The Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Eastern Europe’s Political Map
Related Articles: The Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Eastern Europe’s Political Map
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Eastern Europe’s Political Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Eastern Europe’s Political Map
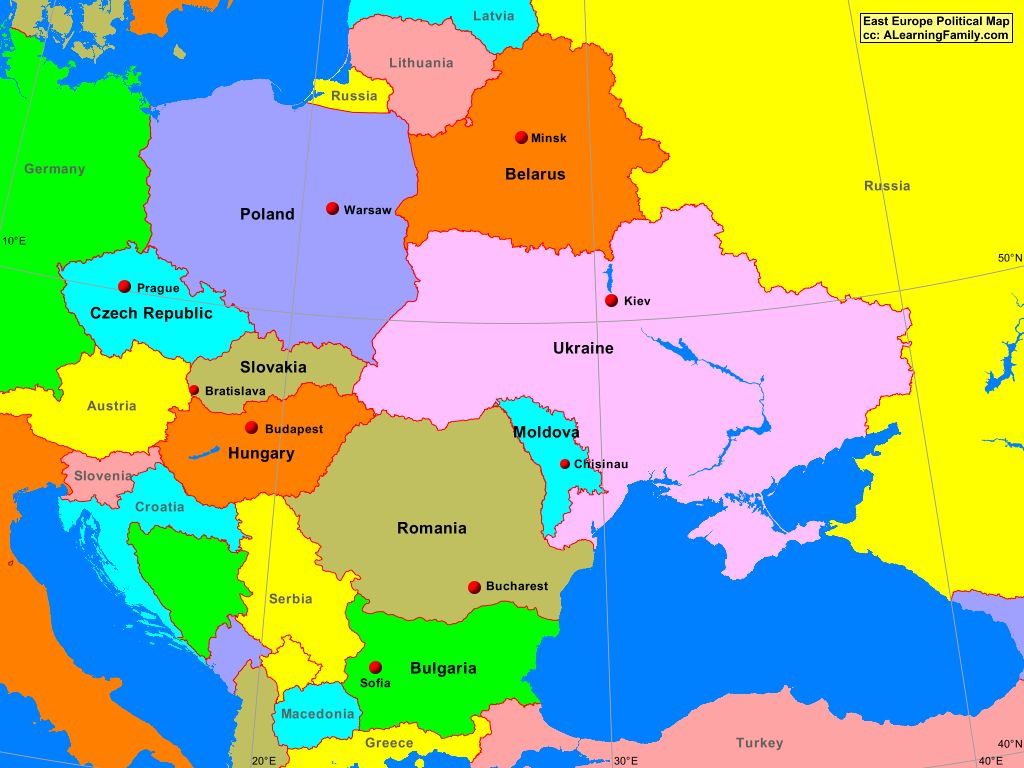
Eastern Europe, a region steeped in history, culture, and complex geopolitical dynamics, presents a fascinating tapestry of political landscapes. Understanding the intricate web of nations, borders, and historical influences that shape this region is crucial for comprehending its present and predicting its future. This article delves into the political map of Eastern Europe, exploring its evolution, key players, and the factors that contribute to its unique character.
Defining the Region: A Matter of Perspective
The precise definition of Eastern Europe remains a subject of debate. Historically, the term encompasses the territories located east of Germany and west of Russia, stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Black Sea. However, contemporary political and economic realities have blurred the lines.
For instance, the European Union (EU) membership of several countries, including Poland, Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, Croatia, Bulgaria, and Romania, has shifted their perceived alignment towards Western Europe. Conversely, countries like Belarus and Ukraine, despite their geographical location, are often considered part of the post-Soviet sphere of influence.
Historical Roots: From Empires to Independence
The political map of Eastern Europe has undergone significant transformations throughout history. The region was once dominated by powerful empires, including the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Russian Empire. These empires left a lasting legacy, shaping the languages, cultures, and political systems of the region.
The 20th century witnessed a dramatic shift, with the rise of communism and the Soviet Union’s dominance over much of Eastern Europe. This period saw the imposition of centralized political systems, the suppression of dissent, and the creation of artificial borders. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 marked a turning point, ushering in a wave of independence for many Eastern European nations.
Key Players and Their Political Systems
Eastern Europe is a diverse region with a range of political systems, ranging from democracies to authoritarian regimes. Here’s a glimpse into some key players:
- Poland: A democratic republic with a strong tradition of solidarity and a significant role in the EU.
- Czech Republic: A parliamentary democracy known for its economic stability and a strong focus on European integration.
- Slovakia: A parliamentary republic with a strong emphasis on social welfare and a commitment to EU membership.
- Hungary: A parliamentary republic with a growing influence of right-wing nationalism and a complex relationship with the EU.
- Romania: A parliamentary republic grappling with corruption and a desire to strengthen its ties with the West.
- Bulgaria: A parliamentary republic struggling with economic challenges and a history of political instability.
- Ukraine: A semi-presidential republic facing a protracted conflict with Russia and seeking closer ties with the West.
- Belarus: A presidential republic under authoritarian rule, characterized by close ties with Russia and a suppression of dissent.
Challenges and Opportunities
Eastern Europe faces numerous challenges, including:
- Economic disparity: While some countries have experienced significant economic growth, others lag behind, leading to regional imbalances and social inequalities.
- Political instability: The region has witnessed political turmoil, including corruption, populism, and the rise of authoritarianism.
- Geopolitical tensions: The ongoing conflict in Ukraine, the presence of Russian military forces in the region, and the increasing influence of China pose significant security concerns.
- Demographic challenges: Many Eastern European countries face declining populations and an aging workforce, impacting economic growth and social stability.
Despite these challenges, Eastern Europe also presents significant opportunities:
- Economic potential: The region offers a skilled workforce, a growing middle class, and access to key markets.
- Strategic location: Eastern Europe serves as a bridge between East and West, offering opportunities for trade and investment.
- Cultural richness: The region boasts a vibrant cultural heritage, attracting tourists and fostering cultural exchange.
- EU membership: For those countries within the EU, membership provides access to a single market, funding opportunities, and political stability.
Understanding the Importance of Eastern Europe’s Political Map
The political map of Eastern Europe is not merely a collection of borders and nations. It reflects the region’s intricate history, its present challenges, and its potential for the future. By analyzing the political landscape, we can gain a deeper understanding of:
- Regional dynamics: The political map reveals the complex relationships between countries, including alliances, rivalries, and dependencies.
- Geopolitical trends: The map helps identify areas of potential conflict, cooperation, and influence.
- Economic development: The distribution of resources, infrastructure, and trade routes provides insights into economic opportunities and challenges.
- Social and cultural trends: The map reflects the diversity of cultures, languages, and religions within the region.
FAQs about Eastern Europe’s Political Map
1. What are the main political systems in Eastern Europe?
Eastern Europe exhibits a diverse range of political systems, including parliamentary democracies, presidential republics, and semi-presidential republics. Some countries, like Belarus, operate under authoritarian regimes.
2. Why is Eastern Europe considered a "transition region"?
Eastern Europe is often referred to as a "transition region" due to its historical shift from communist rule to democratic systems and its ongoing integration into the global economy.
3. What is the impact of EU membership on Eastern European countries?
EU membership has brought significant benefits to Eastern European countries, including economic integration, access to funding, and political stability. However, it has also presented challenges, such as the need to align with EU regulations and the potential for economic disparities.
4. What are the key geopolitical challenges facing Eastern Europe?
Eastern Europe faces significant geopolitical challenges, including the conflict in Ukraine, the presence of Russian military forces, and the growing influence of China.
5. How is the political map of Eastern Europe likely to evolve in the future?
The political map of Eastern Europe is likely to continue evolving, influenced by factors such as economic development, demographic trends, and geopolitical shifts. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine, the rise of populism, and the growing influence of China are likely to shape the region’s political landscape in the years to come.
Tips for Understanding Eastern Europe’s Political Map
- Study the historical context: Understanding the region’s past, including empires, wars, and revolutions, is crucial for comprehending its present.
- Analyze political systems: Familiarize yourself with the different political systems in place, such as parliamentary democracies, presidential republics, and authoritarian regimes.
- Consider geopolitical factors: Pay attention to alliances, rivalries, and the influence of external actors, such as Russia, the EU, and the United States.
- Explore economic indicators: Analyze economic data, such as GDP growth, trade patterns, and unemployment rates, to understand the region’s economic landscape.
- Engage with diverse perspectives: Seek out information from a variety of sources, including academic journals, news reports, and think tank publications, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region.
Conclusion
The political map of Eastern Europe is a dynamic and complex entity. It reflects a region grappling with its past, navigating present challenges, and shaping its future. Understanding this map is essential for grasping the intricate web of relationships, challenges, and opportunities that define this diverse and influential part of the world. By analyzing the region’s political landscape, we can gain valuable insights into the forces shaping the global order and the potential for cooperation, conflict, and progress in the years to come.
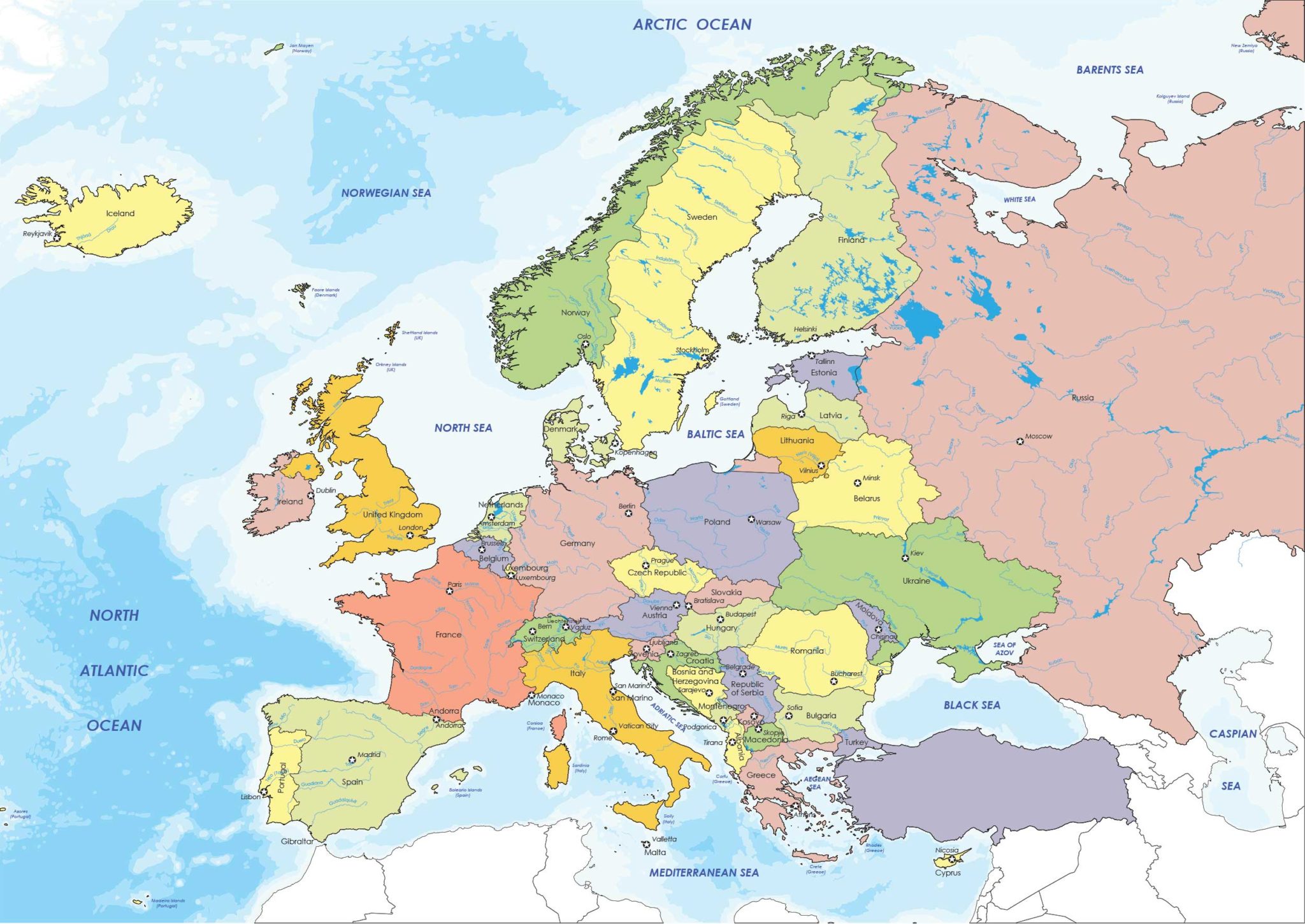





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Shifting Landscape: A Comprehensive Look at Eastern Europe’s Political Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!