The Power of Place: Understanding Contact on Map and its Applications
Related Articles: The Power of Place: Understanding Contact on Map and its Applications
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Power of Place: Understanding Contact on Map and its Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Power of Place: Understanding Contact on Map and its Applications

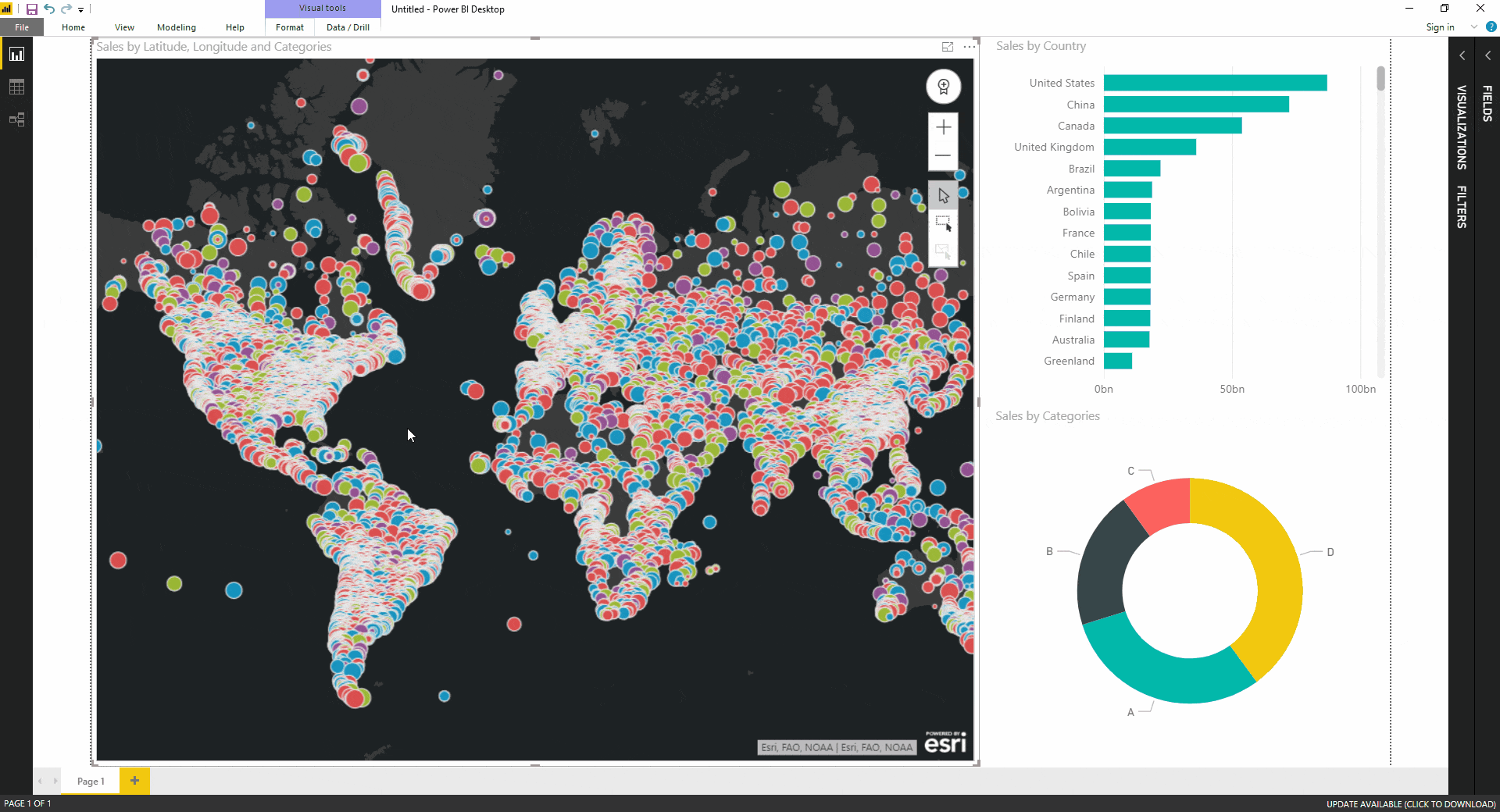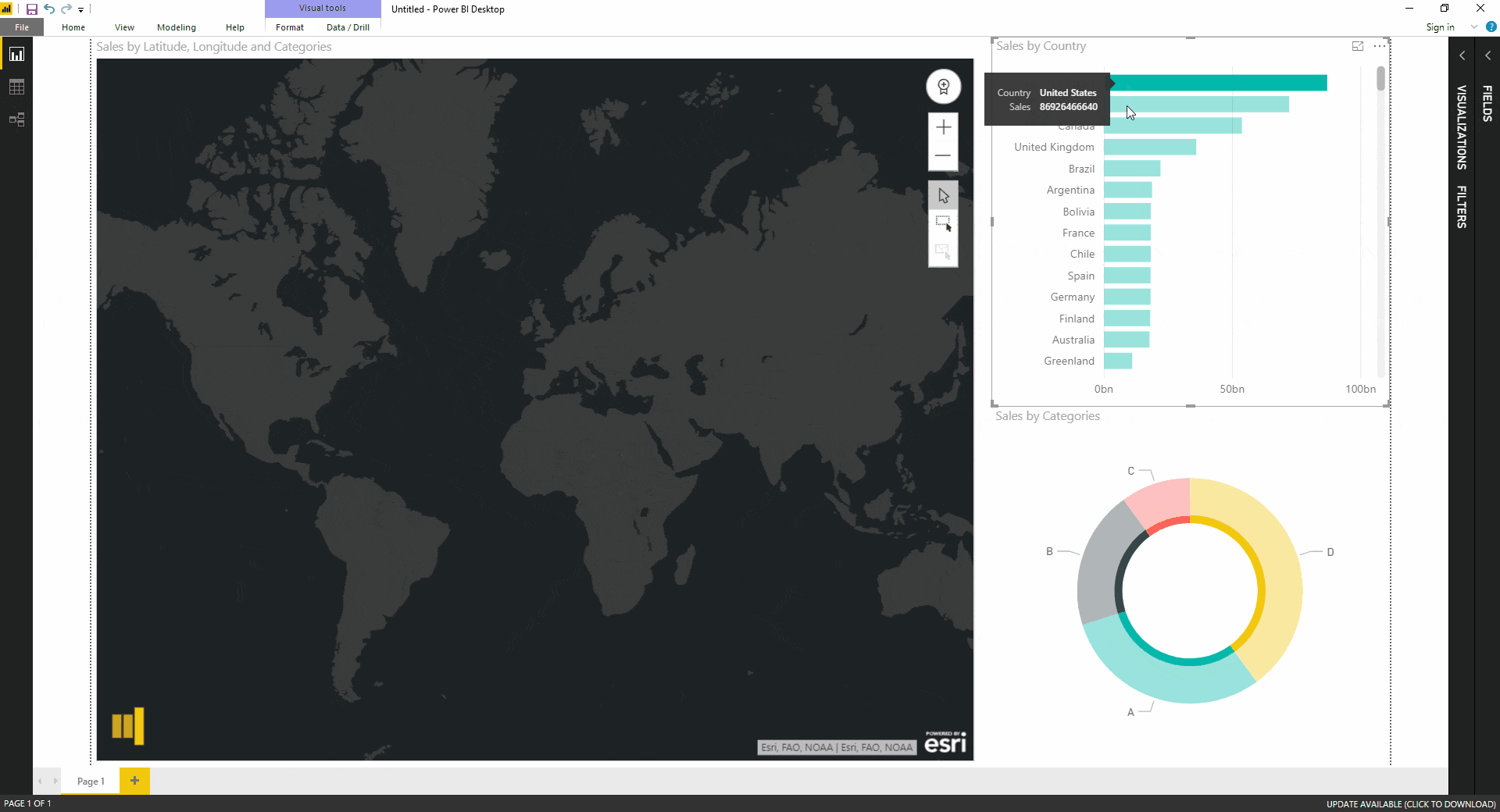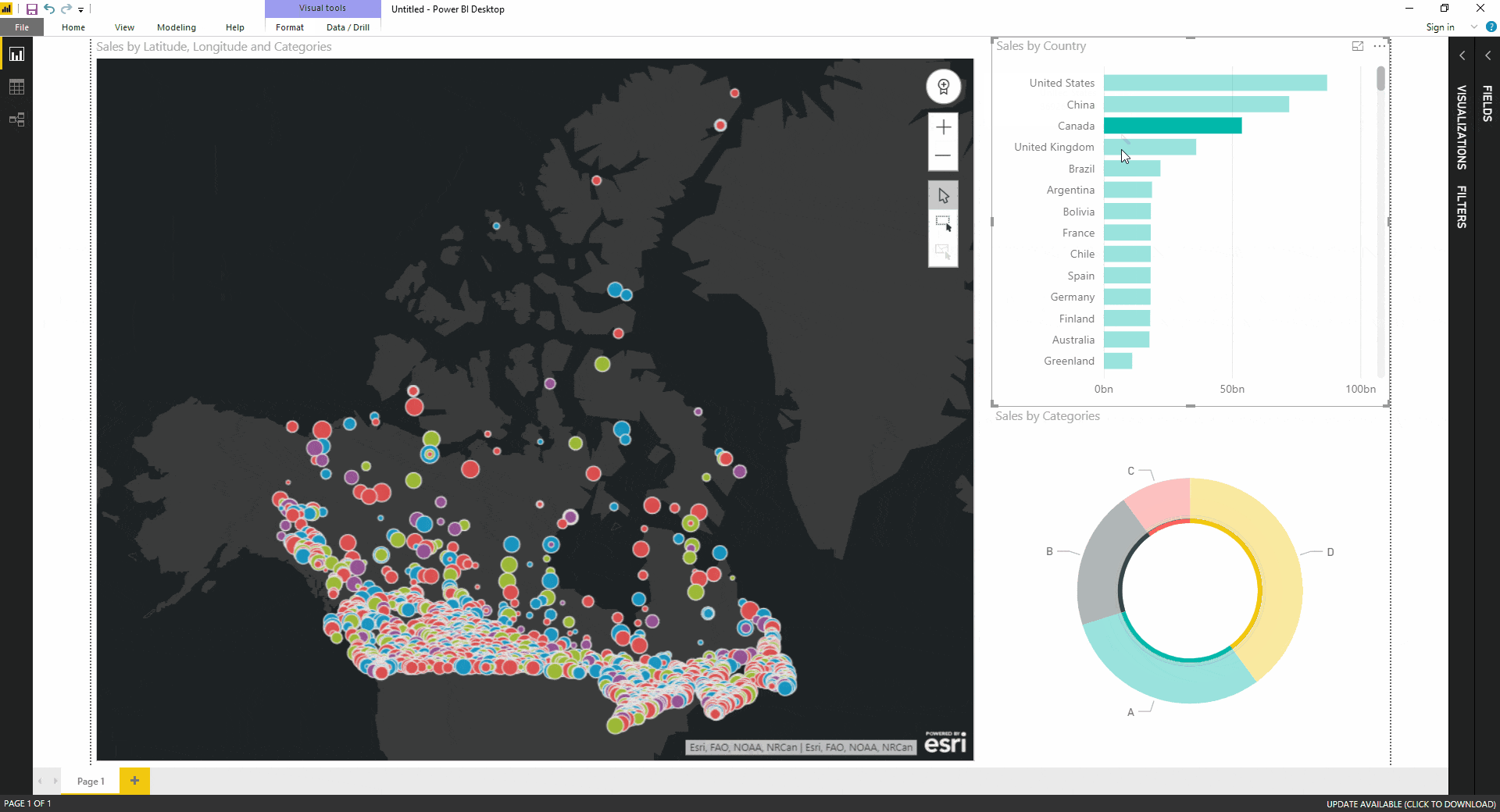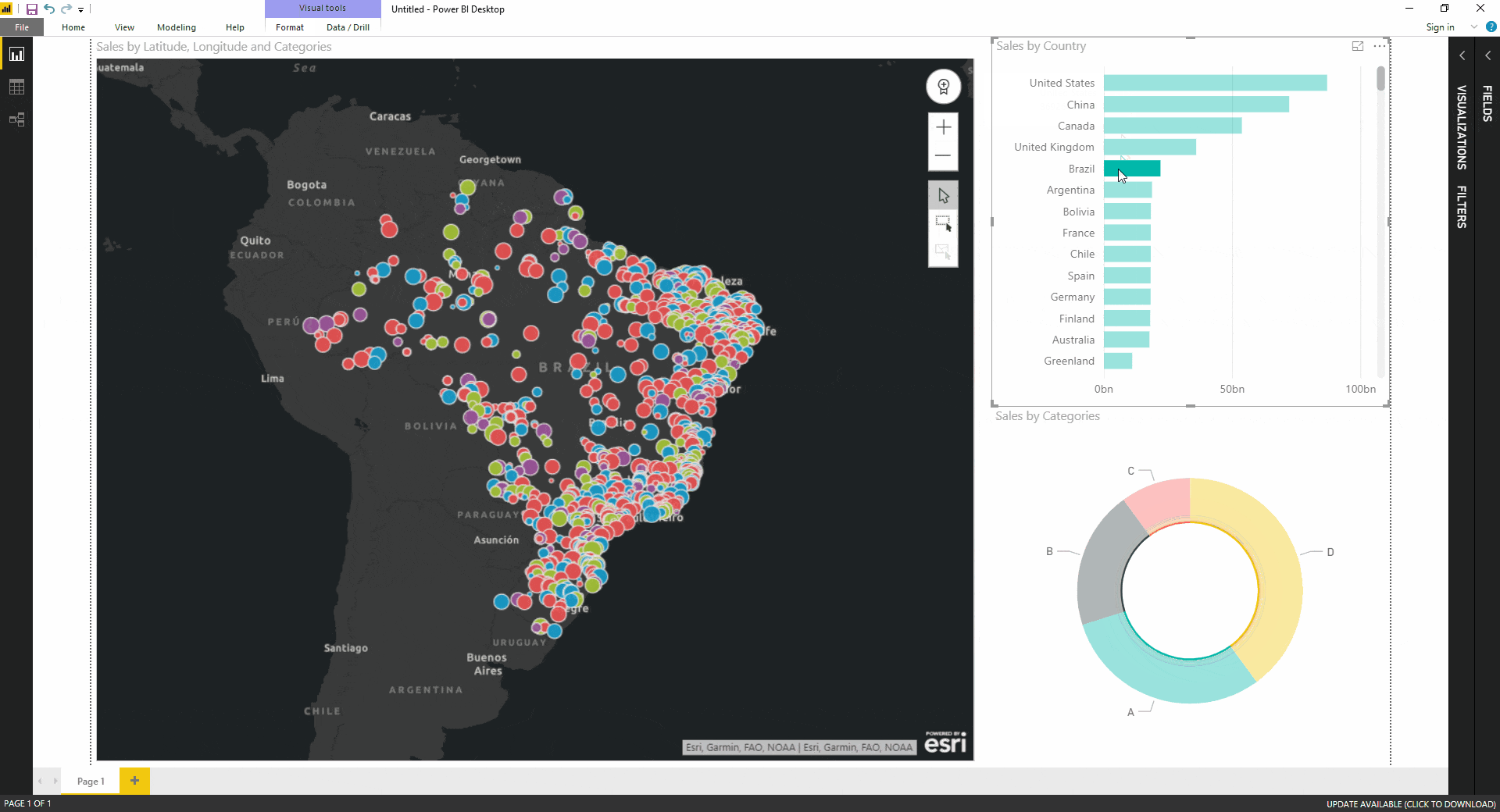
The concept of "contact on map" refers to the intersection of geographical data and human interaction. It signifies the ability to locate and understand the relationships between people, places, and events through the lens of a map. This powerful tool transcends simple navigation, offering insights into social, economic, and environmental phenomena, shaping our understanding of the world and influencing decision-making across various disciplines.
Understanding the Foundation: The Intersection of Geography and Data
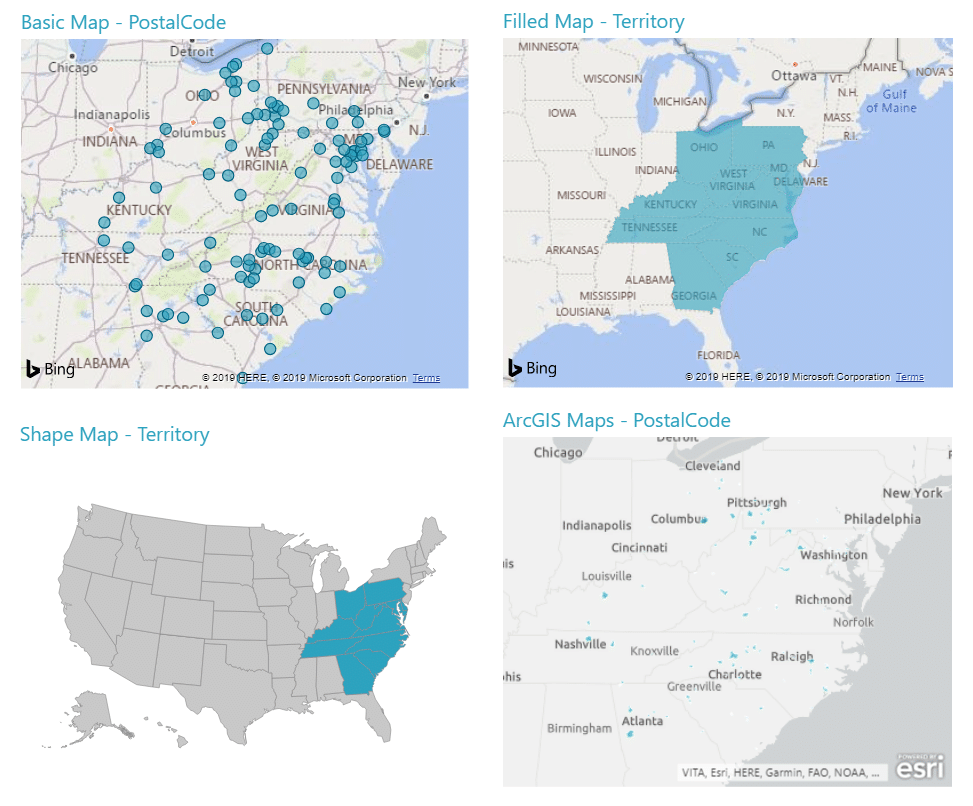
At its core, contact on map relies on the marriage of geographical information systems (GIS) and data analysis. GIS provides the framework for representing spatial data, allowing us to visualize and analyze the distribution of features on a map. This data can encompass a wide range of information, from demographic trends and population density to infrastructure networks and environmental conditions. By overlaying this data on maps, we gain a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and patterns that might otherwise remain hidden.
The Significance of Contact on Map: Unveiling Hidden Connections
The true power of contact on map lies in its ability to reveal connections and patterns that might not be apparent through traditional data analysis alone. By visualizing data spatially, we can identify clusters, outliers, and trends that illuminate underlying relationships between various factors. This enhanced understanding empowers informed decision-making across diverse fields, from urban planning and public health to resource management and disaster response.
Applications Across Disciplines: A Multifaceted Tool
Contact on map has become an indispensable tool in numerous fields, driving innovation and efficiency in various domains:
- Urban Planning and Development: Contact on map allows urban planners to analyze population density, infrastructure networks, and transportation patterns, enabling them to design efficient and sustainable cities. By overlaying data on demographics, land use, and environmental factors, they can identify areas for development, optimize resource allocation, and mitigate potential risks.
- Public Health and Epidemiology: Contact on map plays a crucial role in understanding and responding to public health emergencies. By mapping the spread of diseases, identifying high-risk areas, and analyzing demographic factors, public health officials can develop targeted interventions, allocate resources effectively, and monitor the effectiveness of public health campaigns.
- Environmental Management and Conservation: Contact on map enables researchers and conservationists to analyze environmental data, such as deforestation rates, pollution levels, and biodiversity hotspots. By visualizing this data, they can identify areas of concern, assess the impact of human activities on the environment, and develop strategies for conservation and sustainable resource management.
- Resource Management and Disaster Response: Contact on map empowers resource managers and disaster response teams to analyze the distribution of resources, assess potential risks, and coordinate response efforts during natural disasters. By mapping infrastructure networks, evacuation routes, and vulnerable populations, they can optimize resource allocation, facilitate efficient communication, and ensure timely and effective response.
Beyond Visualization: The Power of Analysis
Contact on map goes beyond simply visualizing data. It allows for powerful analysis techniques that can reveal deeper insights and inform decision-making. These techniques include:
- Spatial Analysis: This involves analyzing the spatial relationships between different features on a map, identifying patterns, clusters, and outliers. For example, analyzing the spatial distribution of crime incidents can help police departments identify hotspots and allocate resources accordingly.
- Network Analysis: This focuses on analyzing the connections and relationships between different nodes in a network, such as transportation systems, communication networks, or social networks. By understanding these connections, we can optimize flow, identify bottlenecks, and improve efficiency.
- Geostatistics: This involves using statistical methods to analyze spatially distributed data, taking into account spatial autocorrelation and other factors. This allows for more accurate predictions and modeling of spatial phenomena, such as the spread of disease or the impact of climate change.
Navigating the Challenges: Addressing the Limitations
While contact on map offers immense potential, it’s important to acknowledge its limitations and address potential challenges:
- Data Availability and Accuracy: The quality and availability of data are crucial for effective contact on map applications. Inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to misleading conclusions and ineffective decision-making.
- Privacy Concerns: The use of location data raises privacy concerns, especially when dealing with sensitive information such as medical records or personal movements. Ensuring data privacy and ethical use is paramount for responsible contact on map applications.
- Accessibility and Technical Expertise: Access to GIS software and the technical expertise required to utilize it can be a barrier for some individuals and organizations. Addressing this barrier through education and training is essential for promoting equitable access to the benefits of contact on map.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
Q: What are some examples of how contact on map is used in real-world applications?
A: Contact on map is used in various real-world applications, such as:
- Mapping the spread of infectious diseases: Public health officials use contact on map to track the spread of diseases, identify high-risk areas, and develop targeted interventions.
- Optimizing transportation routes: Logistics companies utilize contact on map to analyze traffic patterns, optimize delivery routes, and minimize travel time.
- Predicting natural disaster risks: By analyzing geological data, contact on map helps identify areas prone to earthquakes, floods, or other natural disasters, enabling better preparedness and mitigation efforts.
Q: What are the benefits of using contact on map in decision-making?
A: Contact on map offers several benefits for decision-making, including:
- Enhanced spatial understanding: Visualizing data spatially provides a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and patterns.
- Improved resource allocation: Contact on map allows for targeted resource allocation based on spatial analysis and data-driven insights.
- More informed and effective interventions: By identifying trends and patterns, contact on map enables more effective and targeted interventions in various fields.
Q: What are some of the ethical considerations associated with using contact on map?
A: Ethical considerations associated with contact on map include:
- Data privacy: Ensuring the responsible and ethical use of location data is crucial to protect individual privacy.
- Data security: Protecting data from unauthorized access and misuse is essential for maintaining trust and ensuring data integrity.
- Transparency and accountability: Transparency in data collection, analysis, and use is vital for public trust and accountability.
Tips for Effective Contact on Map Applications
- Start with a clear objective: Define the specific questions you are trying to answer or the goals you are trying to achieve.
- Choose appropriate data sources: Ensure the data you use is relevant, accurate, and reliable.
- Utilize appropriate analysis techniques: Select the appropriate analysis techniques based on your research question and the nature of your data.
- Communicate results effectively: Clearly communicate your findings through maps, charts, and other visualizations.
- Consider ethical implications: Always consider the ethical implications of using contact on map, particularly with regards to data privacy and security.
Conclusion: The Future of Spatial Data Integration
Contact on map continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology, data availability, and analytical techniques. The integration of spatial data with other data sources, such as social media data and sensor networks, holds immense potential for unlocking new insights and fostering innovation across various fields. As we navigate the challenges and embrace the opportunities, contact on map will continue to play a crucial role in shaping our understanding of the world and driving informed decision-making for a more sustainable and equitable future.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Place: Understanding Contact on Map and its Applications. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
