Unpacking the Landscape of Pennsylvania: A Look at Population Density
Related Articles: Unpacking the Landscape of Pennsylvania: A Look at Population Density
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unpacking the Landscape of Pennsylvania: A Look at Population Density. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unpacking the Landscape of Pennsylvania: A Look at Population Density

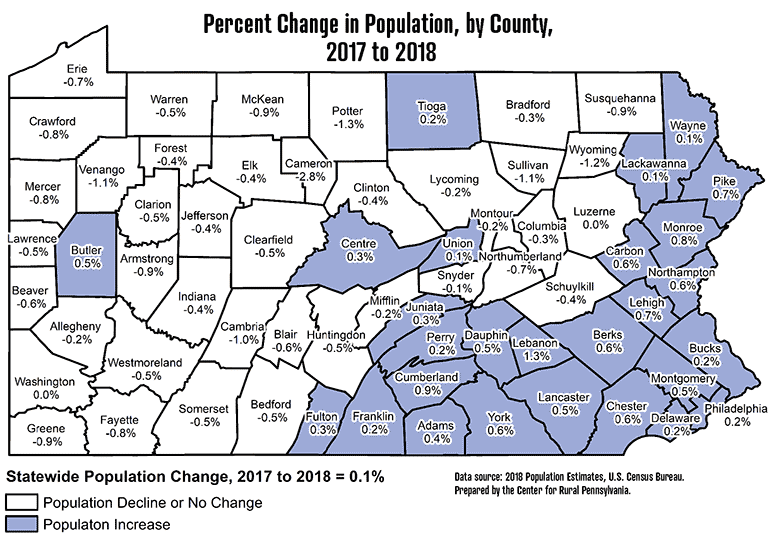
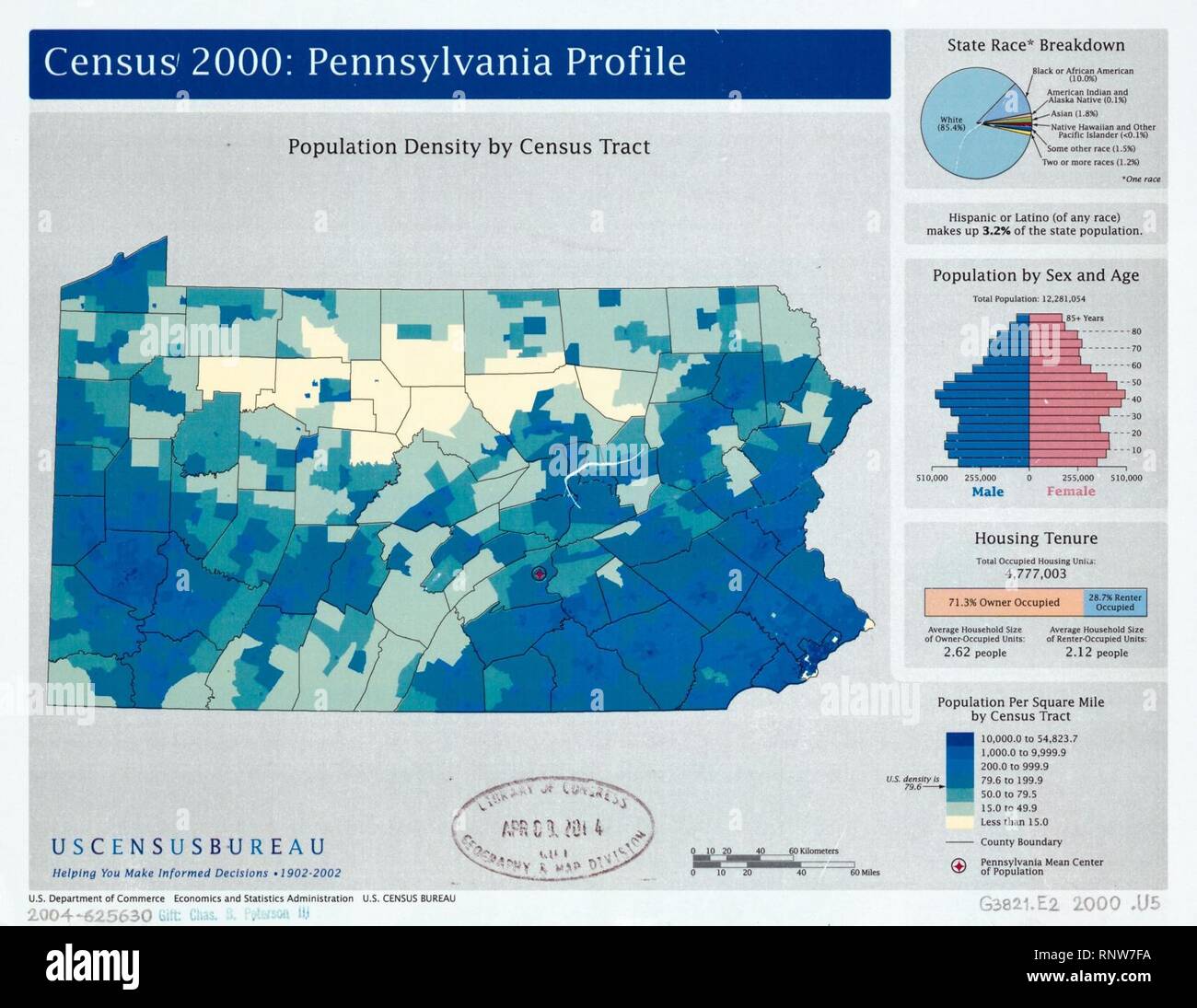
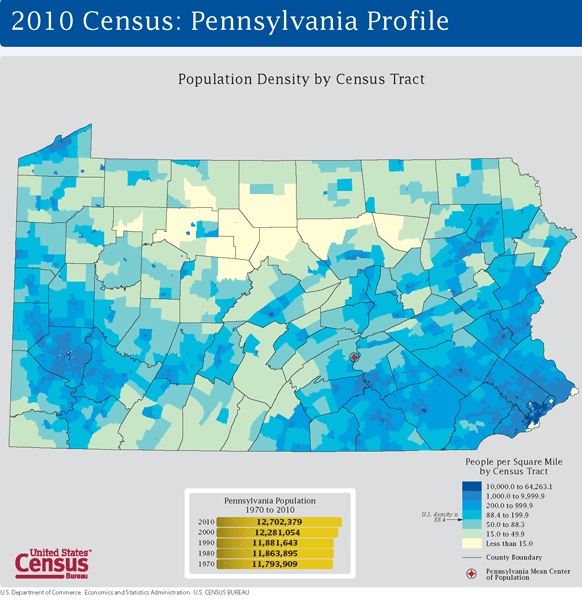
Pennsylvania, a state steeped in history and diverse landscapes, boasts a population distribution that reflects its rich past and evolving present. A population density map, a visual representation of the number of people per unit area, provides a powerful lens through which to understand the dynamics of this state.
Understanding the Map: A Visual Story of Settlement and Growth
The population density map of Pennsylvania reveals a clear pattern of human settlement, with higher concentrations clustered in specific areas and lower densities in others. This uneven distribution is the result of a complex interplay of historical, economic, and environmental factors.
Key Features of the Map:
- Urban Core: The southeastern portion of Pennsylvania, including the cities of Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, and Allentown, exhibits the highest population density. This region, historically a hub of industrial activity and commerce, continues to attract residents seeking employment and urban amenities.
- Suburban Sprawl: The area surrounding the major cities shows a gradual decline in population density, indicating the growth of suburbs. These areas offer a balance of urban convenience with a more spacious living environment.
- Rural Pockets: The northern and western portions of Pennsylvania, characterized by mountainous terrain and agricultural land, display significantly lower population densities. These regions, often associated with traditional industries like farming and mining, experience slower population growth.
- The Appalachian Influence: The Appalachian Mountains, traversing the state from north to south, contribute to the lower population densities in the central and western regions. These areas have historically faced economic challenges and population outmigration.
The Significance of Population Density:
Population density is not merely a static measure; it is a dynamic indicator of societal trends and their impact on the environment, infrastructure, and economy.
- Resource Management: Understanding population density helps policymakers allocate resources effectively. Areas with higher population densities require more public services, transportation infrastructure, and environmental management.
- Economic Development: Population density can influence the location of businesses and industries. Areas with a dense population offer a larger workforce and market, attracting investment and driving economic growth.
- Environmental Impact: Population density plays a crucial role in environmental sustainability. Densely populated areas can experience higher levels of pollution, resource consumption, and habitat fragmentation.
- Social Dynamics: Population density can influence social interactions, community cohesion, and the availability of public services.
Beyond the Numbers: A Deeper Dive into Pennsylvania’s Population Dynamics
While the population density map provides a snapshot of the state’s demographic landscape, it is essential to consider the nuances and complexities that contribute to this distribution.
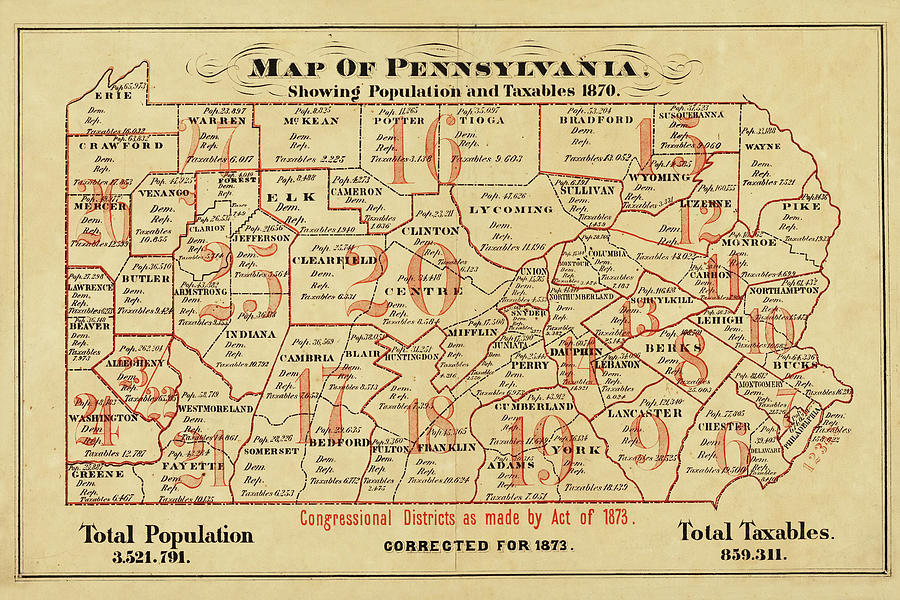
- Historical Migration Patterns: Pennsylvania’s settlement history, marked by waves of immigration and internal migration, has shaped its current population distribution. Industrialization in the 19th and 20th centuries attracted people to urban centers, while agricultural opportunities drew settlers to rural areas.
- Economic Development: The state’s economic landscape has significantly influenced population density. The decline of traditional industries, such as manufacturing and mining, has led to population outmigration in some areas. Conversely, the growth of sectors like healthcare, education, and technology has attracted residents to specific regions.
- Environmental Factors: Pennsylvania’s diverse terrain, ranging from rolling hills to rugged mountains, has influenced population distribution. Areas with fertile farmland and access to water resources have historically attracted settlers. Conversely, mountainous regions with limited arable land have experienced lower population densities.
- Social and Cultural Influences: Factors like community ties, cultural heritage, and lifestyle preferences also contribute to population density patterns. Some regions may attract residents seeking a slower pace of life or access to specific cultural amenities.
FAQs about Population Density in Pennsylvania:
1. What are the most densely populated areas in Pennsylvania?
The southeastern region of Pennsylvania, encompassing Philadelphia, Pittsburgh, and Allentown, exhibits the highest population densities. These urban centers have historically been hubs of industry and commerce, attracting a large population.
2. What factors contribute to the lower population densities in rural areas?
Rural areas in Pennsylvania, particularly in the north and west, are characterized by mountainous terrain, limited agricultural land, and a decline in traditional industries like mining and farming. These factors have contributed to lower population densities.
3. How does population density impact economic development?
Higher population densities can attract businesses and industries seeking a larger workforce and market. This can lead to economic growth and job creation. However, areas with low population densities may face challenges in attracting investment due to a smaller workforce and market.
4. What are the environmental implications of population density?
Densely populated areas can experience higher levels of pollution, resource consumption, and habitat fragmentation. It is crucial to implement sustainable practices to mitigate these impacts.
5. How can population density data be used for planning and policymaking?
Population density data can be used to inform planning decisions regarding infrastructure development, resource allocation, and environmental protection. It helps policymakers understand the needs of different communities and allocate resources effectively.
Tips for Understanding and Interpreting Population Density Maps:
- Pay attention to the scale: The map’s scale will indicate the size of the area represented by each unit of population density.
- Consider the data source: Ensure the data is accurate and reliable.
- Look for patterns and trends: Identify areas with high and low population densities and consider the factors contributing to these patterns.
- Compare data over time: Analyze population density maps from different years to observe changes and trends.
- Connect the data to other variables: Analyze population density in relation to other factors like income, education, and access to services.
Conclusion:
The population density map of Pennsylvania serves as a valuable tool for understanding the state’s demographic landscape and its evolving dynamics. By analyzing the spatial distribution of population, we gain insights into the interplay of historical, economic, and environmental factors that have shaped the state’s development. This knowledge is crucial for informed decision-making in areas like resource management, economic development, and environmental protection. The map offers a visual representation of the complex story of human settlement and growth in Pennsylvania, providing a foundation for understanding the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unpacking the Landscape of Pennsylvania: A Look at Population Density. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!