for Understanding the Political Map of Eastern Europe:
- Stay informed: Follow news and analysis from reputable sources to stay up-to-date on current events and political developments.
- Study history: Understanding the historical context is crucial for comprehending the current political landscape.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from a variety of sources, including academics, journalists, and political analysts.
- Consider the economic context: Economic factors play a significant role in shaping the political map of Eastern Europe.
- Recognize the influence of external actors: External actors, such as Russia and the EU, exert considerable influence on the region’s political dynamics.
Conclusion:
The political map of Eastern Europe is a dynamic and complex landscape, reflecting a region in constant flux. Understanding the diverse political systems, the challenges and opportunities, and the historical context is crucial for comprehending the region’s present and future. By staying informed and engaging with diverse perspectives, we can gain a deeper understanding of this vital region and its role in shaping the world.

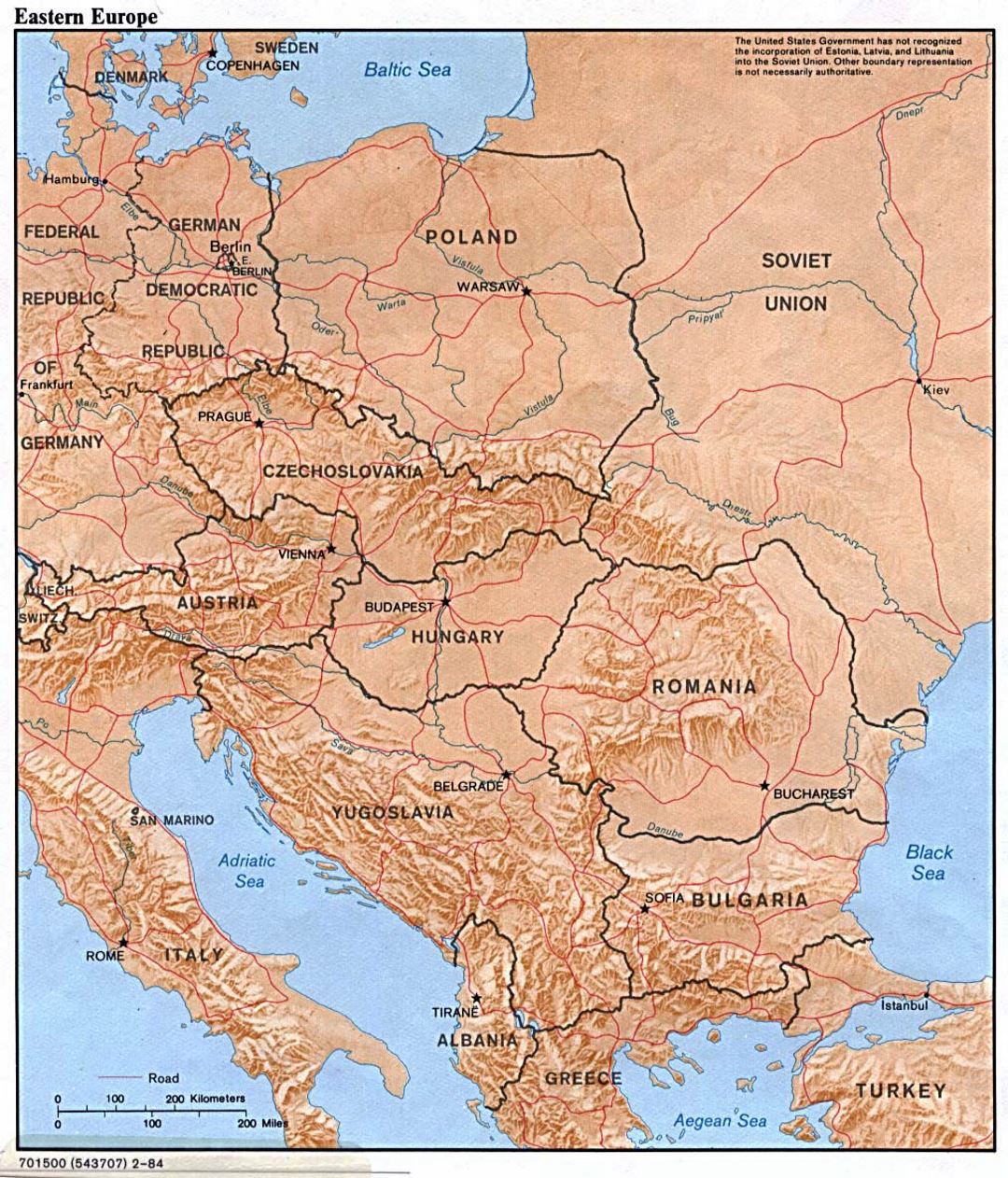

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Political Landscape of Eastern Europe: A Shifting Mosaic. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!