Unveiling the Land of Moab: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Related Articles: Unveiling the Land of Moab: A Geographical and Historical Exploration
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Land of Moab: A Geographical and Historical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Land of Moab: A Geographical and Historical Exploration

The land of Moab, etched into the annals of biblical history, holds a captivating allure for scholars and enthusiasts alike. Its strategic location, nestled between the Jordan River and the Dead Sea, positioned Moab as a crossroads of civilizations and a key player in the unfolding narratives of the Old Testament. Understanding the geographical and historical context of Moab is crucial for deciphering the complex tapestry of biblical events and appreciating the cultural significance of this ancient land.
A Landscape Shaped by Nature:
The Moabite territory, as depicted in biblical accounts and archaeological findings, encompassed a diverse and challenging terrain. The eastern edge of the Dead Sea served as its western boundary, with the Jordan River forming its western edge. The Moabite plateau, a high, arid plateau, stretched eastward, punctuated by rugged canyons and deep ravines carved by ancient rivers. The region’s dramatic landscape, characterized by towering cliffs, stark deserts, and fertile oases, presented both opportunities and obstacles for its inhabitants.
A History Woven with Biblical Threads:
Moab’s story is deeply intertwined with the narratives of the Israelites. The Moabites, descendants of Lot, Abraham’s nephew, shared a common ancestry with the Israelites. This shared heritage, however, often gave way to tensions and conflicts, as depicted in the biblical accounts.
The Book of Numbers recounts the Israelites’ encounter with the Moabites during their journey to the Promised Land. The Moabite King Balak, fearing the growing power of the Israelites, sought to thwart their advance by hiring the prophet Balaam to curse them. This episode highlights the complex relationship between the two nations, characterized by both animosity and moments of cooperation.
The Book of Judges narrates the Moabite oppression of the Israelites for eighteen years, highlighting the vulnerability of the Israelites and the enduring threat posed by their neighbors. The story of Ruth, a Moabite woman who becomes a prominent figure in the lineage of King David, underscores the interconnectedness of the two cultures.
A Land of Archaeological Treasures:
Beyond the biblical narratives, archaeological evidence offers invaluable insights into the civilization of Moab. The discovery of the Moabite Stone, a large basalt stele inscribed with an account of King Mesha’s victory over the Israelites, provides a firsthand glimpse into the Moabite language and culture.
Archaeological excavations at the ancient Moabite cities of Dibon, Nebo, and Beth-Jesimoth have unearthed remnants of temples, palaces, and fortifications, offering tangible evidence of the Moabite civilization’s sophistication and resilience.
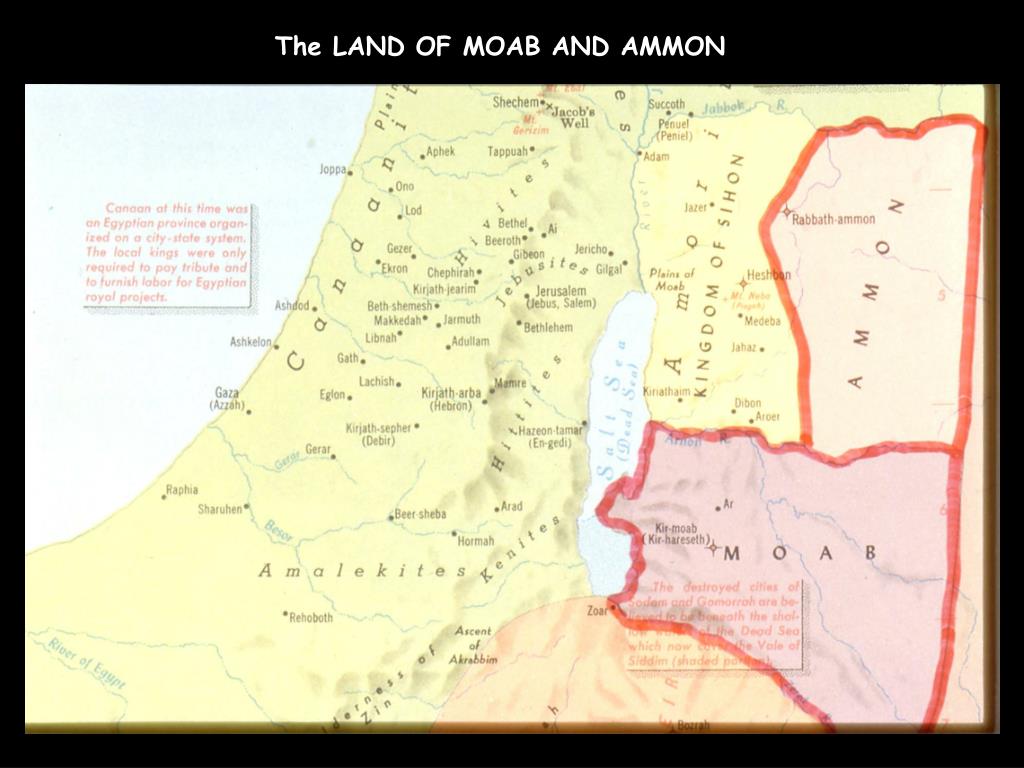
The Significance of the Moabite Map:
Understanding the geography of Moab is essential for comprehending the biblical narratives and appreciating the historical context of the region. A Moabite map, a visual representation of the land, serves as a vital tool for scholars and enthusiasts alike.
Benefits of a Moabite Map:
- Visualizing Biblical Narratives: A map helps readers visualize the locations of key events and understand the geographical context of biblical stories. For example, tracing the Israelites’ journey through Moab on a map clarifies their encounters with the Moabites and the challenges they faced.
- Understanding the Historical Context: A map provides a spatial framework for understanding the interactions between Moab and neighboring civilizations, including the Israelites, Edomites, and Ammonites.
- Appreciating the Cultural Significance: A map showcases the strategic location of Moab, highlighting its role as a crossroads of trade routes and a gateway between civilizations.
- Enhancing Archaeological Exploration: A map serves as a guide for archaeological expeditions, directing researchers to potential sites of interest and facilitating the reconstruction of ancient settlements and structures.
FAQs about the Moabite Map:
Q: What are the key geographical features of Moab depicted on a Moabite map?
A: A Moabite map typically highlights the following features:
- The Moabite Plateau: This high, arid plateau forms the heart of the Moabite territory, characterized by its rugged canyons and steep slopes.
- The Dead Sea: The eastern edge of the Dead Sea serves as Moab’s western boundary, offering a dramatic and unique geographical feature.
- The Jordan River: The Jordan River forms the western edge of Moab, separating it from the land of Israel.
- The Arnon River: This river, mentioned in the Bible, served as a natural border between Moab and the Ammonites.
- Ancient Cities: The map identifies major Moabite cities, including Dibon, Nebo, and Beth-Jesimoth, showcasing the region’s urban centers.
Q: How accurate are the Moabite maps available today?
A: The accuracy of Moabite maps varies depending on the source and the time period. Modern maps, based on archaeological evidence and historical research, offer a more accurate representation of the region than ancient maps. However, even modern maps rely on interpretation and reconstruction, as the precise boundaries of Moab and the locations of some ancient settlements remain uncertain.
Q: What are some resources for obtaining a Moabite map?
A: Several resources offer Moabite maps, including:
- Biblical Atlases: Many biblical atlases include detailed maps of Moab, highlighting its geographical features and key biblical sites.
- Archaeological Publications: Publications from archaeological expeditions in Moab often include maps showcasing the locations of excavated sites and the reconstructed layouts of ancient cities.
- Online Resources: Websites dedicated to biblical studies and archaeology often offer downloadable maps of Moab, providing a visual guide to the region.
Tips for Using a Moabite Map:
- Study the Map’s Key: Before using a Moabite map, familiarize yourself with the map’s legend, which explains the symbols used to represent different features.
- Compare Maps: Consult multiple maps from different sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the region and identify potential discrepancies in interpretations.
- Integrate with Biblical Texts: Use the map to visualize the locations mentioned in biblical narratives, enhancing your understanding of the geographical context of the stories.
- Explore Archaeological Sites: If you have the opportunity to visit Moab, use the map to plan your itinerary and explore ancient sites firsthand, enriching your understanding of the region’s history and culture.
Conclusion:
The Moabite map serves as a powerful tool for understanding the geographical and historical context of the land of Moab. By visualizing the region’s unique landscape, tracing the paths of biblical narratives, and exploring archaeological evidence, a Moabite map unlocks a deeper appreciation for the cultural significance of this ancient land, enriching our understanding of the biblical world and the enduring legacy of the Moabite civilization.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Land of Moab: A Geographical and Historical Exploration. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!