Understanding "Culvert" in Maps: A Guide to Navigating Underground Waterways
Related Articles: Understanding "Culvert" in Maps: A Guide to Navigating Underground Waterways
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding "Culvert" in Maps: A Guide to Navigating Underground Waterways. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding "Culvert" in Maps: A Guide to Navigating Underground Waterways
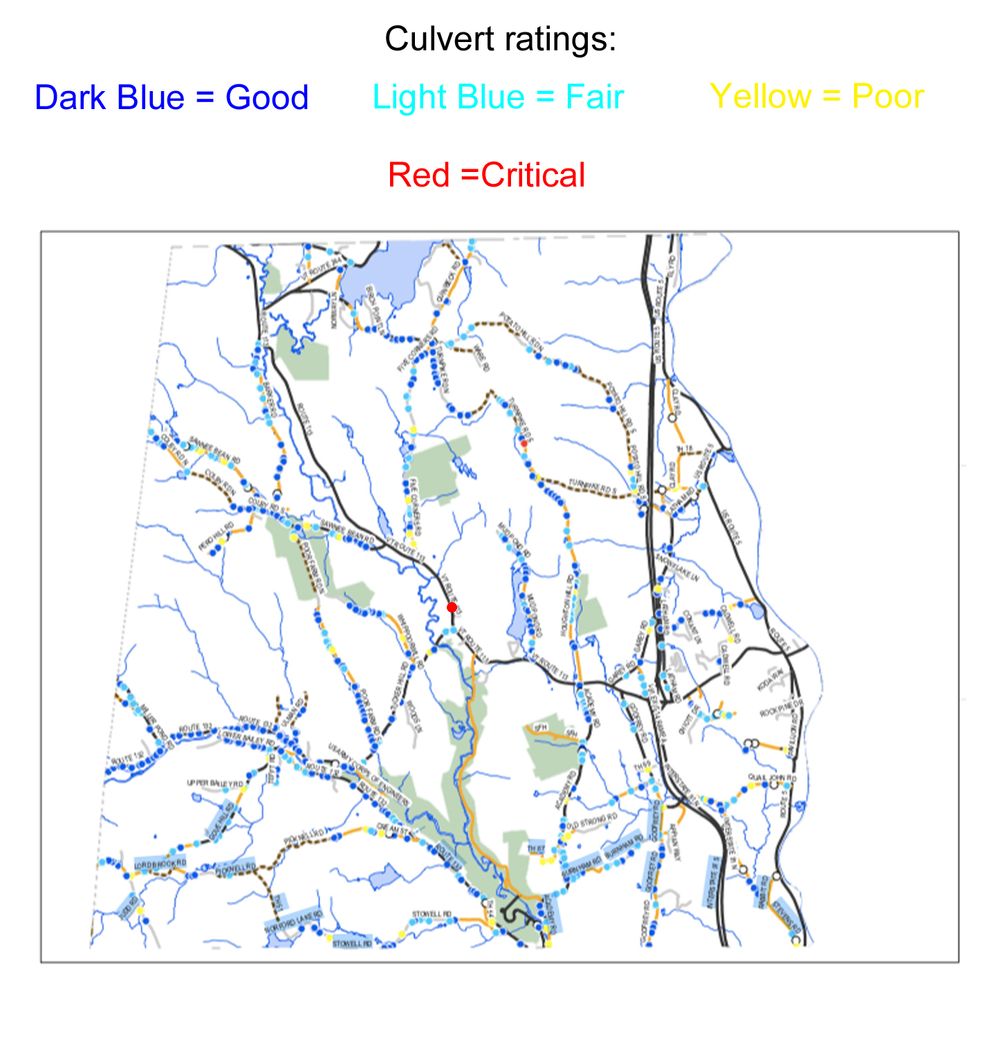
In the realm of cartography, the term "culvert" often appears, denoting a crucial yet often overlooked element of infrastructure. This article delves into the significance of culverts within the context of maps, elucidating their function, importance, and practical applications.
What is a Culvert?
A culvert is essentially a tunnel or conduit constructed beneath a road, railway, or other surface feature, allowing water to flow underneath. Typically made of concrete, metal, or plastic, culverts serve as a crucial drainage system, preventing water from accumulating on roadways, obstructing traffic, or causing erosion.
Why are Culverts Important?
The significance of culverts extends beyond mere drainage. They play a vital role in:
- Managing Water Flow: Culverts facilitate the controlled passage of water, preventing flooding and ensuring the safe and efficient movement of watercourses.
- Maintaining Infrastructure: By channeling water away from roads and bridges, culverts protect these structures from damage caused by erosion, runoff, and flooding.
- Protecting the Environment: Culverts help maintain the natural flow of watercourses, preserving habitats and preventing erosion in surrounding areas.
- Facilitating Transportation: By allowing water to flow underneath roadways, culverts ensure uninterrupted traffic flow, even during periods of heavy rainfall.
Types of Culverts and their Representation on Maps
Culverts come in various shapes, sizes, and materials, each suited for specific applications. Some common types include:
- Box Culverts: Rectangular or square structures, often used for larger waterways.
- Arch Culverts: Semi-circular structures, typically used for smaller streams and drainage ditches.
- Pipe Culverts: Circular structures, often made of concrete, metal, or plastic, used for smaller waterways and drainage.
On maps, culverts are typically represented by a specific symbol, often a dashed line with a small circle or rectangle at the end, indicating the entrance or exit of the culvert. The size and shape of the symbol may vary depending on the type and size of the culvert.
How to Interpret Culverts on Maps
Understanding the information conveyed by culvert symbols on maps is crucial for various purposes:
- Civil Engineers: Culvert information is essential for planning and designing road and bridge construction, ensuring proper drainage and avoiding potential flooding.
- Environmentalists: Culvert data is crucial for assessing the impact of infrastructure on watercourses and implementing strategies to mitigate negative impacts.
- Emergency Responders: During flooding events, knowing the location and capacity of culverts can help in planning evacuation routes and managing water flow.
- Landowners: Understanding the location and function of culverts can help landowners manage drainage on their properties, preventing erosion and flooding.
FAQs about Culverts on Maps:
-
Q: Why are some culverts marked with a dashed line while others are solid?
- A: A dashed line typically indicates a culvert that is below ground level, while a solid line may represent a culvert that is partially visible or above ground.
-
Q: How can I tell the size of a culvert from a map?
- A: The size of the culvert symbol on a map may give an indication of its approximate size. However, more detailed information about the culvert’s dimensions is often available in accompanying documentation or databases.
-
Q: What is the significance of the circle or rectangle at the end of the culvert symbol?
- A: The circle or rectangle represents the entrance or exit of the culvert, indicating the direction of water flow.
-
Q: Can I find information about the material of a culvert on a map?
- A: Maps may not always specify the material of a culvert. However, additional information about the culvert’s construction can be obtained from accompanying documentation or by contacting the relevant authorities.
Tips for Using Culvert Information from Maps:
- Consult Multiple Sources: For comprehensive information, refer to multiple maps, including topographic maps, drainage maps, and infrastructure maps.
- Consider the Scale: The level of detail provided on a map depends on its scale. Larger-scale maps may provide more detailed information about culverts.
- Seek Additional Information: If the map does not provide sufficient information about a specific culvert, contact the relevant authorities or consult specialized databases.
- Understand the Context: Consider the surrounding landscape and the location of the culvert within the overall drainage system to interpret its function effectively.
Conclusion:
Culverts, though often unseen, play a critical role in managing water flow, protecting infrastructure, and preserving the environment. Maps serve as valuable tools for understanding the location and function of these essential structures. By interpreting culvert symbols and utilizing the information provided on maps, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions regarding infrastructure planning, environmental protection, and emergency response. Understanding the significance of culverts in the context of maps empowers us to navigate the complex interplay of water, infrastructure, and the natural environment.

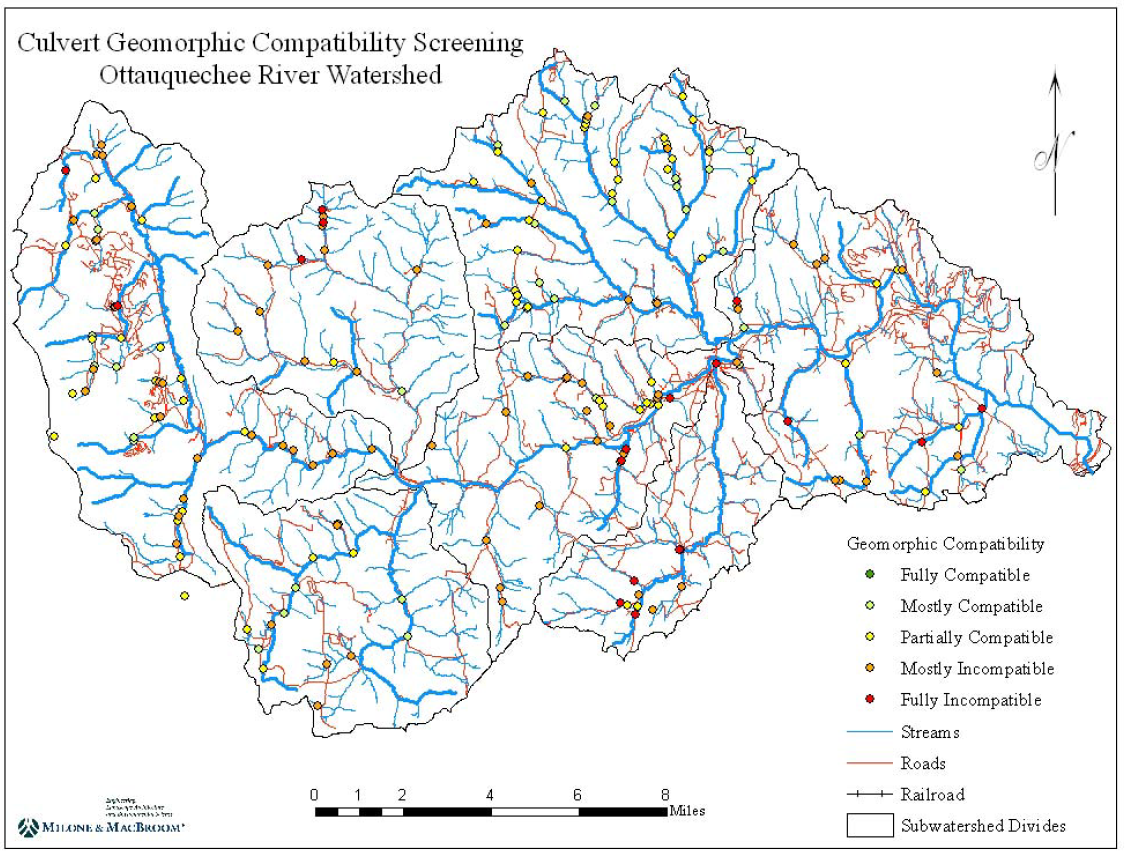


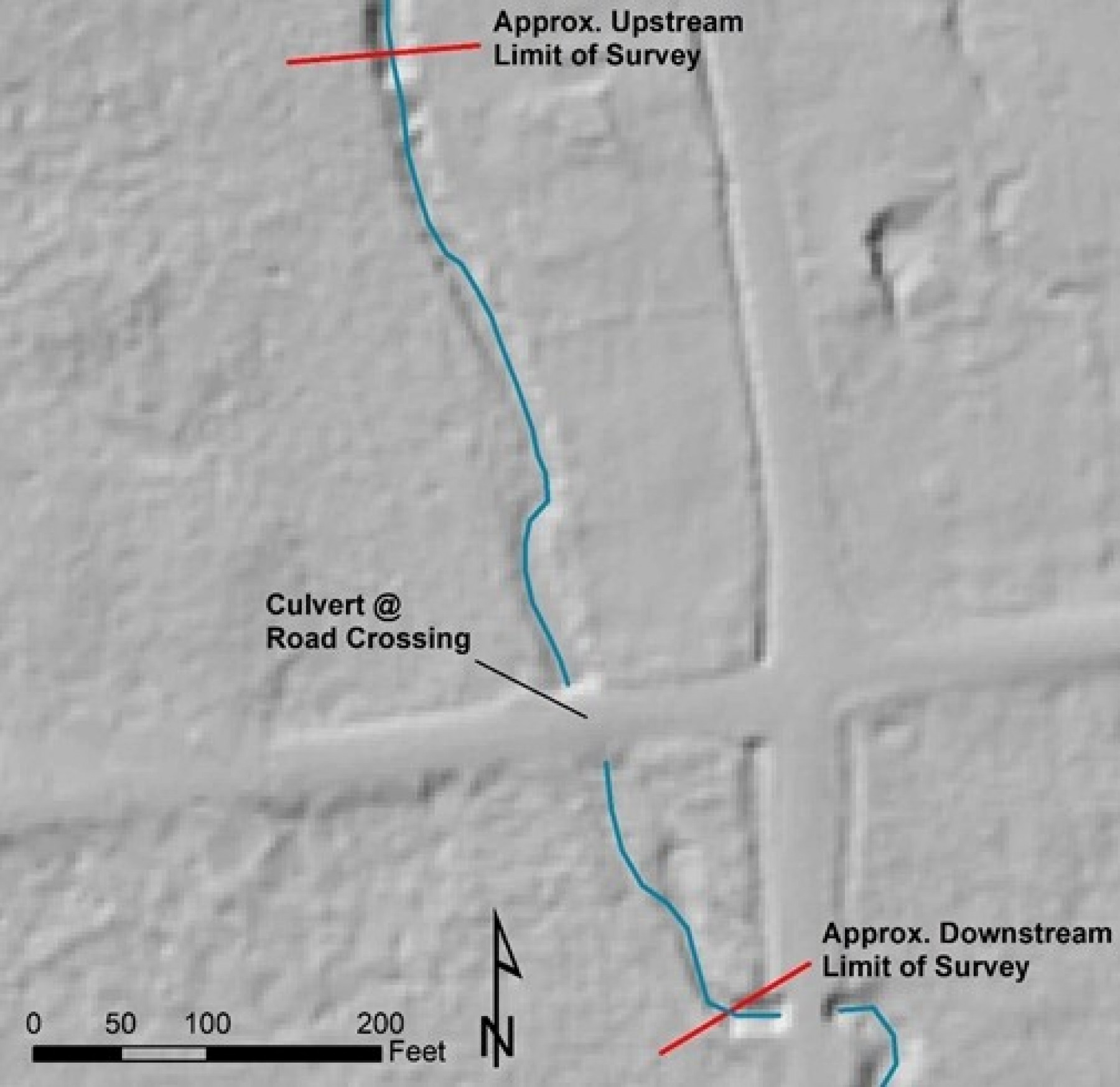


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding "Culvert" in Maps: A Guide to Navigating Underground Waterways. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!