The San Joaquin River: A Lifeline Traversing California’s Interior
Related Articles: The San Joaquin River: A Lifeline Traversing California’s Interior
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The San Joaquin River: A Lifeline Traversing California’s Interior. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The San Joaquin River: A Lifeline Traversing California’s Interior
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The San Joaquin River: A Lifeline Traversing California’s Interior
- 3.1 A Geographic Overview: Tracing the River’s Path
- 3.2 Tributaries: A Network of Life
- 3.3 Historical Significance: A Legacy of Human Interaction
- 3.4 The River’s Importance: A Lifeline for California
- 3.5 Challenges and Solutions: Balancing Needs and Sustainability
- 3.6 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
- 3.7 Tips: Engaging with the San Joaquin River
- 3.8 Conclusion: A Lifeline for Generations to Come
- 4 Closure
The San Joaquin River: A Lifeline Traversing California’s Interior

The San Joaquin River, a vital artery of California’s interior, flows for approximately 360 miles, traversing a diverse landscape from the Sierra Nevada foothills to the vast San Joaquin Valley. This river, along with its tributaries, plays a crucial role in the state’s economy, environment, and history. Understanding the San Joaquin River’s geography, its intricate network of tributaries, and its historical significance is essential for appreciating its multifaceted impact on California.
A Geographic Overview: Tracing the River’s Path
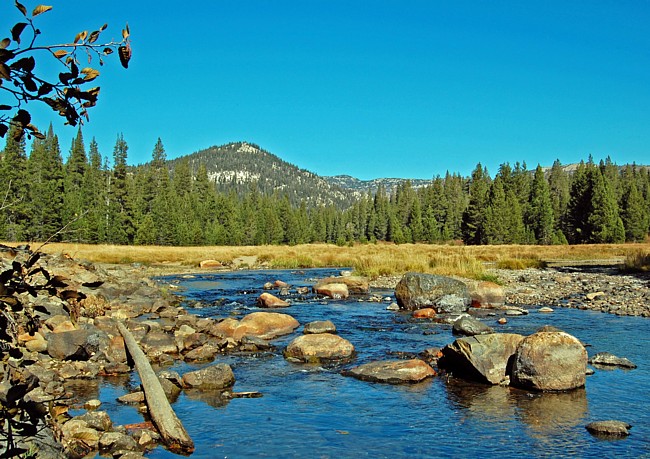
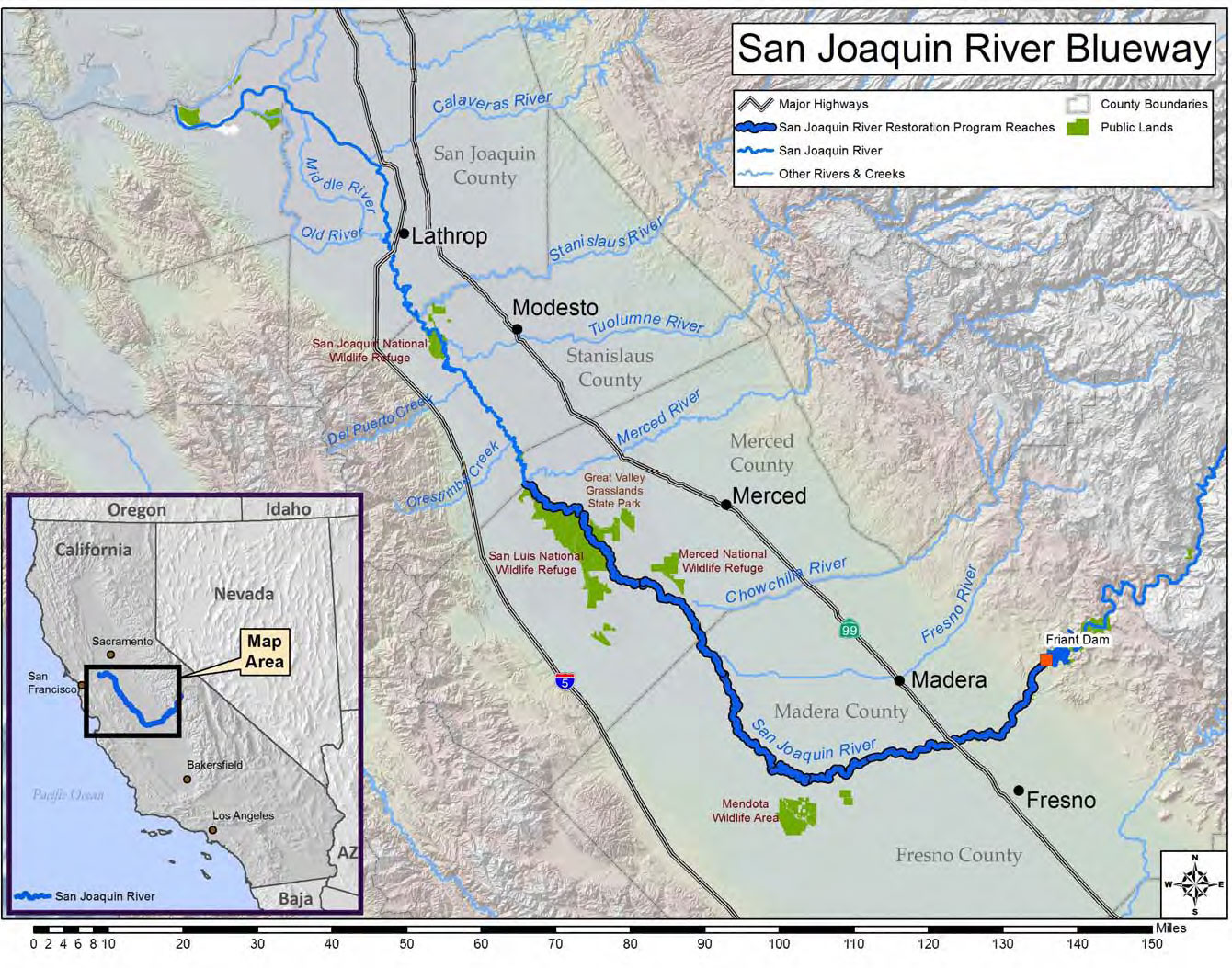
The San Joaquin River originates in the high Sierra Nevada, specifically in the southern portion of Yosemite National Park. Its headwaters emerge from a series of alpine lakes and streams, including the South Fork of the San Joaquin River and the Kings River, which contribute significantly to its flow. As the river descends eastward, it carves through the rugged foothills, creating a picturesque canyon with steep slopes and rocky outcroppings.
Upon reaching the San Joaquin Valley, the river transforms into a wide, meandering waterway, traversing a vast expanse of fertile farmland. It receives water from numerous tributaries, including the Merced River, the Tuolumne River, and the Stanislaus River, all of which originate in the Sierra Nevada. These tributaries contribute to the river’s volume and its ability to support a rich ecosystem.
The San Joaquin River’s journey ends in the vast expanse of the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, a complex network of waterways and islands formed by the confluence of the Sacramento and San Joaquin rivers. This delta region is a critical habitat for a wide array of wildlife and a vital source of water for California’s agricultural industry.
Tributaries: A Network of Life
The San Joaquin River’s tributaries are integral to its overall health and function. Each tributary contributes unique characteristics to the river’s flow, water quality, and biodiversity.
- The Merced River: Known for its scenic beauty and its contribution to the Central Valley’s agricultural productivity, the Merced River flows through Yosemite National Park and joins the San Joaquin River near the city of Merced.
- The Tuolumne River: Originating in the high Sierra Nevada, the Tuolumne River is renowned for its pristine waters and its role in providing hydroelectric power to the region. It joins the San Joaquin River near the city of Modesto.
- The Stanislaus River: With its headwaters in the Stanislaus National Forest, the Stanislaus River supports a thriving salmon population and plays a vital role in the region’s water supply. It joins the San Joaquin River near the city of Stockton.
These tributaries, along with others, contribute significantly to the San Joaquin River’s ecological integrity and its role in sustaining California’s diverse ecosystems.
Historical Significance: A Legacy of Human Interaction
The San Joaquin River has been a central element in California’s history, influencing the state’s development and shaping the lives of its inhabitants.
- Native American Cultures: The river served as a vital resource for Native American tribes, who relied on its waters for sustenance, transportation, and cultural practices. Archaeological evidence reveals the presence of various indigenous cultures along the river’s banks, with remnants of their settlements and tools discovered in the region.
- Early European Exploration: Spanish explorers, seeking new lands and resources, traversed the San Joaquin River in the 18th century, marking the beginning of European influence in the region. Their expeditions opened the way for further exploration and settlement.
- Agricultural Expansion: The arrival of European settlers in the 19th century spurred the development of large-scale agriculture in the San Joaquin Valley. The river’s water became crucial for irrigation, transforming the region into a major agricultural hub.
- Water Management and Development: The 20th century witnessed the construction of numerous dams and reservoirs along the San Joaquin River, transforming its flow and influencing water distribution throughout the state. This period marked a shift towards centralized water management and the development of complex infrastructure to meet California’s growing water needs.
These historical events have shaped the San Joaquin River’s current state, influencing its ecological health, water management, and the lives of communities that rely on its resources.
The River’s Importance: A Lifeline for California
The San Joaquin River plays a critical role in the life of California, supporting a diverse range of ecosystems, industries, and communities.
- Ecological Importance: The river and its tributaries provide essential habitat for a wide array of wildlife, including fish, birds, reptiles, and amphibians. The river’s riparian zones, the areas along its banks, are particularly important for providing shelter, food, and breeding grounds for various species.
- Agricultural Productivity: The San Joaquin Valley, irrigated by the river and its tributaries, is one of the most productive agricultural regions in the world. The river’s water sustains a vast network of farms, producing a wide range of crops, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and livestock.
- Economic Contribution: The river’s water is essential for the region’s economic prosperity, supporting industries such as agriculture, tourism, and recreation. The river also plays a role in the state’s energy production, with hydroelectric power generated from dams along its course.
- Recreation and Tourism: The San Joaquin River offers a variety of recreational opportunities, including fishing, boating, kayaking, and hiking. Its scenic beauty attracts tourists and provides opportunities for outdoor recreation and relaxation.
The San Joaquin River’s importance extends far beyond its physical boundaries, influencing the well-being of California’s economy, environment, and its people.
Challenges and Solutions: Balancing Needs and Sustainability
The San Joaquin River faces a number of challenges, primarily related to water management, habitat degradation, and climate change.
- Water Scarcity: California’s growing population and expanding agricultural industry have placed increasing demands on the state’s water resources. The San Joaquin River, like many other waterways in the state, is subject to water shortages, particularly during periods of drought.
- Habitat Degradation: Human activities, including agriculture, urbanization, and dam construction, have significantly altered the river’s natural flow and habitat. These changes have negatively impacted fish populations, riparian ecosystems, and overall biodiversity.
- Climate Change Impacts: Climate change is expected to exacerbate existing challenges, leading to more frequent and severe droughts, increased water temperatures, and alterations in precipitation patterns. These changes will further impact the river’s flow, water quality, and ecological health.
Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach, involving collaboration among stakeholders, sustainable water management practices, and habitat restoration efforts.
- Water Conservation: Implementing water-efficient irrigation techniques, promoting urban water conservation, and exploring alternative water sources can help reduce the strain on the river’s water supply.
- Habitat Restoration: Restoring degraded riparian areas, removing barriers to fish migration, and creating more natural flow regimes can help improve the river’s ecological health and biodiversity.
- Climate Change Adaptation: Planning for future climate change impacts, including increased water scarcity and extreme weather events, is crucial for ensuring the river’s long-term sustainability.
By addressing these challenges through collaborative efforts and sustainable practices, it is possible to ensure the San Joaquin River’s continued role as a vital lifeline for California.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q: How does the San Joaquin River affect the California economy?
A: The San Joaquin River plays a significant role in the California economy, supporting a diverse range of industries. Its water is essential for agriculture, contributing to the state’s agricultural productivity and generating revenue through crop sales and related industries. The river also supports tourism, recreation, and hydroelectric power generation, further contributing to the state’s economic well-being.
Q: What are the major threats to the San Joaquin River’s ecosystem?
A: The San Joaquin River faces several threats to its ecosystem, including water scarcity, habitat degradation, and climate change. Water scarcity, driven by population growth and agricultural demands, reduces the river’s flow and impacts its aquatic life. Habitat degradation, caused by human activities such as dam construction and urbanization, alters the river’s natural flow and reduces its capacity to support biodiversity. Climate change is expected to exacerbate these challenges, leading to more frequent droughts, increased water temperatures, and changes in precipitation patterns, further impacting the river’s ecosystem.
Q: What are some ongoing efforts to protect and restore the San Joaquin River?
A: Several organizations and government agencies are actively working to protect and restore the San Joaquin River. These efforts include habitat restoration projects, water conservation programs, and initiatives to address climate change impacts. For example, the San Joaquin River Restoration Program aims to restore the river’s natural flow and improve its ecological health. Water conservation efforts focus on promoting efficient irrigation techniques and reducing water consumption in urban areas. Climate change adaptation strategies aim to prepare for future impacts and ensure the river’s long-term sustainability.
Q: How can individuals contribute to the protection of the San Joaquin River?
A: Individuals can contribute to the protection of the San Joaquin River by adopting water conservation practices in their daily lives, supporting organizations involved in river restoration, and advocating for policies that promote sustainable water management. Simple actions like reducing water usage in the home, choosing water-efficient appliances, and supporting businesses that practice responsible water use can make a difference. Additionally, engaging in community initiatives and supporting organizations dedicated to river conservation can amplify individual efforts and contribute to a collective impact.
Tips: Engaging with the San Joaquin River
- Visit the San Joaquin River: Explore the river’s beauty by visiting its banks, taking a boat trip, or hiking along its trails. Observing the river firsthand allows for a deeper appreciation of its significance and the challenges it faces.
- Learn about the river’s history: Research the river’s historical role in California’s development, its cultural significance for Native American tribes, and the impact of European settlement on its ecosystem. Understanding the river’s past provides context for its present state and its future challenges.
- Support organizations dedicated to river conservation: Donate to organizations working to restore the river’s habitat, promote sustainable water management, and address climate change impacts. These organizations are actively working to protect the river’s ecosystem and ensure its long-term health.
- Advocate for policies that protect the river: Engage with local and state governments to support policies that promote water conservation, habitat restoration, and climate change adaptation. These policies are crucial for ensuring the river’s continued role as a vital lifeline for California.
Conclusion: A Lifeline for Generations to Come
The San Joaquin River, a vital artery of California’s interior, is a testament to the interconnectedness of nature, human history, and the future of our planet. Its journey from the high Sierra Nevada to the vast San Joaquin Valley reflects the diverse landscapes, ecosystems, and communities it sustains.
The river’s history, marked by human interaction and adaptation, highlights the importance of responsible water management, habitat conservation, and climate change adaptation. By understanding the San Joaquin River’s significance and the challenges it faces, we can work towards ensuring its continued role as a lifeline for California and its people for generations to come.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The San Joaquin River: A Lifeline Traversing California’s Interior. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!