Unlocking the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Property Mapping
Related Articles: Unlocking the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Property Mapping
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Property Mapping. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Unlocking the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Property Mapping
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Unlocking the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Property Mapping
- 3.1 The Essence of GIS Property Mapping
- 3.2 Applications of GIS Property Mapping
- 3.3 Benefits of GIS Property Mapping
- 3.4 FAQs Regarding GIS Property Mapping
- 3.5 Tips for Effective GIS Property Mapping
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Unlocking the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Property Mapping

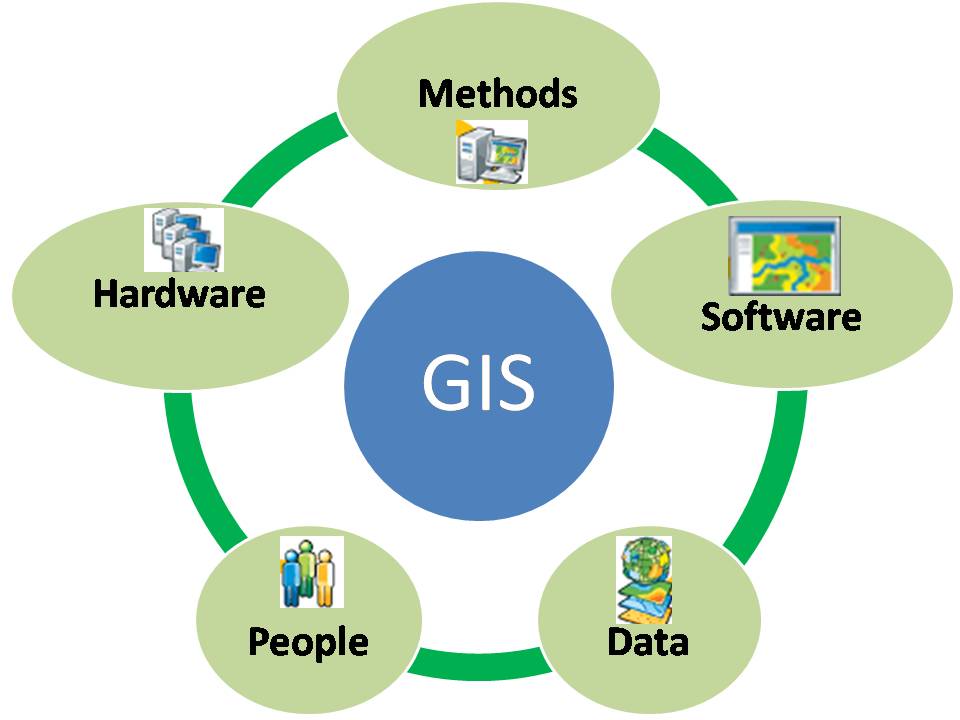
In the realm of property management, accurate and comprehensive data is paramount. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) have emerged as an indispensable tool for visualizing, analyzing, and managing property information, transforming the way we understand and interact with the built environment. This article delves into the intricacies of GIS property mapping, exploring its applications, benefits, and potential impact on various sectors.
The Essence of GIS Property Mapping
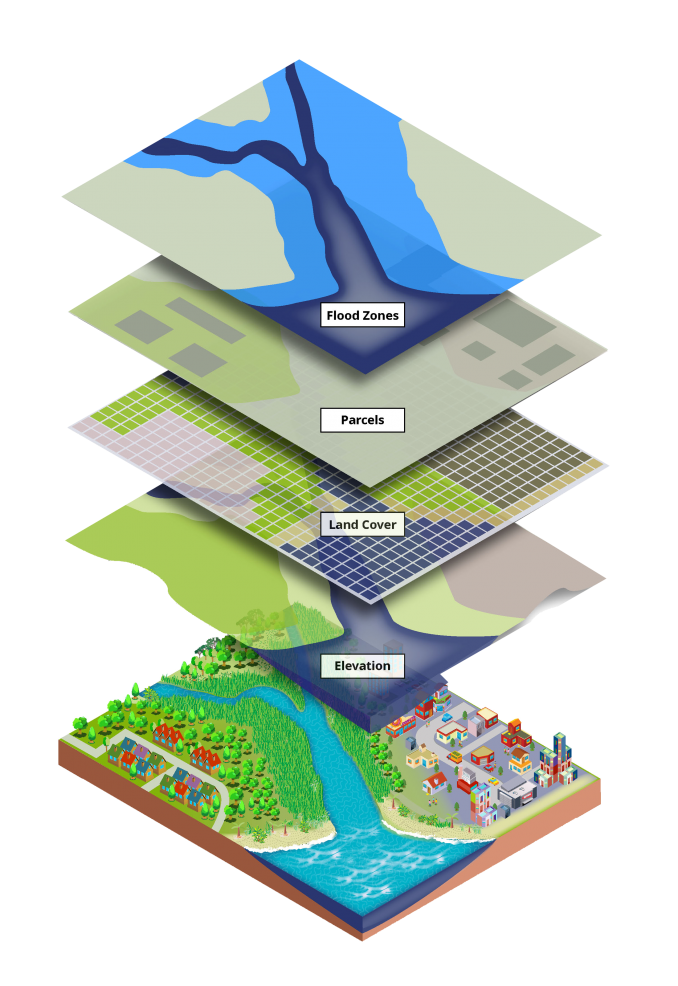
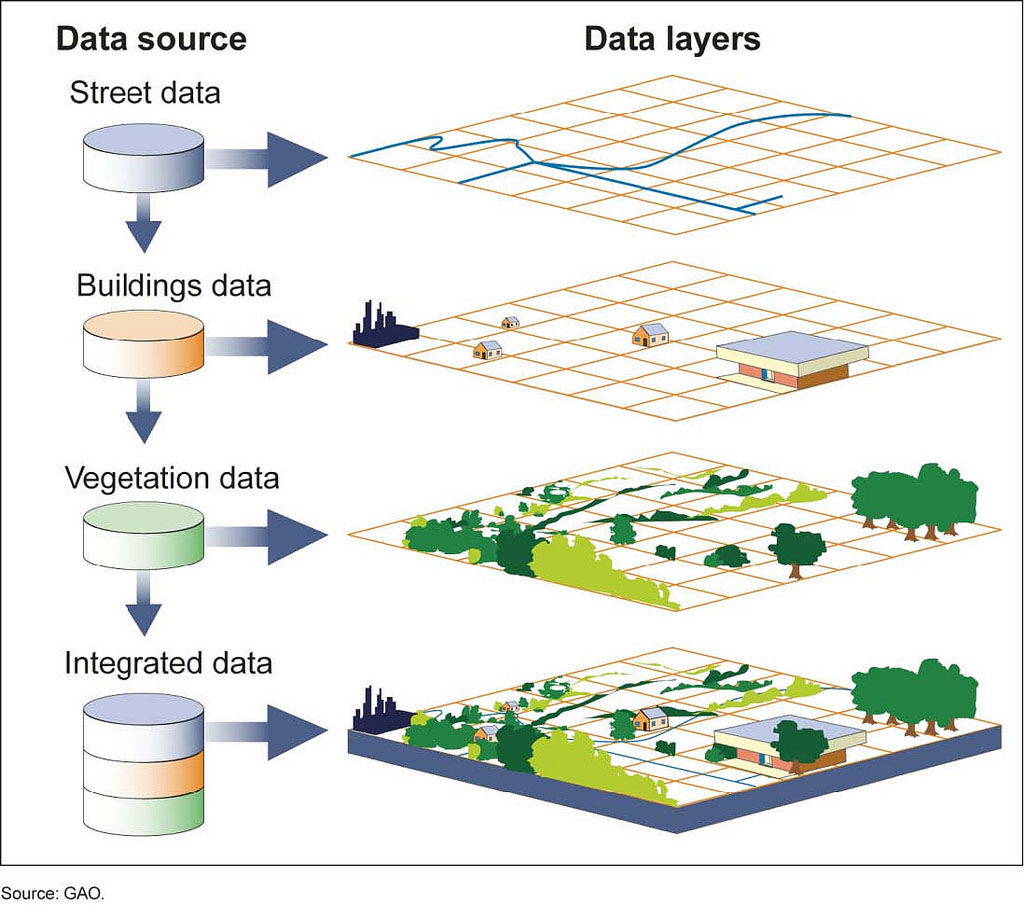
GIS property mapping utilizes geographic data, such as coordinates, addresses, and boundaries, to create interactive digital representations of real estate assets. These maps are not merely static visual aids; they are dynamic platforms that integrate diverse data layers, allowing users to analyze spatial relationships, perform complex calculations, and generate insightful reports.
Key Components of a GIS Property Map:
- Spatial Data: This forms the foundation of GIS property maps, encompassing coordinates, addresses, boundaries, and other geographical information.
- Attribute Data: This complements spatial data by providing descriptive information about each property, such as ownership details, property type, zoning regulations, and tax assessments.
- Visualization Tools: GIS software offers a range of visualization tools, enabling users to create maps, charts, and graphs that effectively communicate spatial patterns and relationships.
- Analytical Capabilities: GIS goes beyond mere visualization by providing powerful analytical tools for spatial analysis, overlay analysis, proximity analysis, and network analysis, enabling informed decision-making.
Applications of GIS Property Mapping
GIS property mapping finds applications across a wide spectrum of sectors, including:
1. Real Estate:
- Property Valuation: GIS helps assess property values by analyzing comparable properties, neighborhood characteristics, and market trends, providing valuable insights for pricing strategies.
- Site Selection: Developers and investors utilize GIS to identify suitable locations for new projects, considering factors like accessibility, zoning regulations, and proximity to amenities.
- Property Management: GIS simplifies property management by providing a centralized platform for tracking maintenance schedules, lease agreements, and tenant information, facilitating efficient operations.
2. Urban Planning:
- Land Use Planning: GIS assists in developing comprehensive land use plans, considering factors like population density, infrastructure capacity, and environmental constraints.
- Infrastructure Development: GIS facilitates the planning and construction of infrastructure projects, optimizing routes, minimizing environmental impact, and ensuring efficient resource allocation.
- Disaster Management: GIS plays a crucial role in disaster preparedness and response, providing real-time situational awareness, identifying vulnerable areas, and facilitating efficient emergency response.
3. Environmental Management:
- Environmental Monitoring: GIS enables monitoring environmental conditions, such as air quality, water pollution, and deforestation, providing valuable data for environmental conservation efforts.
- Natural Resource Management: GIS assists in managing natural resources, including forests, wildlife, and water bodies, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing environmental degradation.
- Climate Change Adaptation: GIS helps assess climate change impacts, identify vulnerable areas, and develop adaptation strategies to mitigate risks and enhance resilience.
4. Public Safety:
- Crime Mapping: GIS enables law enforcement agencies to analyze crime patterns, identify hotspots, and deploy resources effectively to combat crime.
- Emergency Response: GIS facilitates rapid response to emergencies, providing real-time situational awareness, optimizing resource allocation, and coordinating response efforts.
- Public Health: GIS assists in tracking disease outbreaks, identifying vulnerable populations, and implementing targeted public health interventions.
Benefits of GIS Property Mapping
The application of GIS in property mapping yields numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Data Accuracy: GIS eliminates the limitations of manual data collection, providing accurate and consistent property information.
- Enhanced Spatial Analysis: GIS empowers users to analyze spatial relationships, identify trends, and uncover hidden patterns within property data.
- Data Integration and Sharing: GIS facilitates the integration of diverse data sources, allowing for a holistic understanding of property information and enabling seamless data sharing among stakeholders.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: GIS provides a comprehensive view of property data, enabling informed decision-making in real estate, urban planning, environmental management, and public safety.
- Cost-Effectiveness: GIS streamlines workflows, reduces manual effort, and optimizes resource allocation, ultimately leading to cost savings.
- Improved Communication: GIS facilitates effective communication of spatial information through maps, charts, and reports, promoting collaboration and understanding among stakeholders.
FAQs Regarding GIS Property Mapping
1. What data is used in GIS property mapping?
GIS property mapping utilizes a wide range of data, including:
- Geographic Data: Coordinates, addresses, boundaries, property outlines, and other spatial information.
- Attribute Data: Ownership details, property type, zoning regulations, tax assessments, building permits, and other descriptive information.
- Imagery Data: Aerial photographs, satellite imagery, and other visual representations of the landscape.
- Demographic Data: Population density, income levels, and other socio-economic data.
2. How is GIS used for property valuation?
GIS analyzes comparable properties, neighborhood characteristics, and market trends to assess property values. By overlaying data layers such as property size, amenities, and proximity to amenities, GIS identifies similar properties and estimates market value.
3. Can GIS be used for property management?
Yes, GIS simplifies property management by:
- Centralizing property information: Tracking maintenance schedules, lease agreements, and tenant information on a single platform.
- Visualizing property assets: Creating maps that show the location and status of properties, facilitating efficient maintenance planning.
- Analyzing property performance: Tracking occupancy rates, rental income, and other key metrics to optimize property management strategies.
4. What are the benefits of using GIS for urban planning?
GIS benefits urban planning by:
- Optimizing land use: Identifying suitable locations for residential, commercial, and industrial development based on factors like accessibility, infrastructure capacity, and environmental constraints.
- Facilitating infrastructure planning: Designing optimal routes for roads, utilities, and public transportation, minimizing environmental impact and ensuring efficient resource allocation.
- Assessing urban development impacts: Analyzing the potential effects of new development projects on traffic patterns, environmental conditions, and social equity.
5. How can GIS be used for environmental management?
GIS assists in environmental management by:
- Monitoring environmental conditions: Tracking air quality, water pollution, deforestation, and other environmental indicators to identify areas of concern and implement conservation efforts.
- Managing natural resources: Optimizing the use of forests, wildlife, and water bodies, ensuring sustainable resource utilization and minimizing environmental degradation.
- Assessing climate change impacts: Identifying vulnerable areas and developing adaptation strategies to mitigate risks and enhance resilience.
Tips for Effective GIS Property Mapping
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly define the goals of the GIS project to ensure that the data collected, analysis conducted, and visualizations created are relevant and meet specific needs.
- Utilize High-Quality Data: Ensure that the data used is accurate, reliable, and up-to-date to avoid inaccuracies and misinterpretations.
- Choose Appropriate Software: Select GIS software that aligns with the project’s requirements, considering factors like functionality, ease of use, and compatibility with existing data sources.
- Embrace Data Visualization: Leverage GIS visualization tools to create maps, charts, and graphs that effectively communicate spatial patterns and relationships, enhancing understanding and facilitating decision-making.
- Collaborate with Stakeholders: Engage with stakeholders to gather input, ensure data accuracy, and facilitate the adoption of GIS-based solutions.
- Continuously Improve: Regularly review and update the GIS system to incorporate new data sources, enhance functionalities, and adapt to changing needs.
Conclusion
GIS property mapping has emerged as a transformative technology, empowering various sectors to manage property information effectively, analyze spatial relationships, and make informed decisions. By integrating geographic data, visualization tools, and analytical capabilities, GIS unlocks the power of location, providing a comprehensive understanding of property assets and their spatial context. As technology continues to evolve, GIS property mapping will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of real estate, urban planning, environmental management, and public safety.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Power of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) in Property Mapping. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!