Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Vector Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Vector Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Vector Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Vector Maps

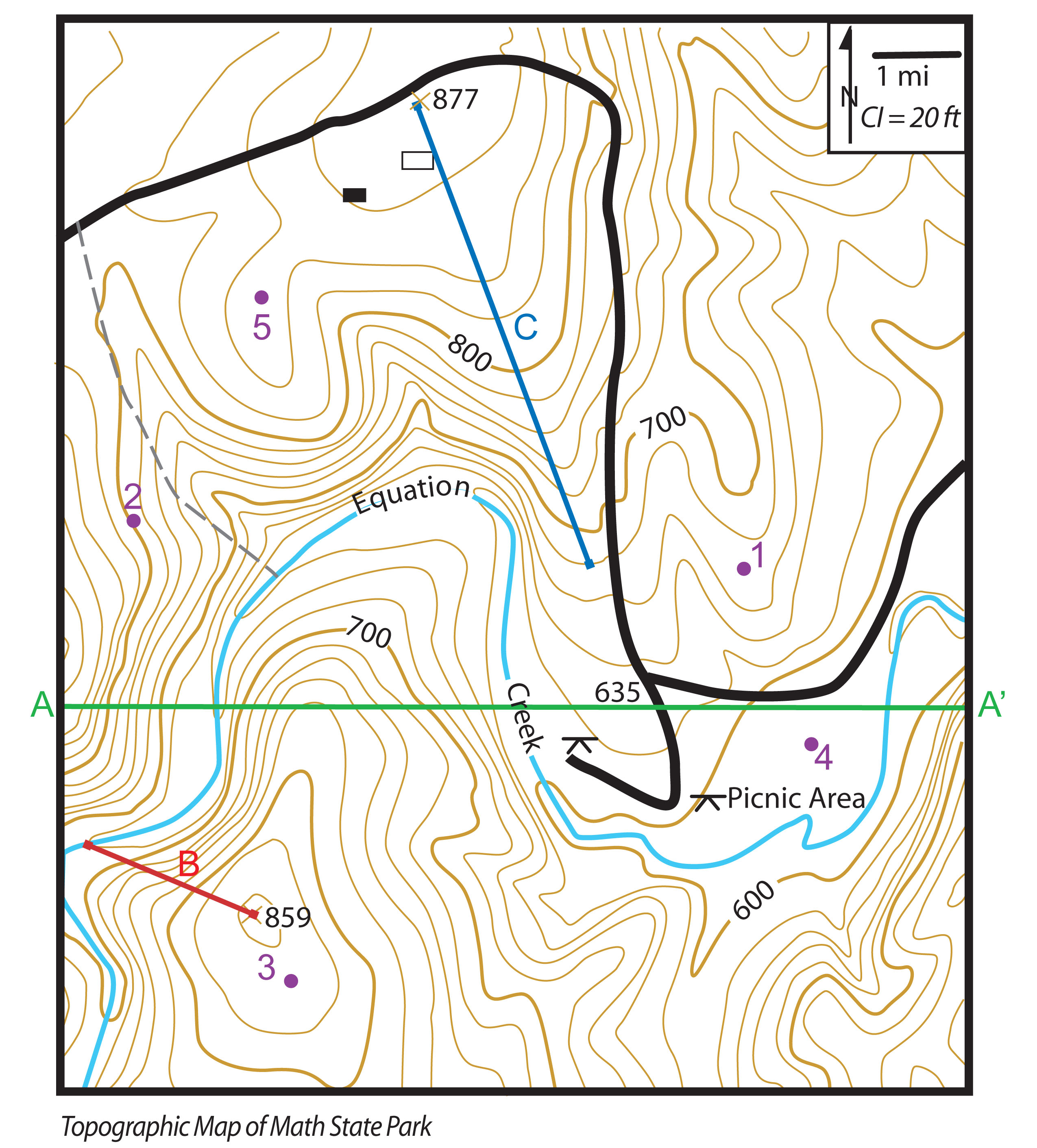
Topographic maps are visual representations of the Earth’s surface, capturing not only the location of features but also their elevation and shape. While traditional topographic maps are often rendered as raster images, a powerful alternative emerges in the form of topographic vector maps. These maps, composed of interconnected lines and points, offer distinct advantages over their raster counterparts, making them indispensable tools for various applications.
Understanding the Essence of Vector Maps
In essence, vector maps represent geographic data using mathematical equations. Unlike raster maps, which store information in a grid of pixels, vector maps store data as points, lines, and polygons. Each point, line, or polygon holds specific attributes, defining its characteristics and relationships with other elements.
Advantages of Topographic Vector Maps
The vector format offers significant benefits for topographic mapping:
- Scalability and Resolution: Vector maps can be scaled without losing detail, enabling users to zoom in and out seamlessly without pixelation. This adaptability makes them ideal for displaying information at various levels of granularity.
- Data Accuracy and Precision: The mathematical representation of features in vector maps allows for precise measurements and calculations. This accuracy is crucial for applications requiring precise spatial information, such as land surveying, infrastructure planning, and environmental analysis.
- Efficient Storage and Processing: Vector maps require significantly less storage space than raster maps, particularly when dealing with complex data sets. This efficiency translates to faster processing and analysis, making them suitable for large-scale projects.
- Flexibility and Editing: Vector maps are easily editable, allowing users to modify features, add new information, and update data without compromising the integrity of the map. This flexibility is vital for dynamic applications where information is constantly evolving.
- Symbology and Styling: Vector maps offer immense flexibility in symbolizing and styling map elements. This allows users to highlight specific features, convey different types of information, and create visually appealing and informative maps tailored to specific needs.
Applications of Topographic Vector Maps
The versatility and precision of topographic vector maps make them essential tools in diverse fields:
- Urban Planning and Development: Vector maps provide detailed information about terrain, elevation, and infrastructure, enabling urban planners to design efficient and sustainable urban environments.
- Infrastructure Development: From road construction and power line installation to pipeline planning and communication network design, vector maps provide the necessary spatial data for efficient and accurate infrastructure development.
- Environmental Management: Topographic vector maps are invaluable for environmental monitoring and analysis, aiding in understanding terrain, identifying potential hazards, and mapping ecological features.
- Disaster Response and Emergency Management: In disaster situations, vector maps provide crucial information about terrain, infrastructure, and population distribution, facilitating effective response and evacuation planning.
- Navigation and Location Services: Vector maps form the foundation for navigation systems, providing accurate location data and facilitating efficient route planning.
- Scientific Research and Analysis: Vector maps are widely used in scientific research, particularly in fields like geology, hydrology, and climatology, enabling the analysis of spatial patterns and trends.
Commonly Asked Questions about Topographic Vector Maps
Q: What are the different types of topographic vector maps?
A: Topographic vector maps can be categorized based on their content and purpose:
- General-purpose maps: These maps provide a comprehensive overview of the terrain, including elevation, landforms, water bodies, and infrastructure.
- Thematic maps: These maps focus on specific themes, such as vegetation, soil types, or population distribution.
- Cadastral maps: These maps depict property boundaries and ownership information.
- Geotechnical maps: These maps provide information about soil conditions, rock formations, and other geological features relevant to construction and infrastructure development.
Q: How are topographic vector maps created?
A: Topographic vector maps are created through a process involving:
- Data acquisition: This involves collecting elevation data, typically using aerial photography, LiDAR scanning, or satellite imagery.
- Data processing: The collected data is then processed and converted into a digital format, creating a digital elevation model (DEM).
- Vectorization: The DEM is then vectorized, converting the elevation data into points, lines, and polygons representing terrain features.
- Attribute assignment: Each vector element is assigned specific attributes, such as elevation, slope, and aspect, providing detailed information about the terrain.
Q: What are the software tools used for working with topographic vector maps?
A: A variety of software tools are available for creating, editing, and analyzing topographic vector maps, including:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software, such as ArcGIS, QGIS, and GRASS GIS, provides comprehensive tools for managing, analyzing, and visualizing geographic data, including vector maps.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software: CAD software, such as AutoCAD and MicroStation, is often used for creating and editing vector maps, particularly for engineering and infrastructure projects.
- Specialized mapping software: Several specialized software applications are designed for specific mapping tasks, such as navigation, route planning, and terrain analysis.
Tips for Using Topographic Vector Maps Effectively
- Understand the map’s projection and datum: Different map projections and datums can distort distances and shapes, so it is crucial to be aware of the map’s projection and datum to ensure accurate analysis.
- Use appropriate symbology and styling: Choose appropriate symbols and colors to effectively convey the information contained in the map.
- Combine vector maps with other data sources: Integrating vector maps with other data sources, such as satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and sensor data, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the landscape.
- Use spatial analysis tools: GIS software provides a range of spatial analysis tools that can be used to extract valuable information from vector maps, such as slope analysis, watershed delineation, and proximity analysis.
- Stay updated with the latest data: Topographic vector maps are dynamic and constantly evolving, so it is essential to use the most up-to-date data for accurate analysis and decision-making.
Conclusion
Topographic vector maps have emerged as indispensable tools in numerous fields, offering unparalleled precision, scalability, and flexibility for representing and analyzing the Earth’s surface. Their ability to store and process complex data, coupled with their adaptability for various applications, makes them invaluable for urban planning, infrastructure development, environmental management, disaster response, navigation, and scientific research. As technology continues to advance, topographic vector maps will continue to play a vital role in our understanding and management of the world around us.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Topographic Vector Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!