Unveiling the Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of France’s Physical Geography
Related Articles: Unveiling the Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of France’s Physical Geography
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of France’s Physical Geography. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of France’s Physical Geography
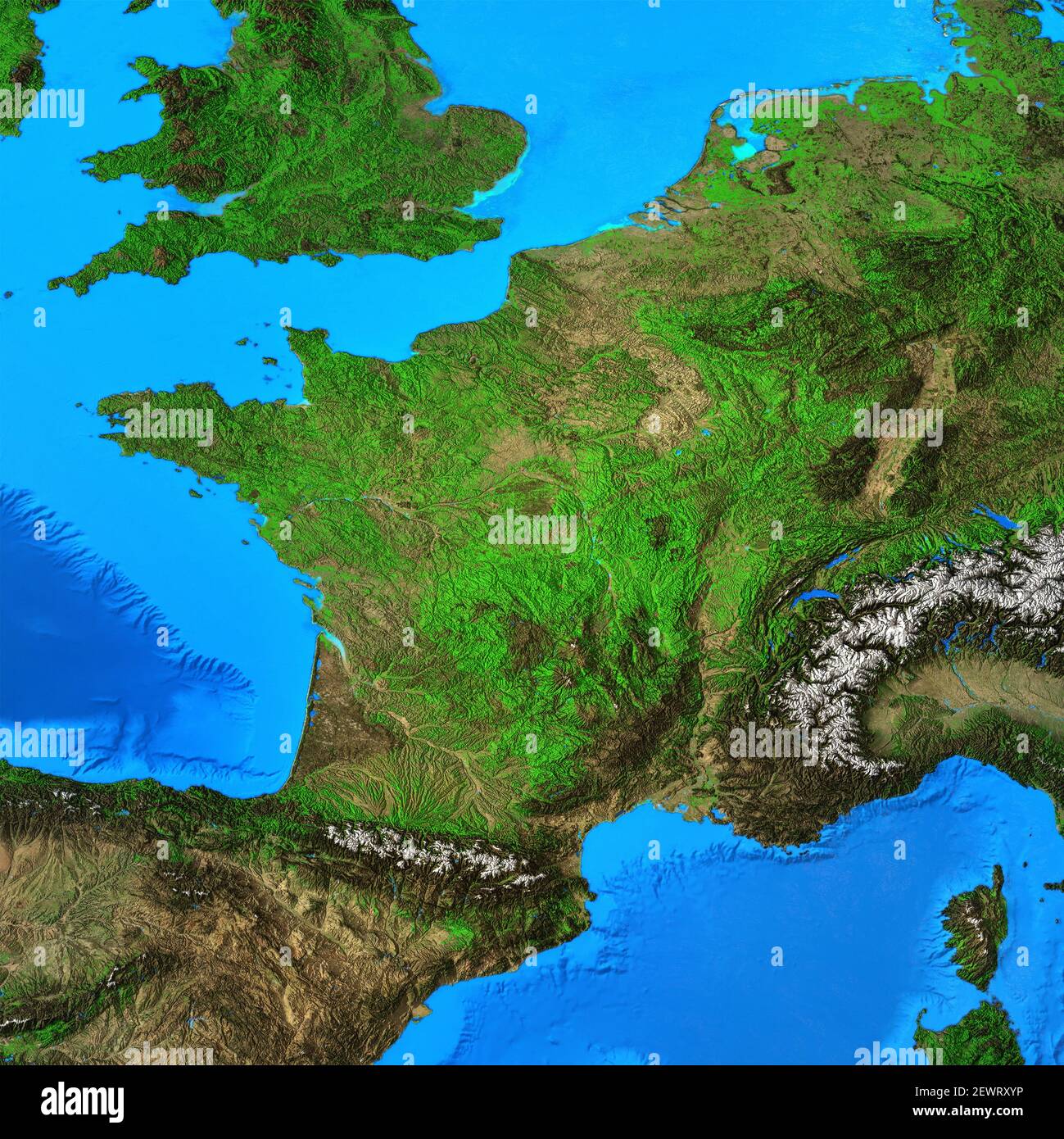
France, a nation steeped in history and culture, boasts a captivating physical geography that has shaped its identity and influenced its development. Understanding the country’s diverse landscape is crucial for appreciating its rich heritage, understanding its economic activities, and comprehending the challenges it faces. This exploration delves into the intricacies of France’s physical map, revealing the interplay of mountains, plains, rivers, and coastlines that define its character.
A Mosaic of Landscapes:
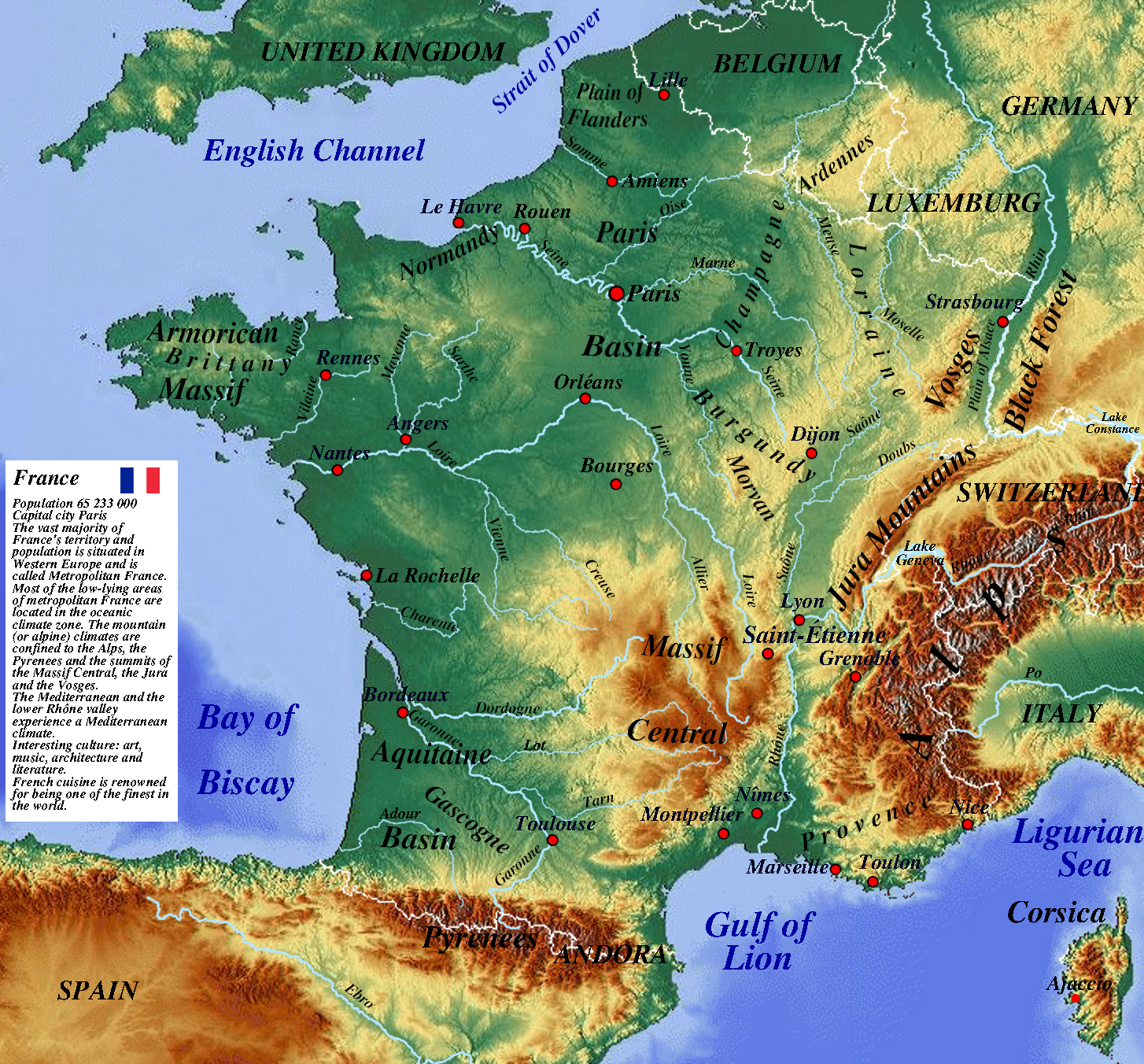
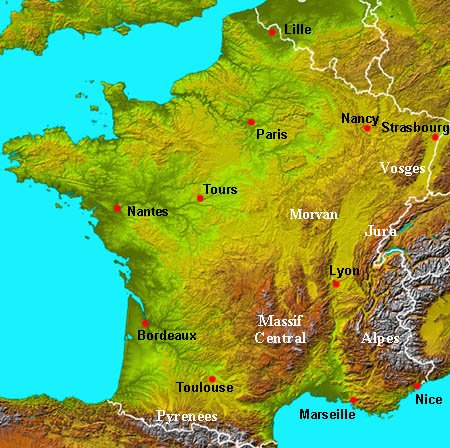
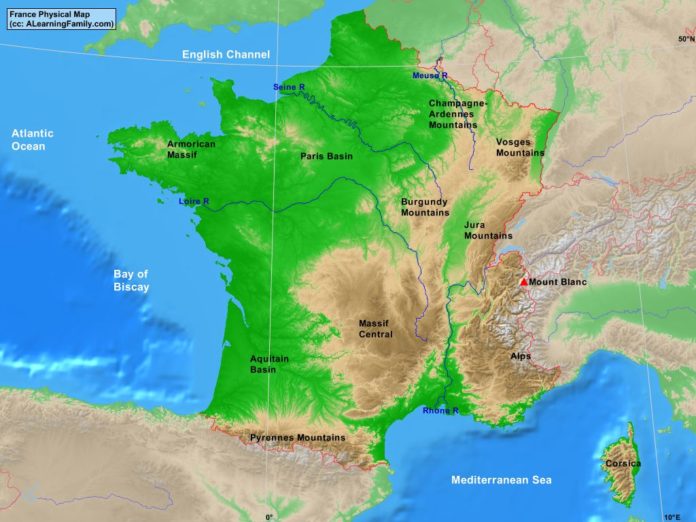
France’s physical geography is a tapestry woven from a diverse array of landscapes. The country can be broadly divided into six distinct regions:
-
The Massif Central: This ancient mountain range, located in the heart of France, is characterized by volcanic plateaus, deep valleys, and rolling hills. Its rugged terrain has traditionally limited agricultural activity, but it provides a haven for biodiversity and offers stunning natural beauty.
-
The Alps: France’s southeastern border is dominated by the majestic Alps, Europe’s highest mountain range. The Alps are a haven for skiers, climbers, and nature enthusiasts, offering breathtaking vistas and challenging terrain.
-
The Pyrenees: Located in the southwest, the Pyrenees form a natural border between France and Spain. This mountain range is known for its dramatic peaks, deep gorges, and lush valleys.
-
The Jura Mountains: Situated in the east, the Jura Mountains are a smaller range known for their rolling hills, dense forests, and picturesque lakes.
-
The Paris Basin: This vast plain, centered around the capital city of Paris, is characterized by fertile soils and gentle slopes. It has long been a hub of agricultural activity and is home to some of France’s most important cities.
-
The Atlantic Coast: France’s western coastline is a blend of sandy beaches, rocky cliffs, and estuaries. It is home to a variety of ecosystems, including coastal forests, wetlands, and marine life.
The Influence of Rivers:
France’s river systems play a vital role in its physical geography and economic life. The most significant rivers are:
-
The Loire: Flowing through the heart of France, the Loire is the longest river in the country. It is known for its fertile valley, historic castles, and vineyards.
-
The Seine: The Seine flows through Paris and is an important waterway for transportation and tourism. Its banks are lined with iconic landmarks and charming villages.
-
The Rhône: Rising in the Swiss Alps, the Rhône flows through southeastern France, providing irrigation and transportation.
-
The Garonne: Originating in the Pyrenees, the Garonne flows westward to the Atlantic Ocean, providing a crucial link between the southwest and the coast.
Coastal Diversity:
France’s coastline offers a remarkable range of landscapes, from the sandy beaches of the Mediterranean to the rugged cliffs of Brittany.
-
The Mediterranean Coast: Known for its sunny climate and beautiful beaches, the Mediterranean coast is a popular destination for tourists.
-
The Atlantic Coast: The Atlantic coast features a variety of landscapes, including sandy beaches, rocky cliffs, and estuaries. It is also home to important fishing ports and harbors.
-
The English Channel: France’s northern coastline borders the English Channel, a vital shipping route and a historical battleground.
The Impact of Climate:
France’s physical geography is closely linked to its climate. The country experiences a range of climates, from the temperate oceanic climate of the north to the Mediterranean climate of the south.
-
Temperate Oceanic Climate: The north and west of France are characterized by mild winters and warm, wet summers.
-
Mediterranean Climate: The south of France enjoys hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters.
-
Continental Climate: The interior of France experiences hot summers and cold winters.
The Significance of Physical Geography:
France’s physical geography has had a profound impact on its history, culture, and economy. The diverse landscapes have shaped its agricultural practices, influenced its architecture, and inspired its art and literature. The country’s rivers have been crucial for transportation, irrigation, and energy production. Its coastline has been a source of food, trade, and tourism.
Understanding the Interplay:
By understanding the interplay of mountains, plains, rivers, and coastlines, we gain a deeper appreciation for France’s unique character. The rugged terrain of the Massif Central has traditionally limited agricultural activity, but it has also fostered a strong sense of local identity and preserved a rich biodiversity. The fertile plains of the Paris Basin have been essential for agriculture, while the majestic Alps have drawn adventurers and artists for centuries. The rivers have served as arteries of commerce and communication, connecting cities and regions. The coastline has been a source of inspiration for artists, writers, and musicians, and it continues to attract tourists from around the world.
Exploring the Benefits of Understanding France’s Physical Geography:
-
Enhanced Travel Experiences: By understanding the country’s diverse landscapes, travelers can plan more meaningful and rewarding trips. They can choose destinations that align with their interests, whether it be hiking in the Alps, exploring the vineyards of the Loire Valley, or relaxing on the beaches of the Mediterranean.
-
Improved Environmental Awareness: Understanding the physical processes that shape France’s landscape helps us appreciate the importance of environmental conservation. We can better understand the threats posed by climate change, pollution, and deforestation, and we can support efforts to protect the country’s natural heritage.
-
Enhanced Historical Perspective: France’s physical geography has played a significant role in its history. Understanding the terrain, the climate, and the river systems helps us to better understand the country’s past, from the Roman Empire to the French Revolution.
-
Economic Insights: France’s physical geography has shaped its economic activities. The country’s fertile plains have supported agriculture, its rivers have facilitated transportation, and its coastline has driven tourism. Understanding these connections helps us to better understand the country’s economic strengths and challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions about France’s Physical Geography:
1. What is the highest point in France?
The highest point in France is Mont Blanc, which stands at 4,808.73 meters (15,777 feet) above sea level. It is located in the French Alps, on the border with Italy.
2. What are the major river systems in France?
The major river systems in France are the Loire, the Seine, the Rhône, and the Garonne. These rivers play a vital role in transportation, irrigation, and energy production.
3. What are the different climate zones in France?
France experiences a range of climates, from the temperate oceanic climate of the north to the Mediterranean climate of the south. The interior of the country experiences a continental climate.
4. What are some of the most important natural resources in France?
France is rich in natural resources, including fertile farmland, forests, and mineral deposits. The country is also a major producer of hydroelectric power.
5. How has France’s physical geography influenced its culture?
France’s physical geography has had a profound impact on its culture. The diverse landscapes have inspired artists, writers, and musicians. The country’s rivers have played a role in its folklore and mythology.
Tips for Understanding France’s Physical Geography:
-
Use a Physical Map: A physical map of France can be an invaluable tool for understanding the country’s diverse landscapes. Pay attention to the location of mountains, plains, rivers, and coastlines.
-
Explore Online Resources: There are numerous online resources available that provide detailed information about France’s physical geography. Look for websites that offer interactive maps, satellite imagery, and articles about the country’s natural features.
-
Read Travel Guides: Travel guides often provide insightful descriptions of France’s landscapes and attractions. They can help you to plan your trip and to appreciate the country’s diverse geography.
-
Watch Documentaries: Documentaries about France’s physical geography can offer a fascinating glimpse into the country’s natural wonders. Look for films that explore the Alps, the Loire Valley, or the Mediterranean coast.
-
Visit France: The best way to understand France’s physical geography is to experience it firsthand. Travel to different regions of the country, explore its landscapes, and learn about the natural processes that have shaped them.
Conclusion:
France’s physical geography is a captivating tapestry woven from a diverse array of landscapes. From the rugged peaks of the Alps to the fertile plains of the Paris Basin, the country offers a rich and varied experience for travelers and residents alike. Understanding the interplay of mountains, plains, rivers, and coastlines provides a deeper appreciation for France’s unique character and helps us to understand the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. By embracing this knowledge, we can better understand the country’s past, present, and future.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Diverse Landscape: A Comprehensive Exploration of France’s Physical Geography. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!